- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
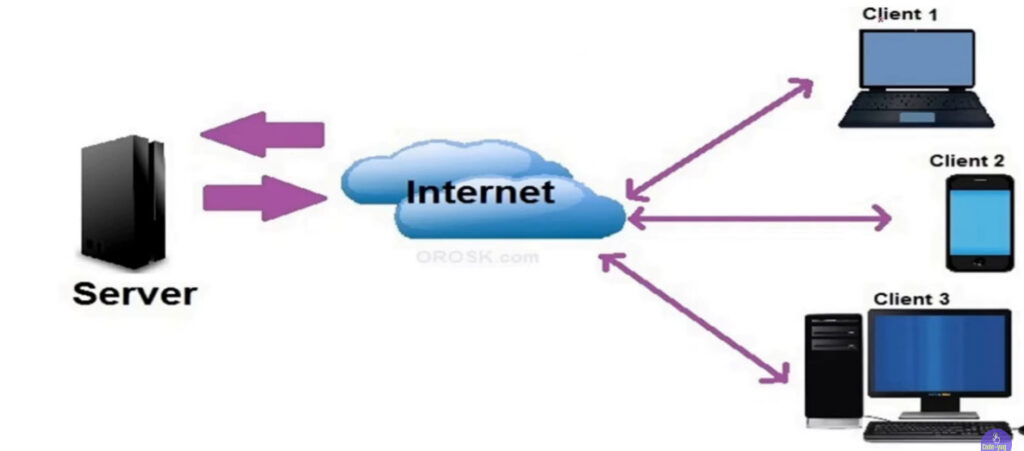
A server is a specialized computer or software system designed to provide services, resources, or data to other computers (known as clients) over a network. Servers are typically more powerful than regular personal computers and are optimized for handling multiple requests, managing resources, and supporting various services.
Here are some key points about servers:
In summary, a server is a vital component in any network, providing essential services like file storage, web hosting, and application hosting, and it plays a central role in modern IT infrastructures.
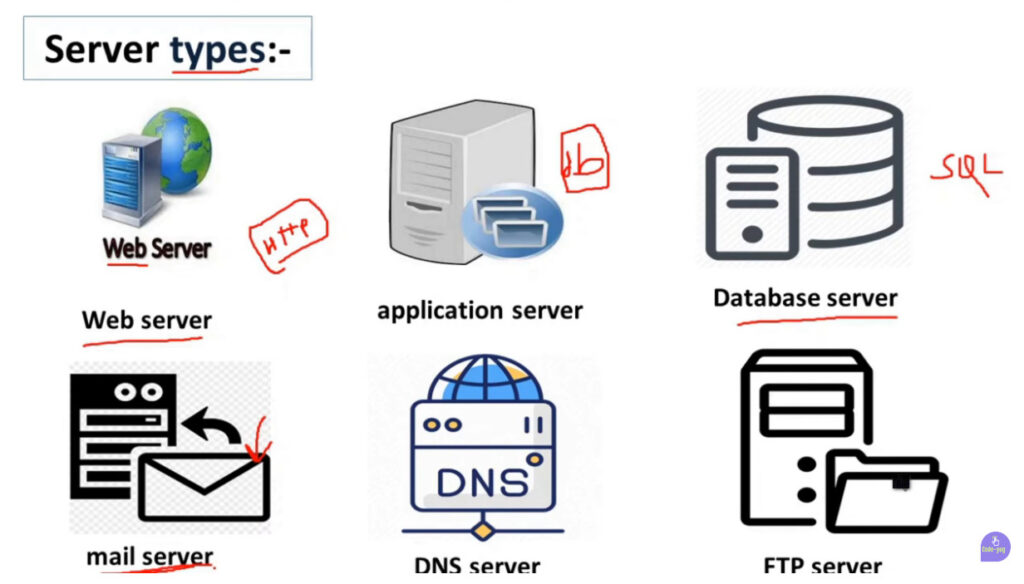


In the context of server machines, there are various types designed to serve specific purposes. These types of server machines vary in their hardware, capabilities, and the tasks they are designed to handle. Here are some common types of server machines:
The type of server machine chosen depends on the organization’s specific needs, such as performance, scalability, reliability, and cost. Servers vary from basic file storage systems to highly complex and powerful systems like mainframes and supercomputers. Choosing the right server depends on factors like the type of application, the amount of traffic, and the level of data processing required.
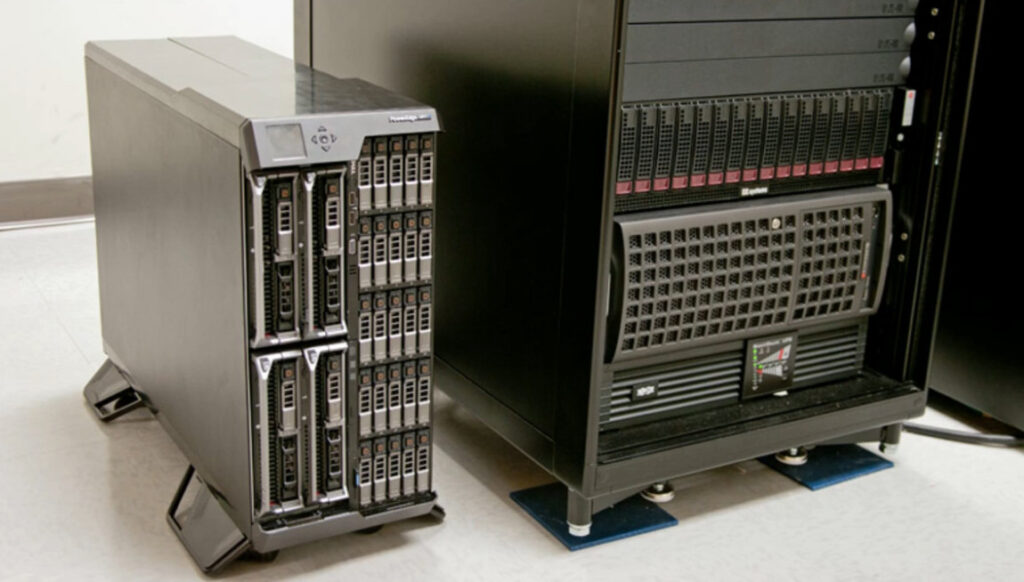
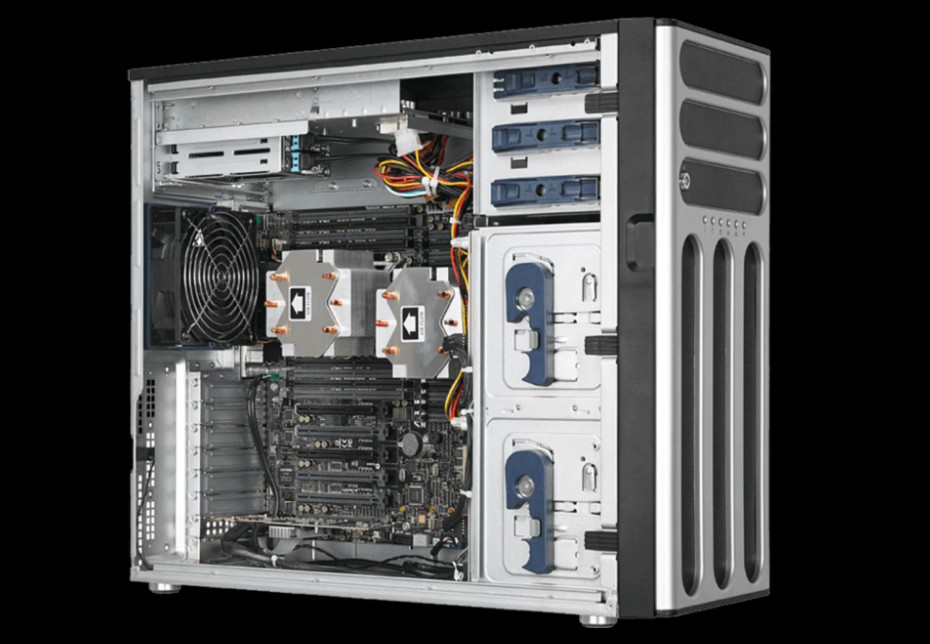
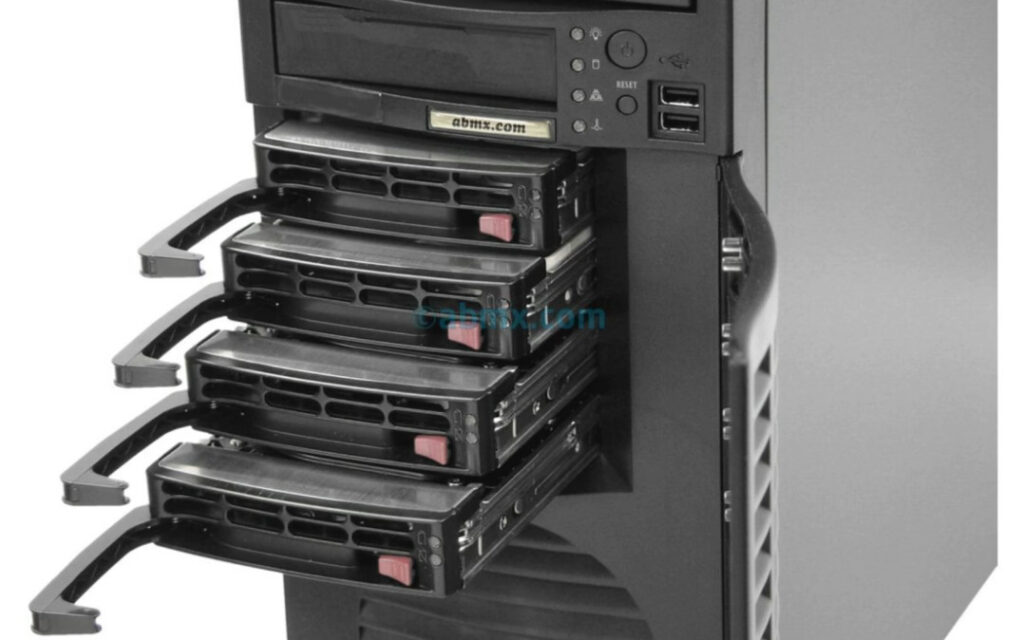















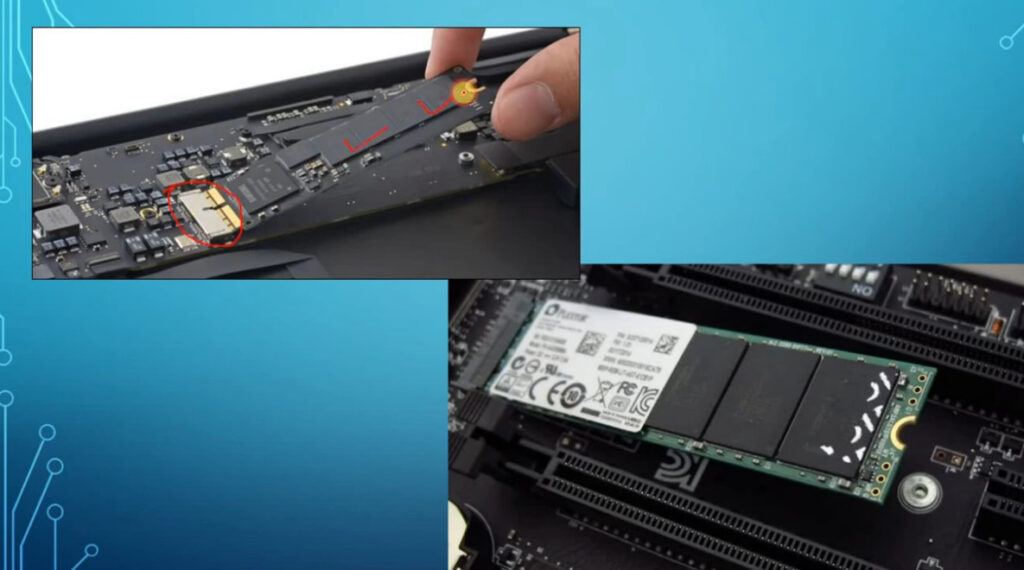
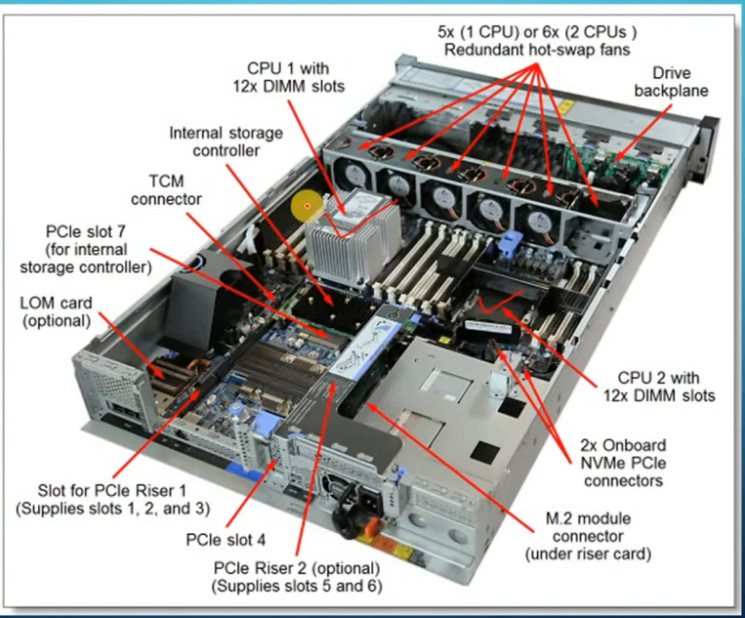

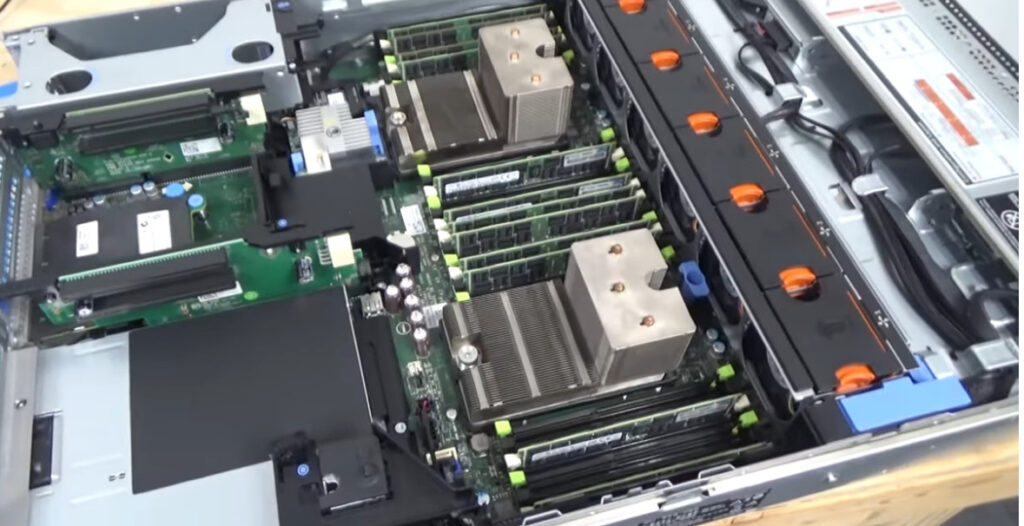
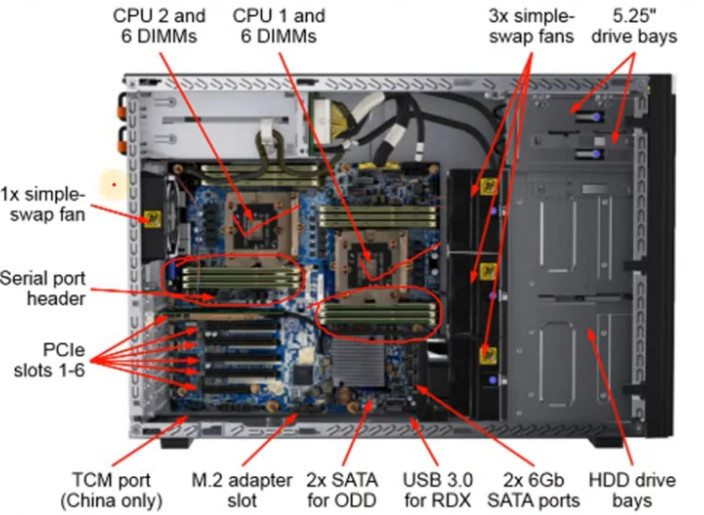












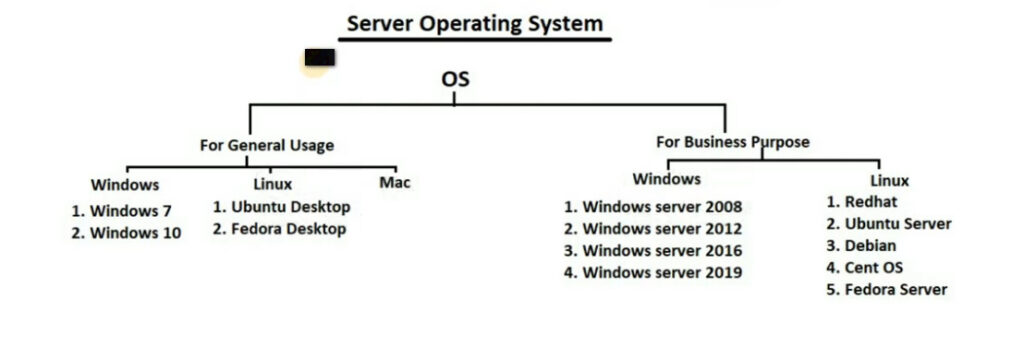
Several companies are known for manufacturing servers, which cater to a wide range of needs, from small businesses to large data centers. Here are some notable server manufacturers:
Each of these companies offers various types of servers, including rack-mounted, blade, tower, and modular servers, designed for specific business needs.
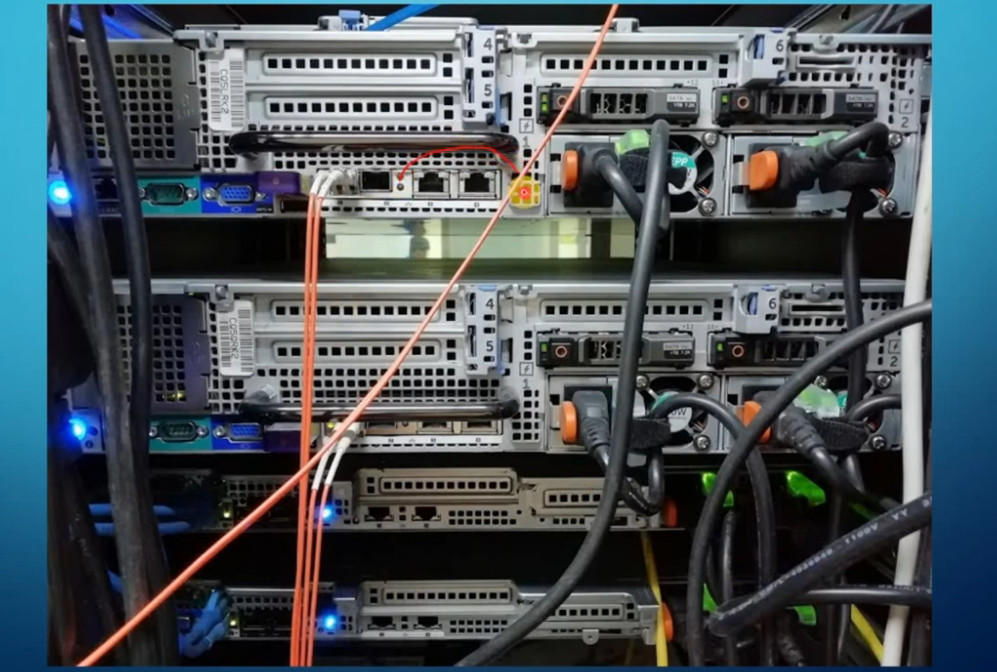
Most server manufacturers provide a dedicated port for remote management of their servers. These remote management solutions allow administrators to manage servers independently of the operating system, which can be useful for tasks like firmware updates, troubleshooting, and rebooting the server.
Here are the remote management ports and technologies for the main server manufacturers:
These remote management ports are typically used for out-of-band management of servers, and different manufacturers may offer additional tools or interfaces to enable advanced remote administration capabilities.
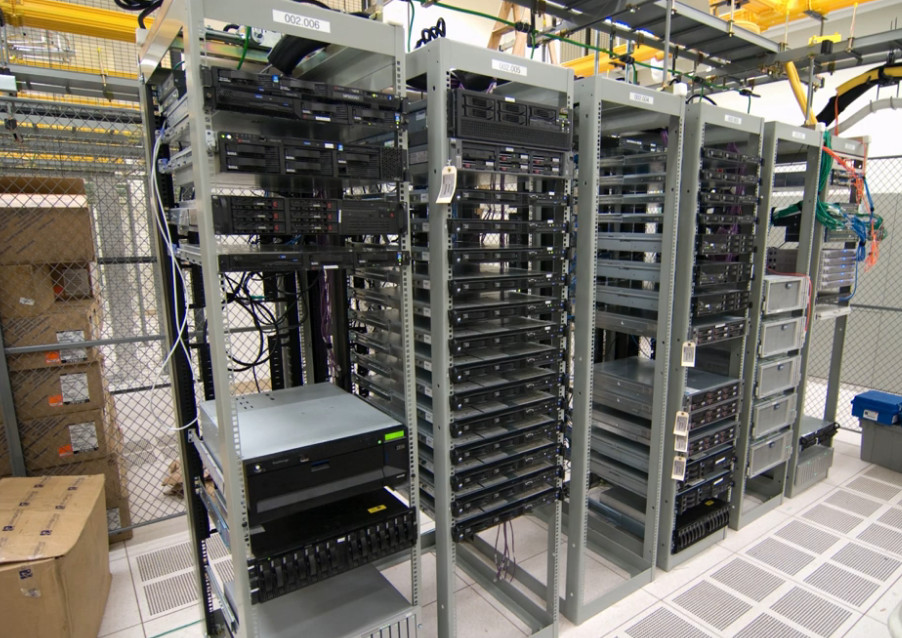
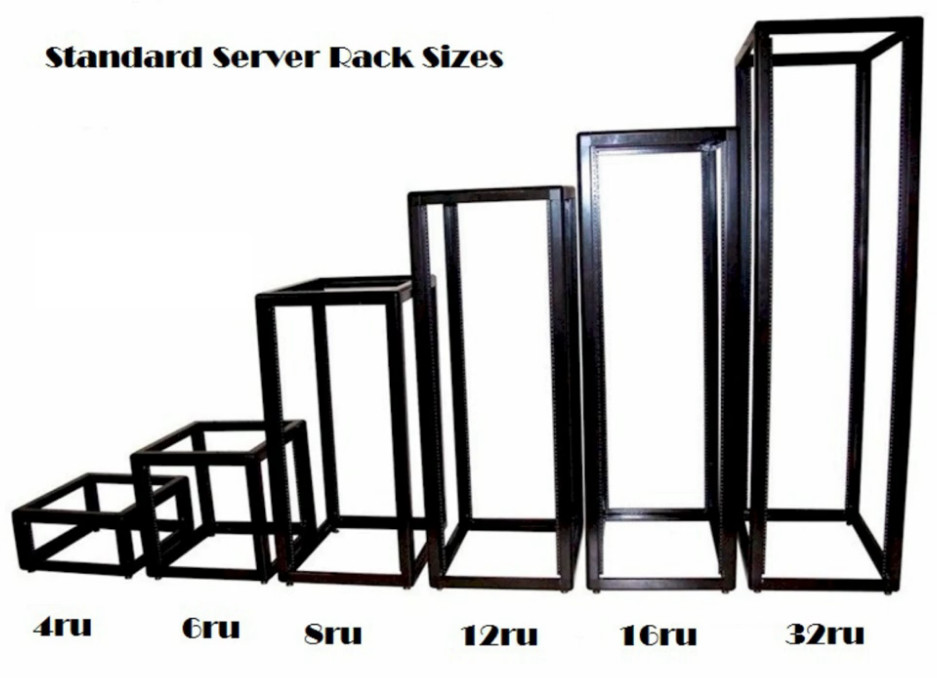
When it comes to cabling huge network connections, Servers are usually considered to manage these networks effectively. Coming to Servers, there are three types of servers classified on the basis of their structure. These Servers are Rack servers, Tower servers, and blade servers. We are going to talk about blade server vs rack server and what are the distinct features which differentiate them from the two.
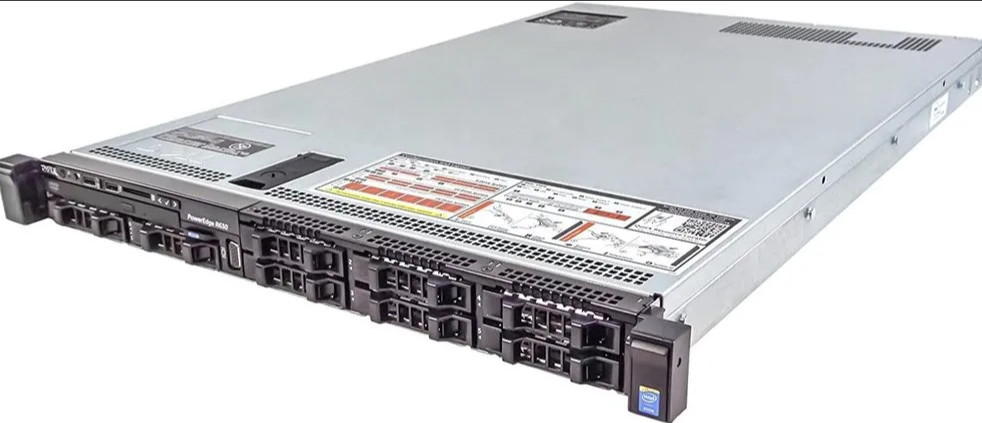
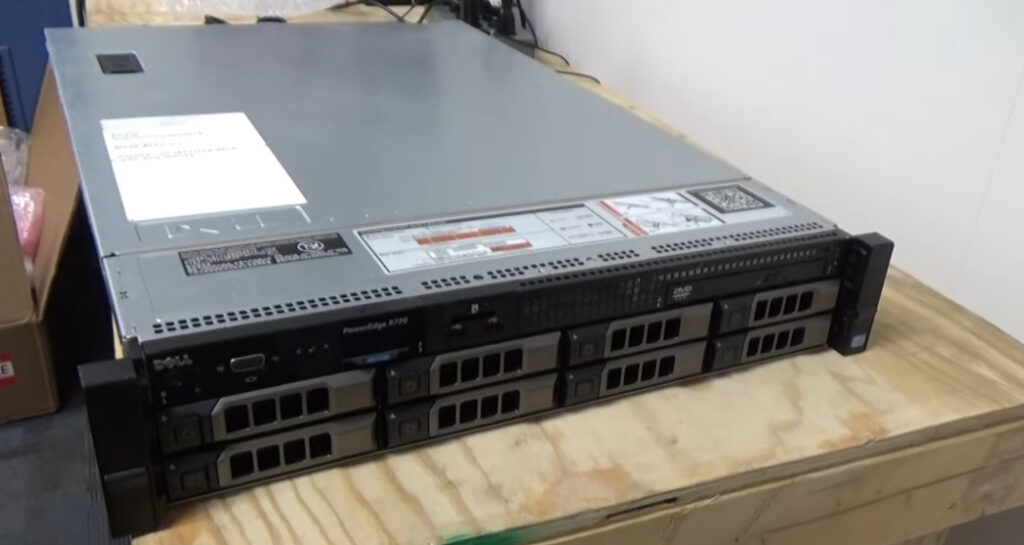
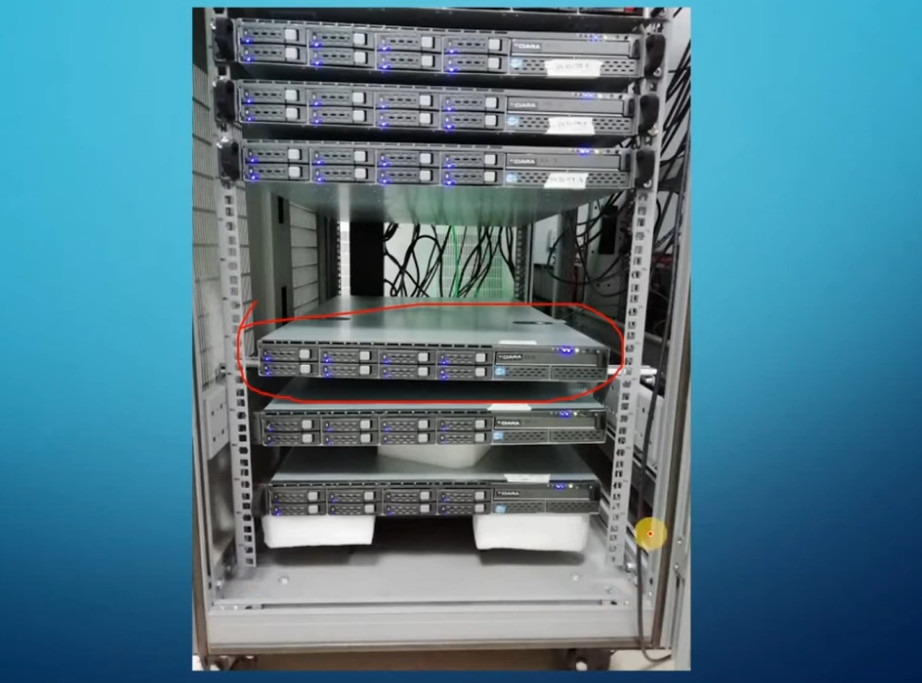
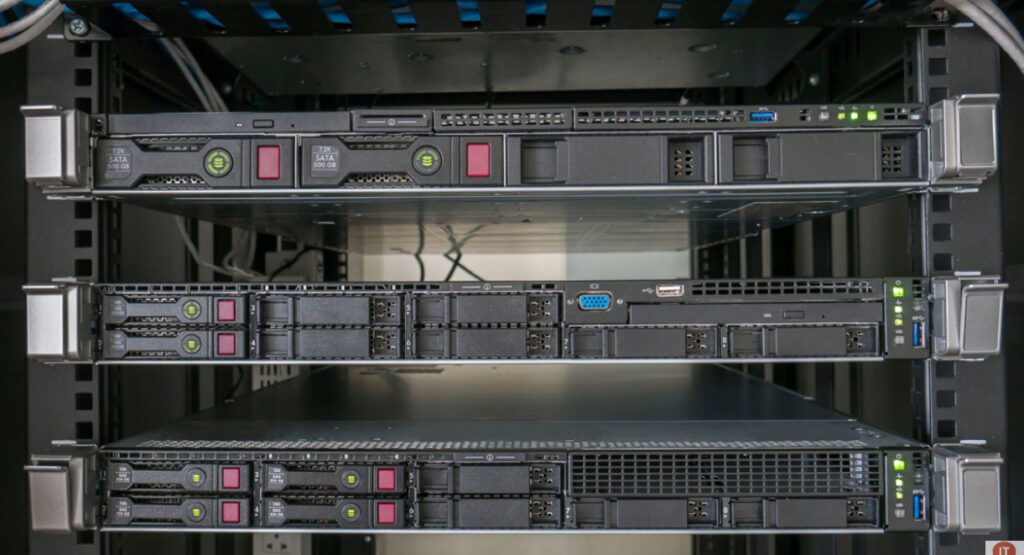
Rack Servers are rack-mounted servers that could specifically be fitted in a server rack. Rack Servers are servers that are made with efficient configurations to support a wide range of requirements.
They are also known for their shape and structure as unlike traditional servers shaped in a PC structure, it is much wider and flatter which could be fit into any server rack. Rack servers are considered beneficial if there’s a requirement of a small number of servers as they pose low upfront costs being highly economical.
Rack servers benefit in minimizing the space consumption as they can be mounted one over the other.
• Rack server acts as the lone rider of all the needed components as a single powerful system. Rack servers could perform powerfully to run high-end applications.
• Rack servers are convenient to fit as it consumes less amount of physical space.
• Rack servers are usually equipped with internal fans, increasing airflows which makes it’s cooling more easier.
• Rack servers can be highly efficient when you require more than one server as they don’t require a huge chassis.
In order to function as a stand-alone system, rack servers are usually built with all the components required. They can be efficient and are used to run high-end applications.
It is convenient to have the ability to easily mount a server within a rack and save a lot of space, particularly when compared to a traditional tower-style server.
When you need more than one server, rack servers are best suited because they do not require a massive chassis.
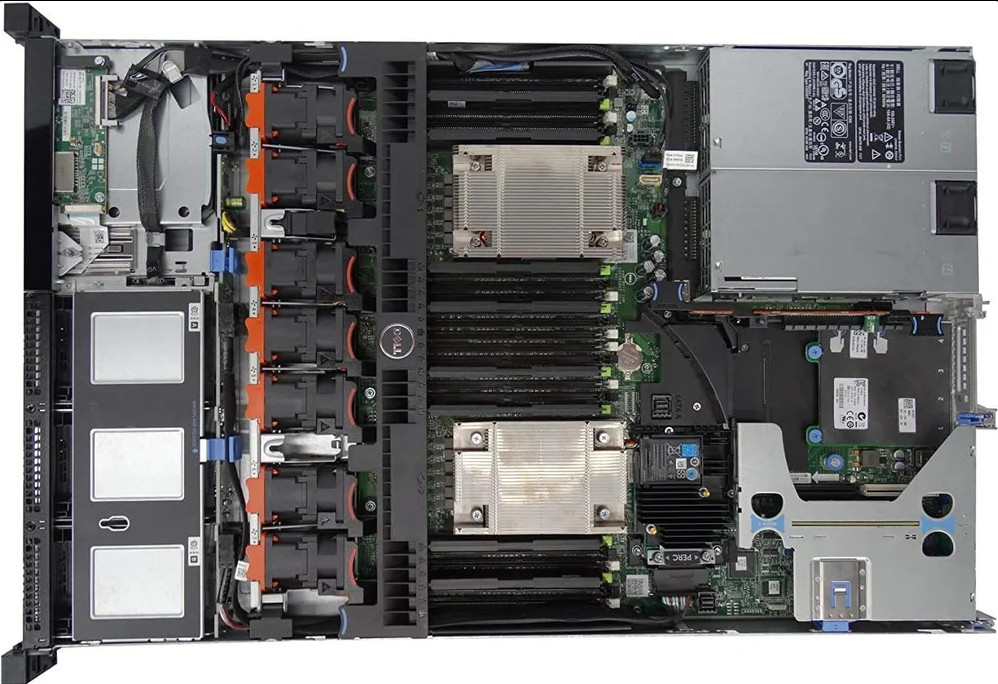
Rack servers come with the necessary hardware, including memory, raid controller data drives, power supply, cooling unit, to perform all a server requires. These are versatile stand-alone devices that can be used to run high-end applications.
Rack mounted servers continue to be the most cost-effective computer network choice for small to medium-size operations.
A rack server comes with an integrated cooling fan, making the server’s cooling process easier than others.
As a stand-alone or networked machine, each rack server has everything required to run: its own power source, CPU, and memory. This allows for intensive computing operations to be performed by rack servers.
Rack-mounted servers and other computing devices make restricted data center space use extremely effective. With additional memory, storage, and processors, rack servers can be extended easily. And if administrators have pooled or clustered the server data for redundancy, it is physically easy to hot-swap rack servers.
Smaller deployments at a lower cost offer management and energy efficiency.
Densely populated racks are needed more cooling units, which increases the energy cost. In total, large numbers of rack servers would increase energy needs.
Dense racks are needed for more troubleshooting and management time.
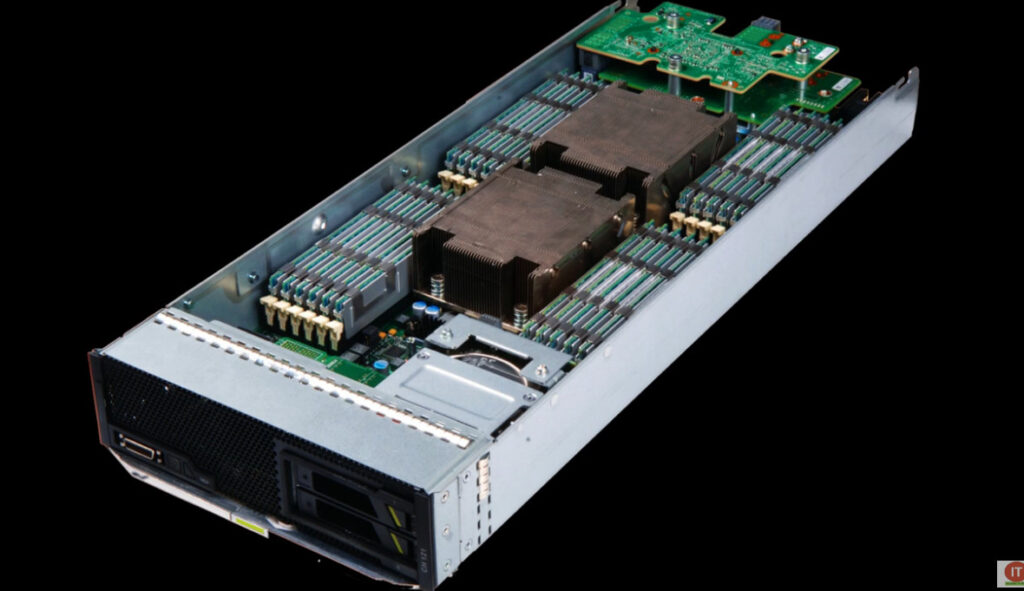
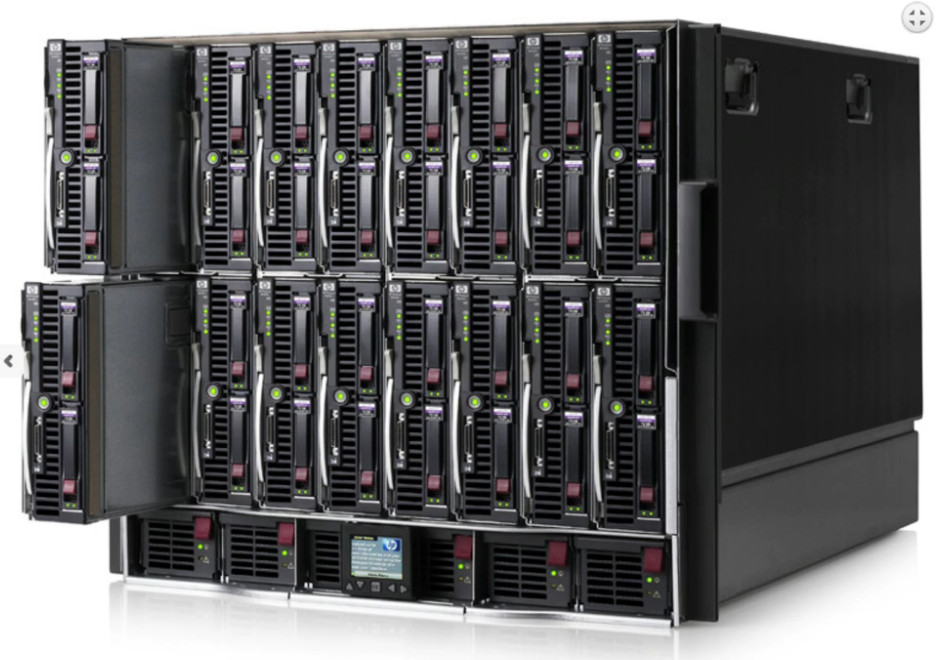
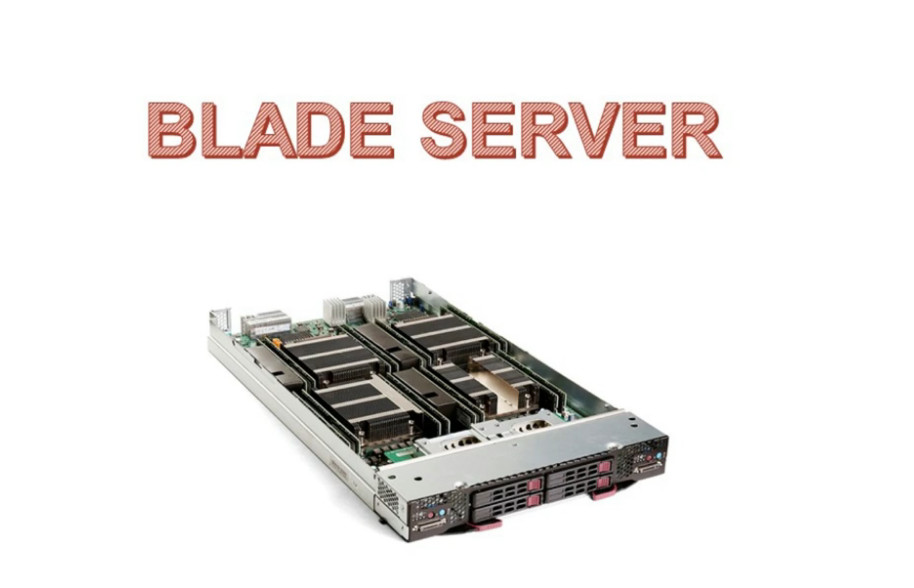
Blade servers are those servers that can accommodate multiple servers in a smaller area. These servers usually have a thin like structure having just the CPUs, memory, integrated network controllers, and sometimes storage drives built-in.
These servers also manage their chassis according to their components required. Because of their thin like structure, blade servers can be conveniently fitted into one single rack along with providing high processing power.
Blade server technology require fewer internal components as on a larger blade chassis, multiple blade servers can be slid and fitted to operate efficiently.
These servers are capable to be used when there are higher computing requirements along with some type of Enterprise Storage System like NAS or SAN. Blade servers provide that kind of architecture that allows you to scale a higher processor density.
• Blade servers can enable their massive chassis to supply power to multiple servers which reduce total power consumption for each blade server.
• Blade servers promote Hot-swappable features which could provide you redundancy when one blade faces a problem making it to be pulled and replaced much more easily.
• Blade servers require only one cable (often fiber) for running to the chassis which reduces the use of individual cables running for each blade chassis server.
• Blade servers require minimal space and at the same time provide high processing power.
In certain instances, the blade server chassis can supply several servers with power, minimizing total consumption.
Blade servers can be designed to be hot-swappable, so much easier to pull and replace if one blade has a problem. This assists in promoting redundancy.
Blade servers, though taking up limited space, can provide extremely high processing power.
Since a blade server is a product with only necessities, minimum space is needed and high processing performance can be provided.
The hot-swappable function enables redundancy to be retained by a blade server. So, without taking the whole system down, it can be taken out and replaced if there is a problem with one of the blades.
All of the blade server system are mounted in a blade enclosure, ensuring that each server does not require individual cables.

The chassis supplies power to multiple blade servers, instead of powering and cooling multiple servers in separate racks. This decreases spending on energy.
Blade servers provide high processing power although taking up limited space.
Leading operating systems and hypervisors, databases, software, web services, and other processes and applications at the enterprise level can be hosted.
The blade server environment is simplify by centralized monitoring and maintenance, load balancing, and clustered failover. Hot swapping also helps improve the availability of systems.
Over time, operating expenses are rational due to streamlined management interfaces and lower energy consumption. Initial costs of capital, deployment, and configuration, however, can be high.
Blade servers with high density require advanced climate control. In order to maintain blade server efficiency, heating, cooling, and ventilation are all required expenses.
Going through the above concepts of Blade server vs Rack server it would be difficult to frame out which one is the best as both of these servers have the same set of functionalities and working. It is particularly, based on your processing needs and layout of your physical space along with considering the thermal and electrical power requirements of your machine and other computing requirements which could let you decide among the two.
Serverstack is one of the leading brands in dealings of Rack servers and provides you the efficient servers of ASUS helping you to manage your huge network connections easily.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are different type of servers?
There are several server types that all perform various functions. Most networks contain one or more different types of servers:
Monitoring and management servers
Q2. What is a chassis server?
A server chassis is a metal frame that is used to house or physically assemble servers in several different form factors. In a single physical body, a server chassis makes it possible to put multiple servers and other storage and peripheral equipment. A server casing or server case may also be called a server chassis.
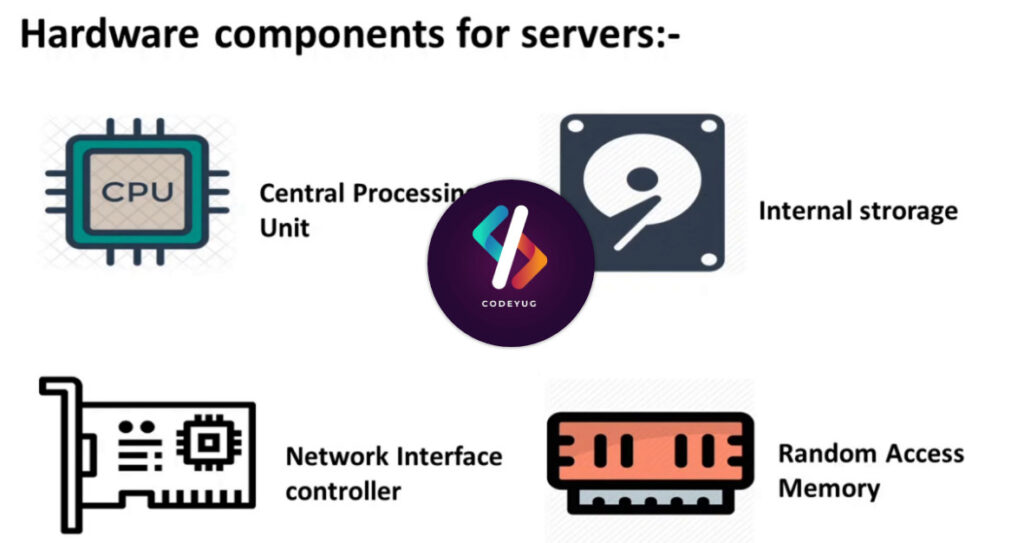
Q3. What are the main components of a server?
There are several main components on all servers, as well as other optional components. Because every time we go online, we all enjoy servers, it is a good idea to obtain a fundamental overview of how they function by looking at their individual components.
Q4. Describe briefly and analyze the functional and architectural features that distinguish the blade server and rack servers?
Rack servers are quite wide and short, allowing one server to fit into a single part of the rack. In comparison a bay of blade servers may fit 20 blades onto a small part of the rack. Blade servers, as opposed to rack servers, are utilized for high-powered processing and are hot-swappable.

