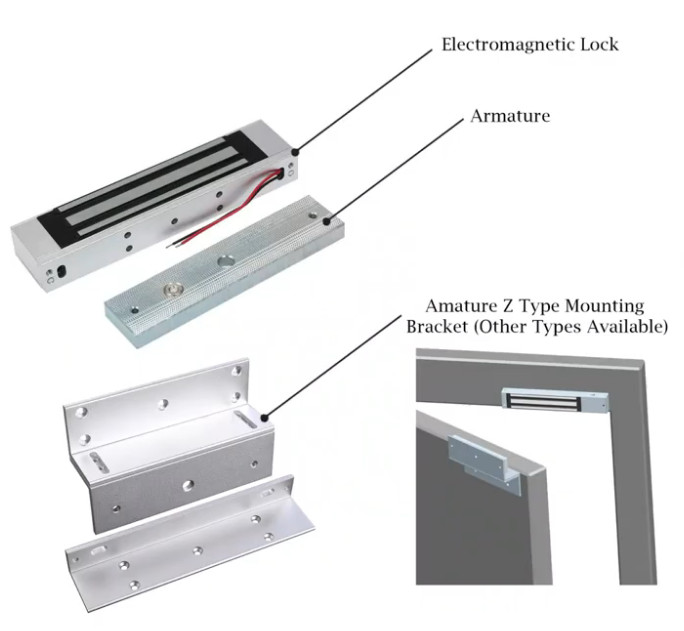
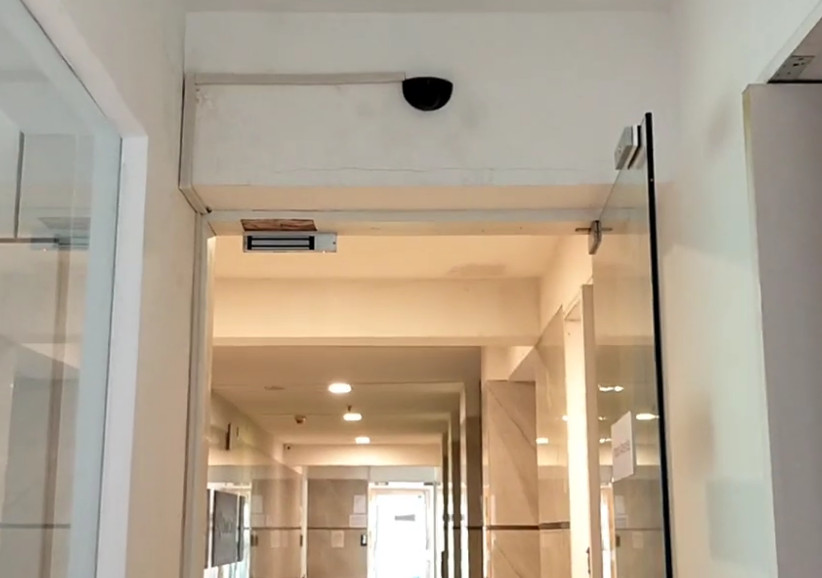
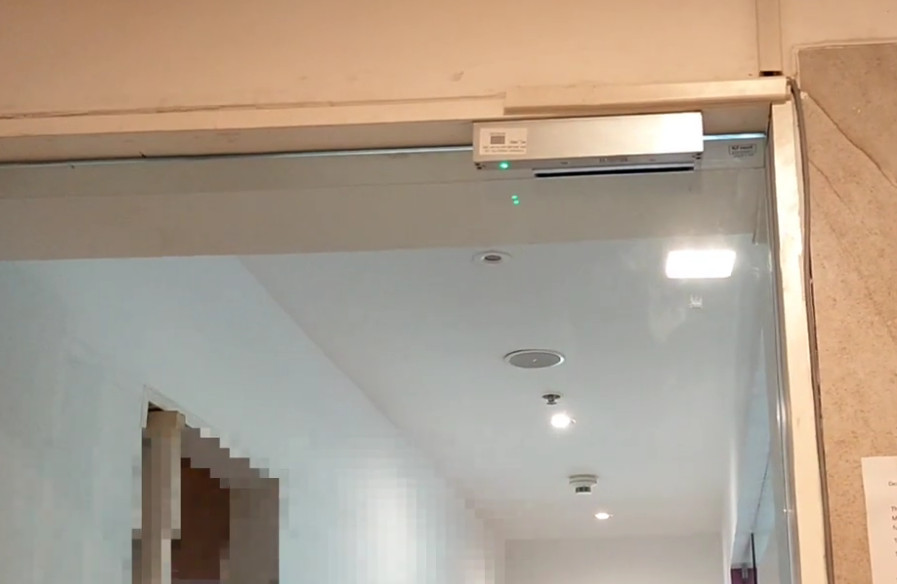
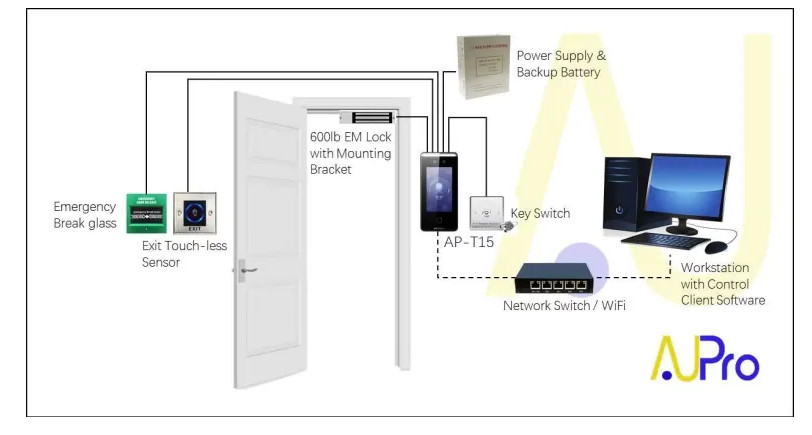
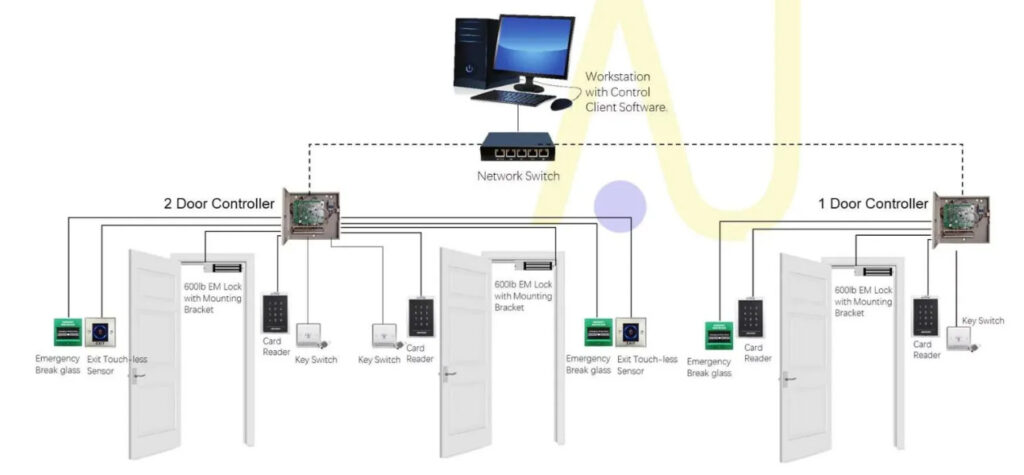
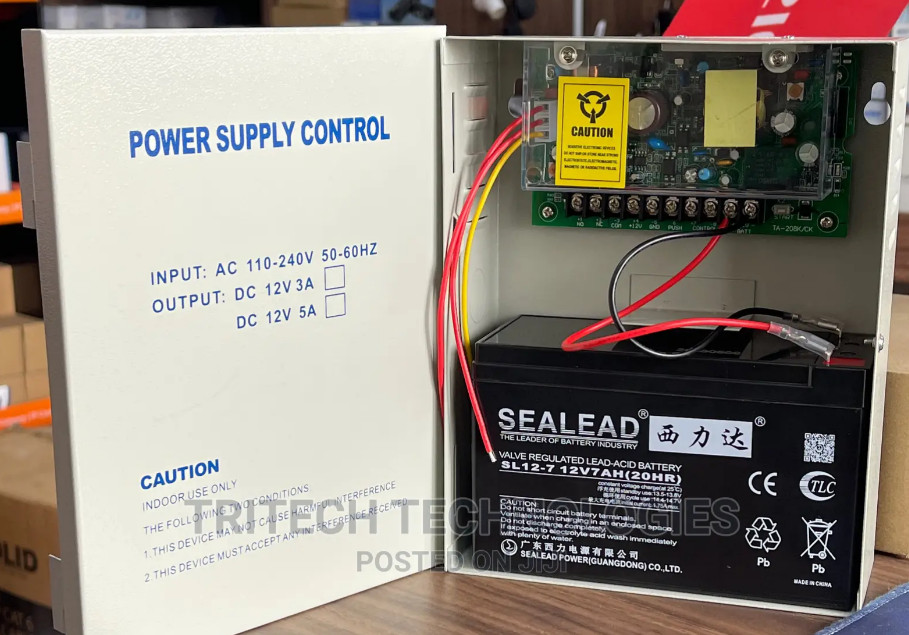
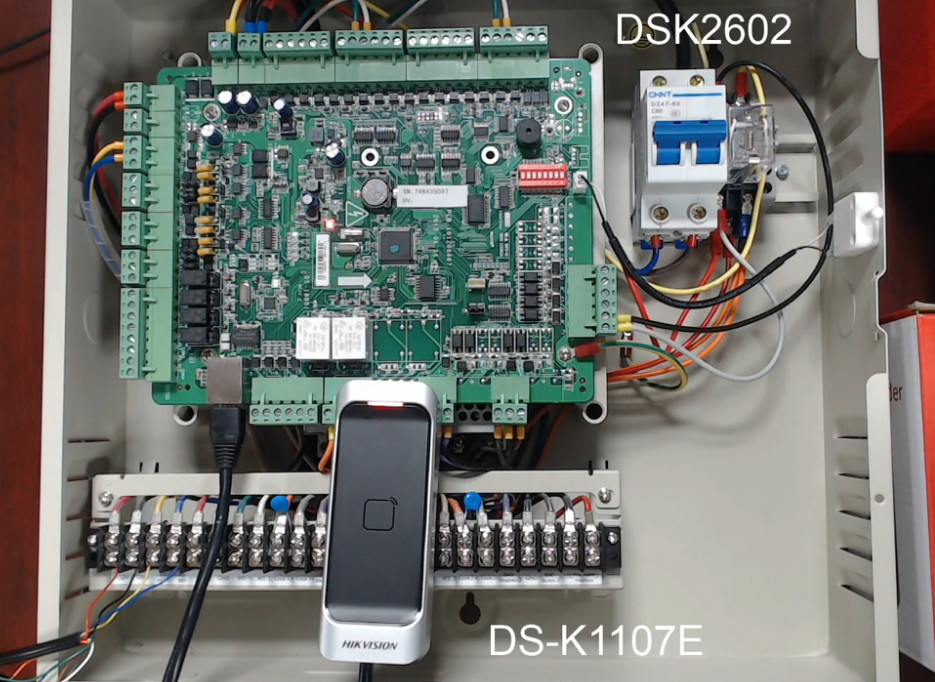
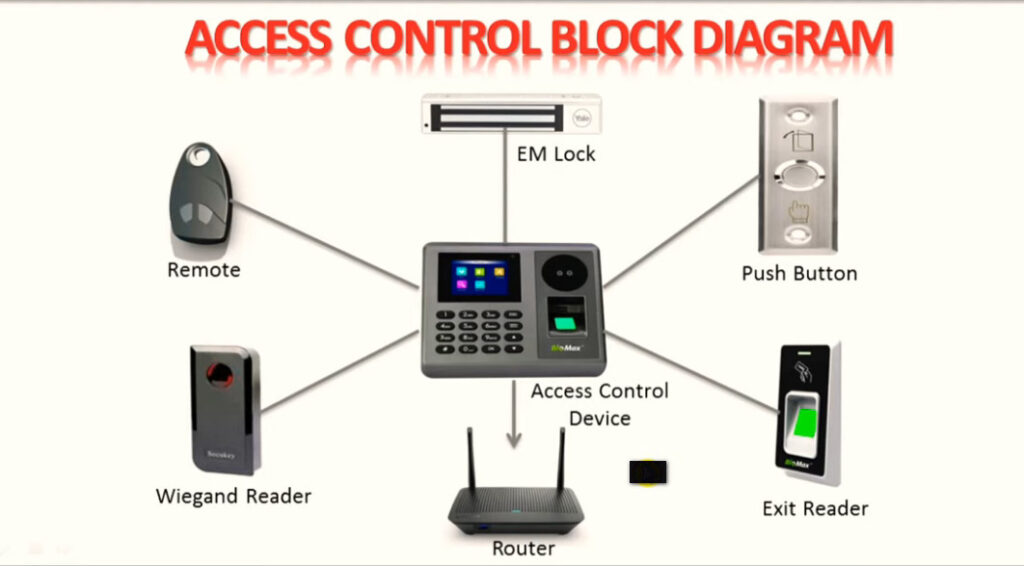
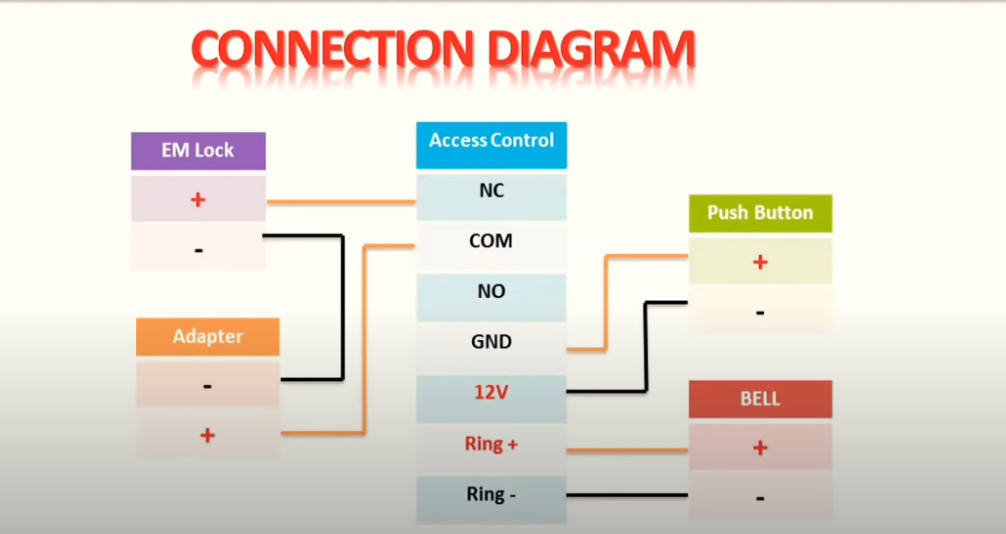
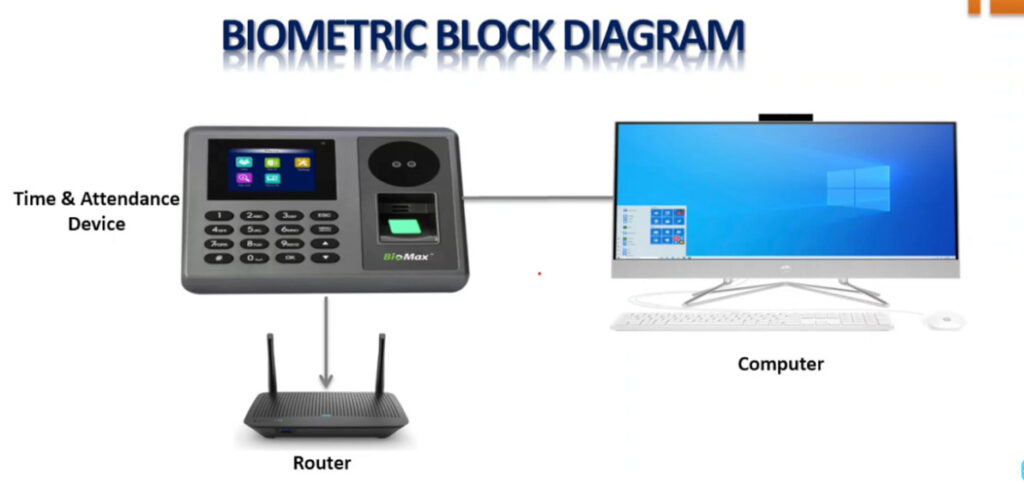
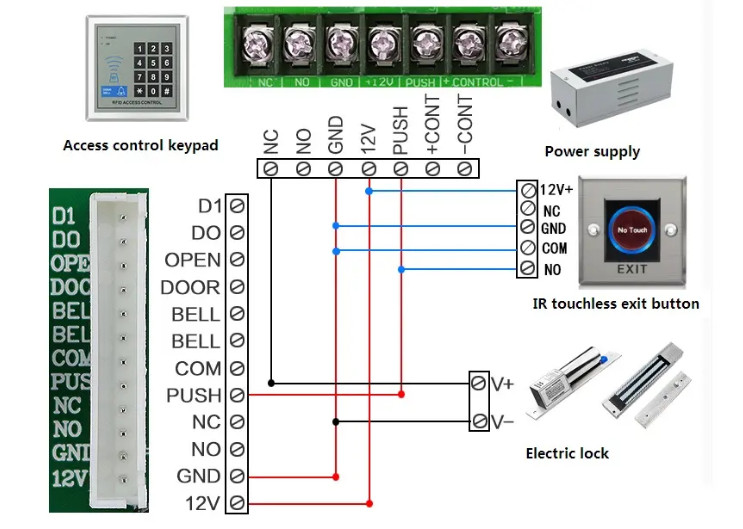
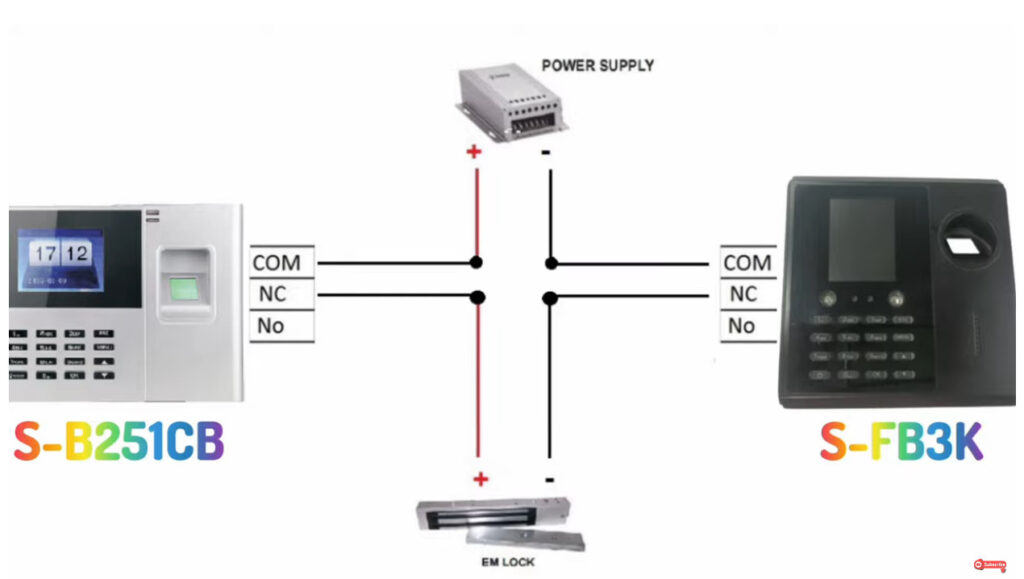
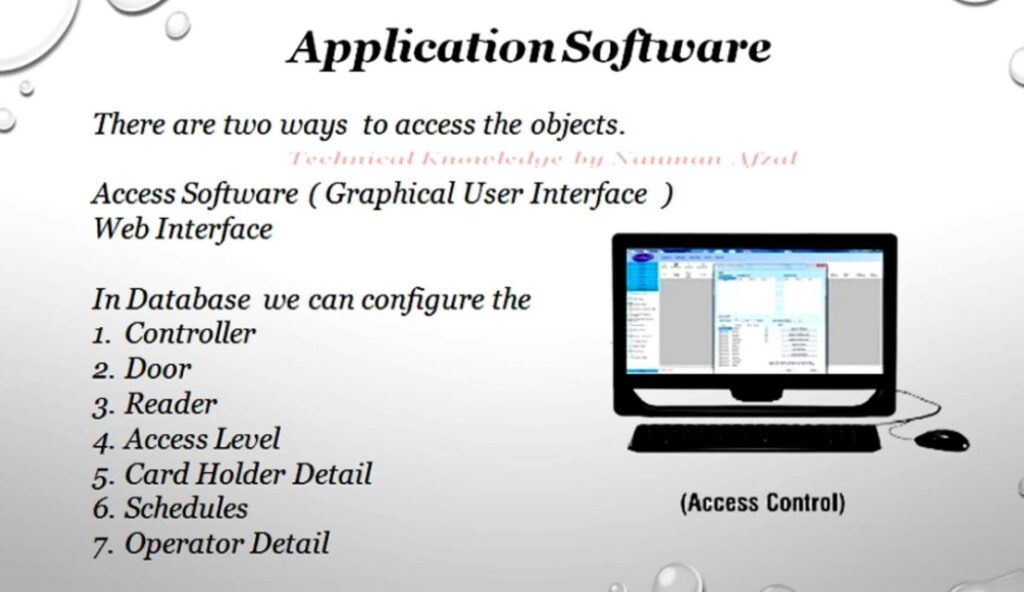
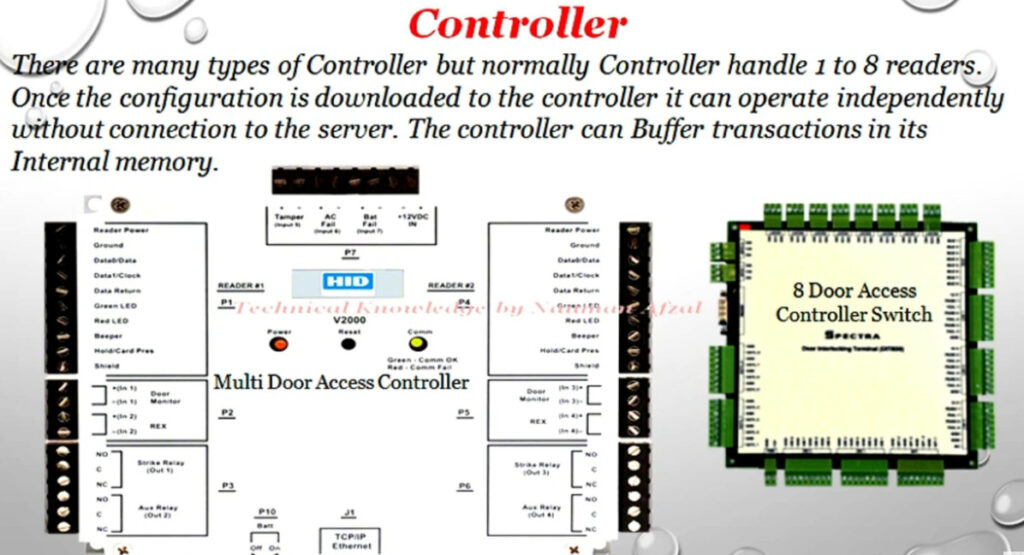
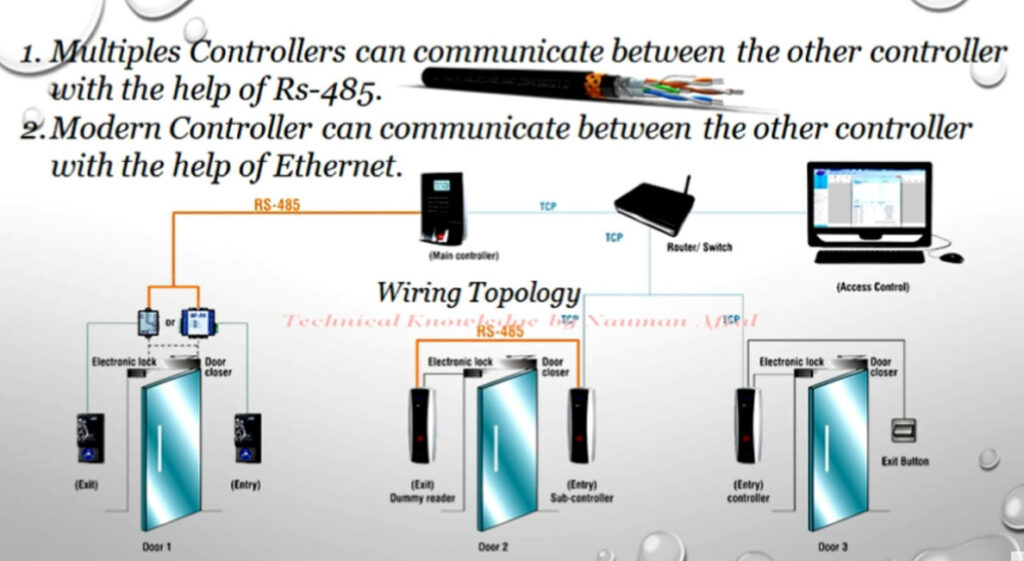
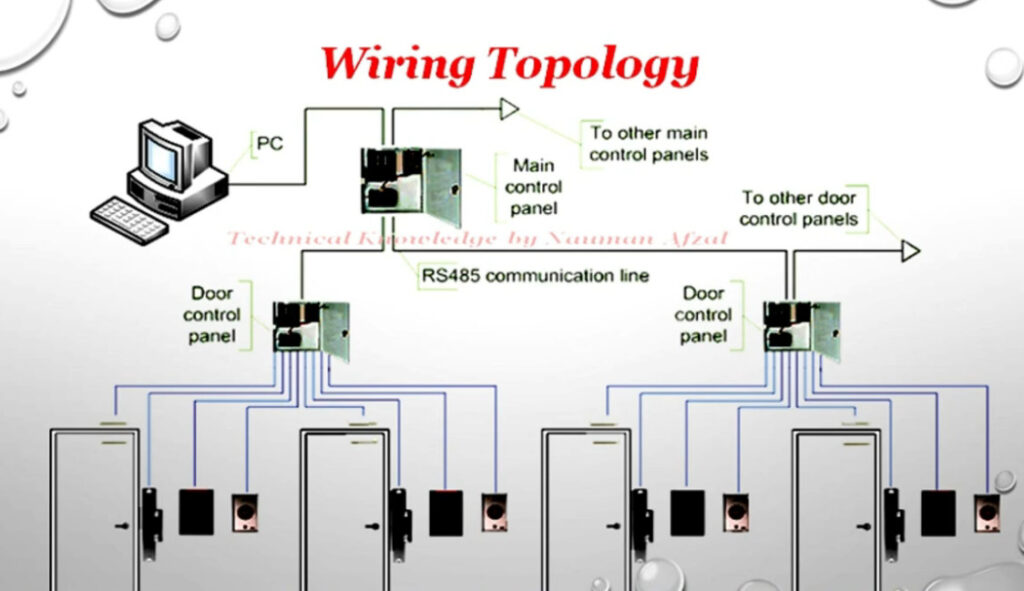
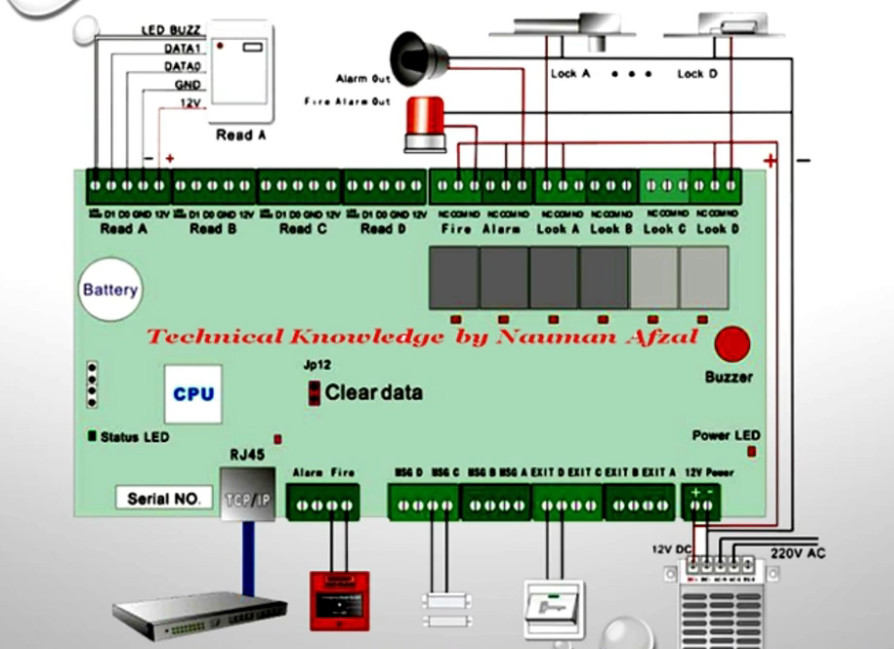
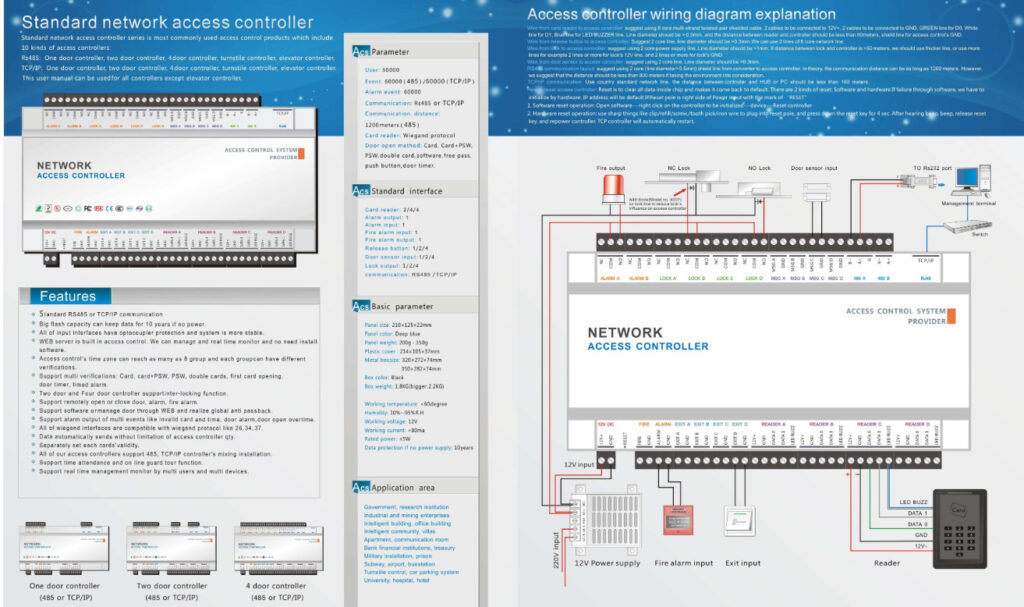
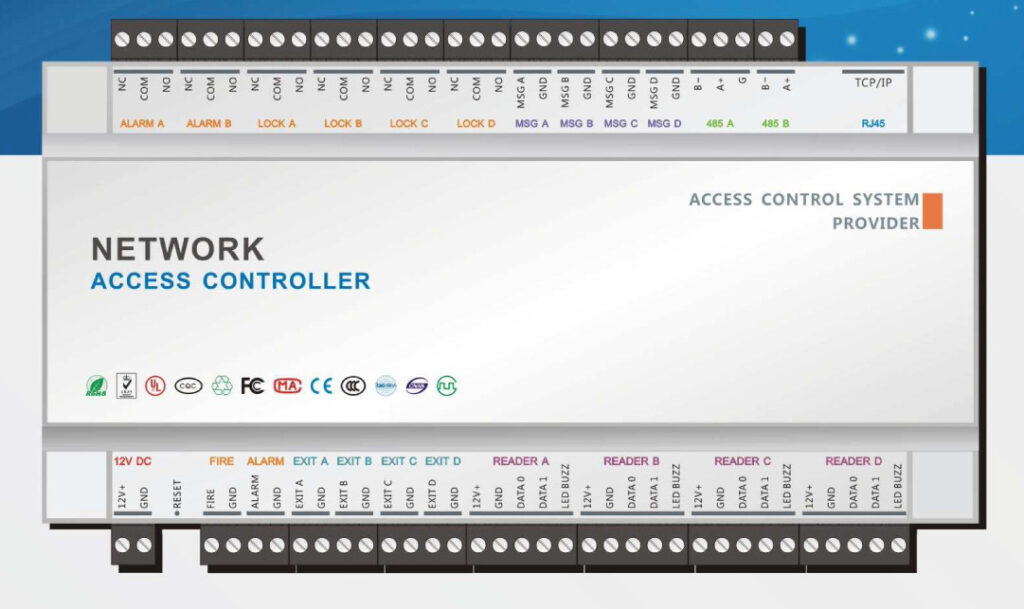
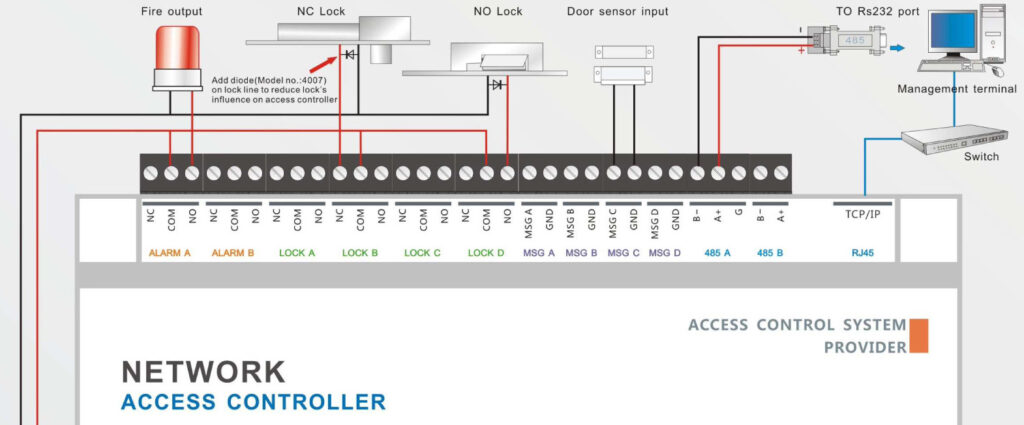
Door Access Control Systems are essential for managing and controlling access to secure areas in buildings or properties. These systems help enhance security by restricting access to authorized individuals while tracking entry and exit. There are various types of access control systems, each designed to meet different security needs. Here are the types of door access control systems:
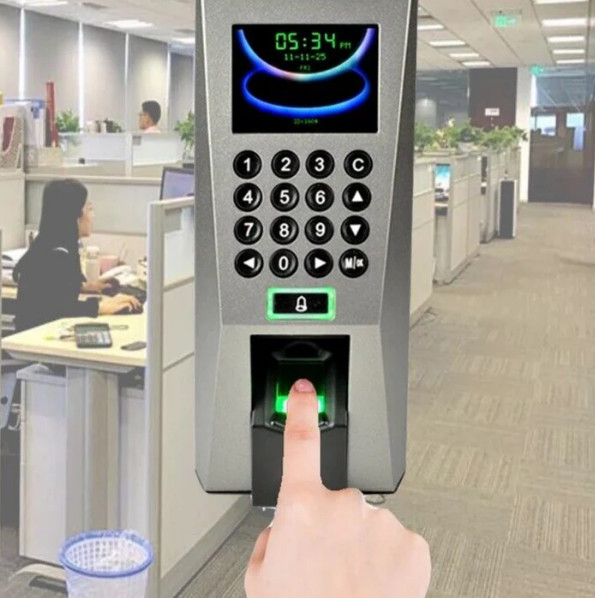
1. Keypad Access Control System
- Overview: Users gain access to the secured area by entering a PIN or password on a keypad.
- Features:
- Simple to install and use.
- Can store multiple access codes for different users.
- Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses or residential areas.
- Types:
- Single Code Keypad: A single PIN code for all users.
- Multiple User Keypad: Different PIN codes for different users.
- Usage: Common in residential areas, offices, or small businesses.
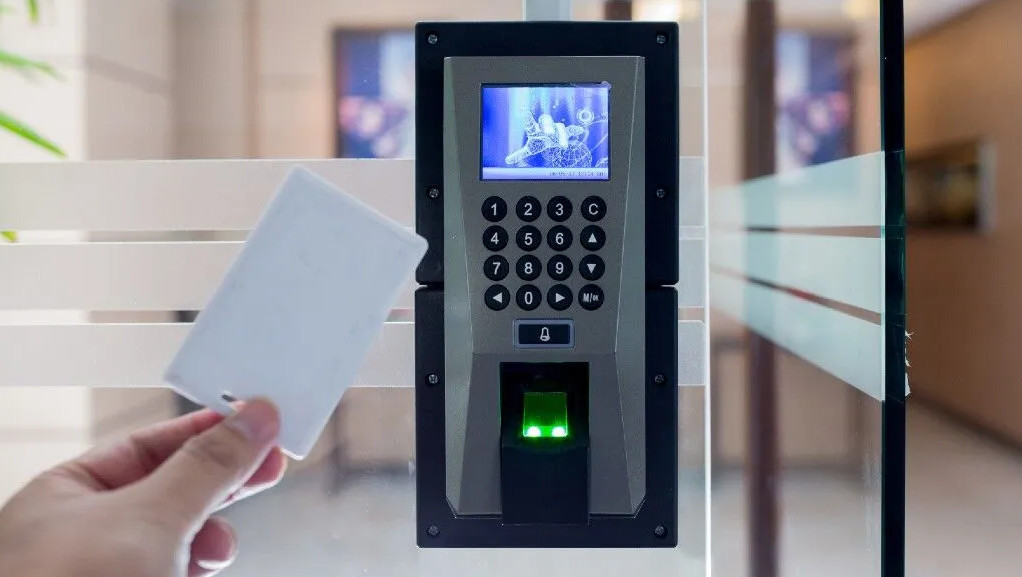
2. Card-Based Access Control System
- Overview: Users are granted access by presenting a key card or smart card (e.g., RFID, proximity cards) to a card reader.
- Features:
- Quick and efficient access control.
- Cards can be easily issued and revoked for employees or visitors.
- Often used with additional features like time-based access and auditing.
- Types:
- Proximity Cards: Use radio frequency identification (RFID) to communicate with the reader.
- Smart Cards: Contain a microchip to store and process data, offering higher security than proximity cards.
- Magnetic Stripe Cards: Similar to a credit card, where a magnetic stripe stores access data.
- Usage: Ideal for offices, schools, and commercial buildings.
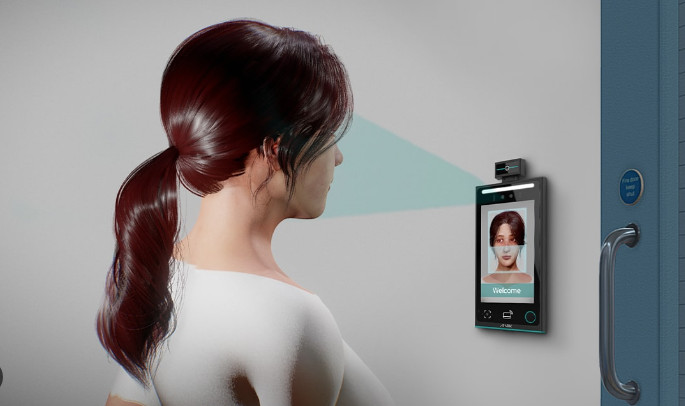
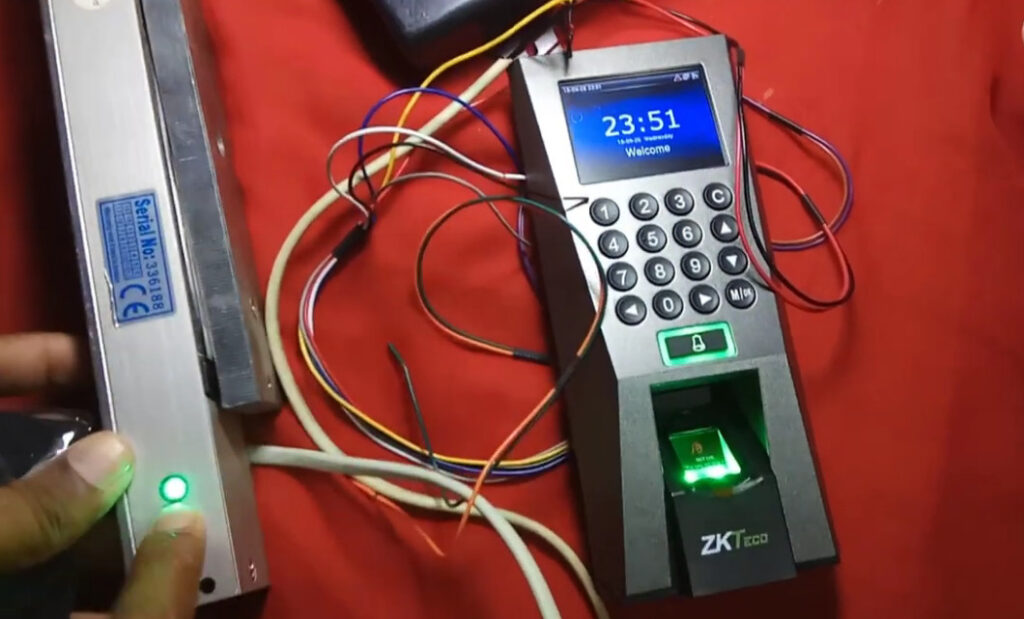
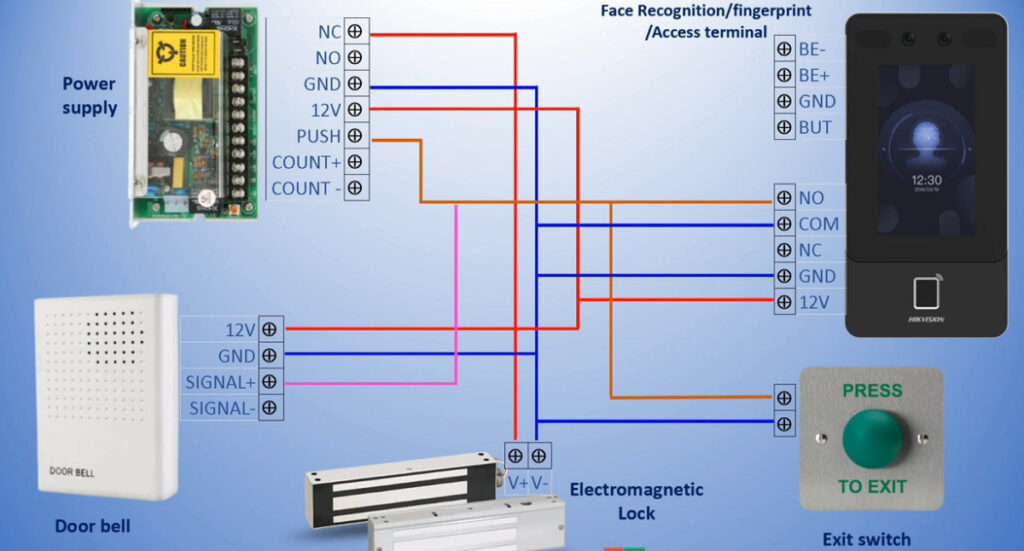
3. Biometric Access Control System
- Overview: This system uses a person’s unique biological characteristics (such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans) for identification and access.
- Features:
- High security due to the use of unique human traits.
- Eliminates the need for physical tokens (cards or keys).
- Can be integrated with other security measures like alarms or CCTV systems.
- Types:
- Fingerprint Recognition: Scans and matches a person’s fingerprint to grant access.
- Facial Recognition: Analyzes facial features and compares them to a stored database.
- Iris Scan: Uses the unique patterns in a person’s eye for identification.
- Palm Print: Identifies individuals based on the unique pattern of their palm.
- Usage: High-security areas such as government buildings, research labs, and financial institutions.
4. Smartphone or Mobile Access Control System
- Overview: Access is granted through a smartphone app using technologies like Bluetooth, NFC (Near Field Communication), or Wi-Fi.
- Features:
- Convenient for users, as they can use their smartphones instead of carrying physical access cards.
- Can be integrated with other smart building systems and IoT devices.
- Some systems allow remote access control and monitoring through apps.
- Types:
- Bluetooth-based: Unlocks doors when the user’s phone is in proximity to the door.
- NFC-based: Uses NFC technology to unlock doors by tapping the smartphone on the reader.
- Wi-Fi-based: Allows remote access control through an internet connection.
- Usage: Ideal for smart homes, offices, or buildings with high-tech integration.
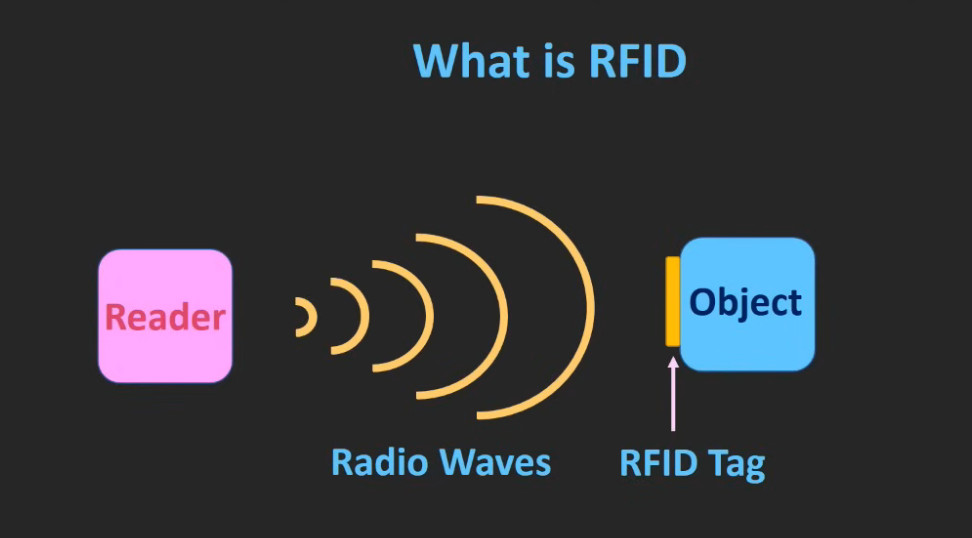
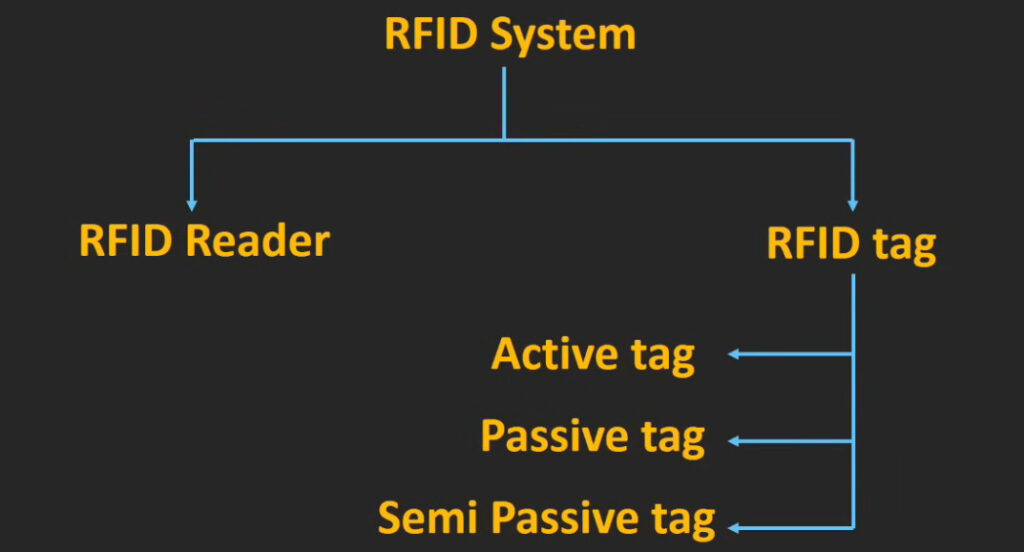
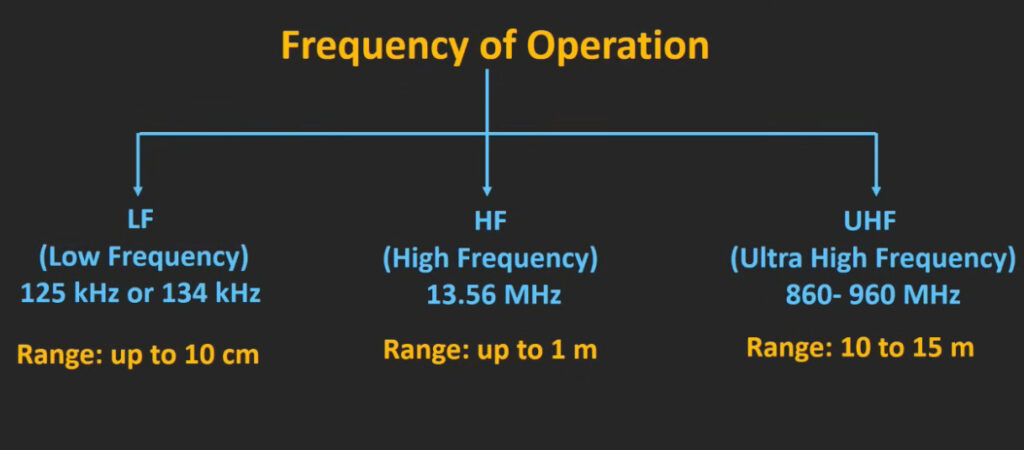
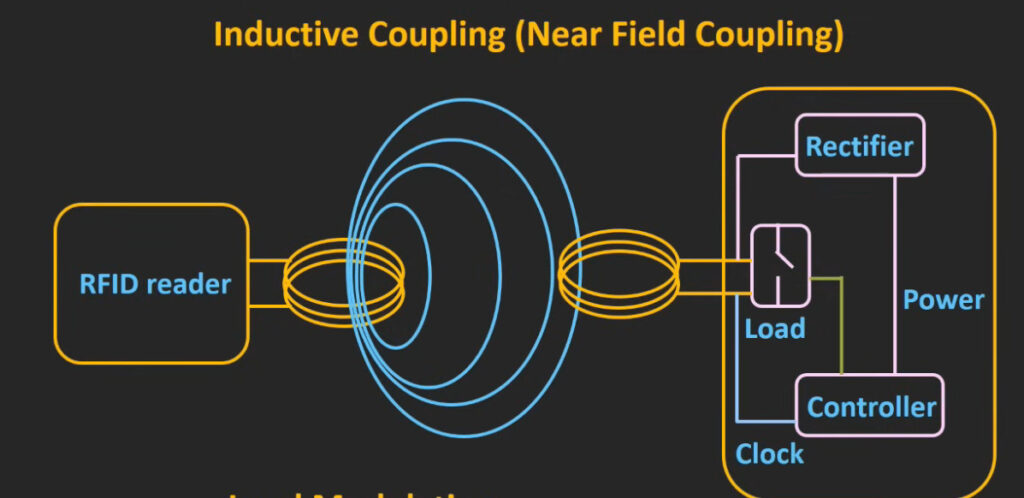
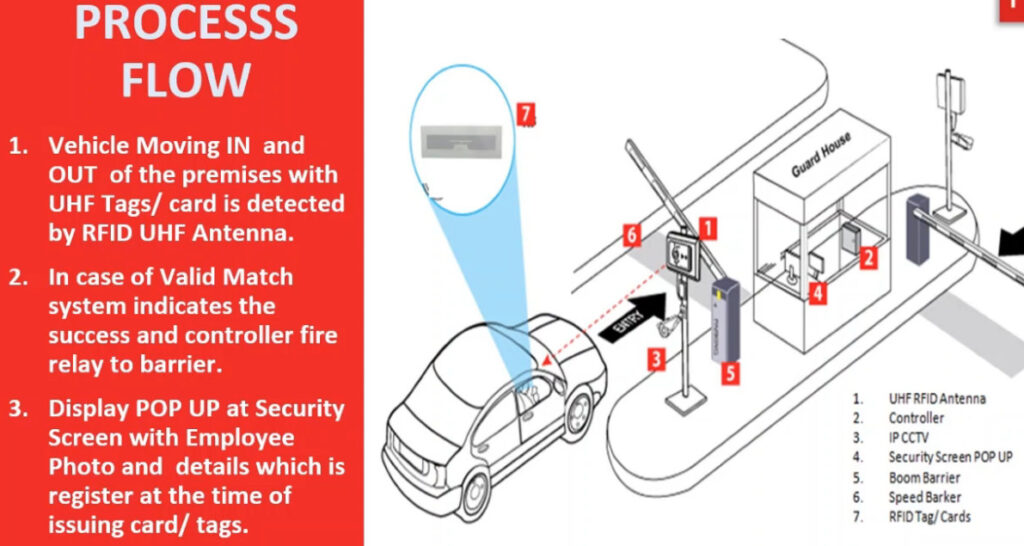
5. RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) Access Control System
- Overview: This system uses RFID technology to grant access to users carrying RFID-enabled cards or key fobs.
- Features:
- Allows contactless entry, making it convenient and fast.
- Cards or fobs can be easily deactivated and replaced if lost.
- Low-cost option for large-scale installations.
- Types:
- Proximity RFID: Uses radio waves to transmit the user’s credentials to the reader.
- Contact RFID: Requires physical contact between the card and the reader to transmit data.
- Usage: Common in offices, commercial buildings, hotels, and parking garages.
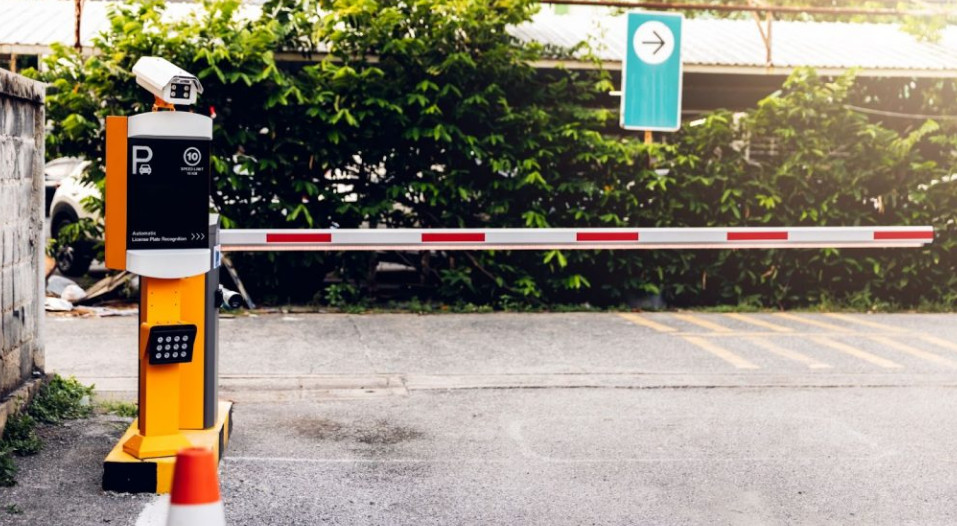
6. Turnstile or Barrier Access Control System
- Overview: Often used for high-traffic areas, turnstile systems control access by restricting movement through physical barriers like rotating gates or arms.
- Features:
- High-security and high-traffic capability.
- Can be used in combination with other access control methods like cards, biometrics, or PINs.
- Can integrate with ticketing systems for events, transportation, or stadiums.
- Types:
- Full-Height Turnstile: A rotating barrier that offers maximum security.
- Half-Height Turnstile: Less secure than full-height but often used in moderate-security environments.
- Usage: Ideal for public transportation stations, stadiums, amusement parks, and office buildings with high foot traffic.
7. Mechanical Keyed Access Control System
- Overview: The most traditional form of access control, involving physical keys to unlock doors.
- Features:
- Easy to install and cost-effective for smaller areas.
- Requires physical keys that can be lost, stolen, or copied.
- No electronic components or infrastructure.
- Types:
- Standard Mechanical Locks: Basic locking systems that use keys for access.
- Master Key Systems: A system where one key can open multiple doors while other keys have access to specific doors.
- Usage: Common in residential homes, small businesses, or temporary access situations.
8. Fingerprint and PIN Hybrid System
- Overview: Combines the security of fingerprint recognition with a PIN code for dual-factor authentication.
- Features:
- Higher security as it requires both biometric identification and a secret PIN.
- Often used in high-security areas where extra precautions are needed.
- Types:
- Biometric + PIN: Requires both a fingerprint scan and PIN for access.
- PIN + RFID: Combines a card or fob with a PIN code for entry.
- Usage: Used in offices, banks, government buildings, or secure areas.
9. Time-Based Access Control System
- Overview: This system allows or restricts access based on specific times or schedules. It is often integrated into other access control methods, such as keypads or cards.
- Features:
- Restricts access during non-working hours or holidays.
- Can be programmed to automatically lock or unlock at specified times.
- Useful for managing employee work hours or access to restricted areas.
- Usage: Common in offices, warehouses, schools, or government buildings.
10. Cloud-Based Access Control System
- Overview: A modern access control system that is hosted on the cloud, allowing remote management and monitoring of access points via an internet connection.
- Features:
- Access can be managed remotely, even from mobile devices.
- Can be integrated with other security systems like CCTV, alarms, and building management systems.
- Provides detailed logs and analytics of who accessed specific doors and when.
- Usage: Ideal for businesses with multiple locations, remote offices, or those looking for scalable, flexible solutions.
11. Video Intercom Access Control System
- Overview: Integrates an intercom system with access control, allowing users to visually verify visitors before granting access through a door.
- Features:
- Combines audio and video communication with door unlocking capabilities.
- Users can visually confirm the identity of visitors and grant access remotely.
- Can be integrated with smartphones or digital screens.
- Usage: Used in residential buildings, offices, gated communities, and commercial properties.
Key Considerations When Choosing an Access Control System:
- Security Level: Higher-risk areas may require biometric, RFID, or multi-factor systems.
- Ease of Use: Systems like keypads or smartphone-based solutions offer ease of use and convenience.
- Scalability: Cloud-based or card-based systems are more flexible for expanding or managing multiple locations.
- Integration: Consider how the system integrates with other security or building management systems.
- Budget: Systems vary in price, so choose one that fits your budget while meeting your security needs.
Conclusion:
There are many types of door access control systems, each suited for different security requirements. Whether you need a simple keypad, an advanced biometric system, or a smart cloud-based solution, choosing the right one will depend on the level of security, convenience, and scalability required for your facility or property.