- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
What is DHCP?
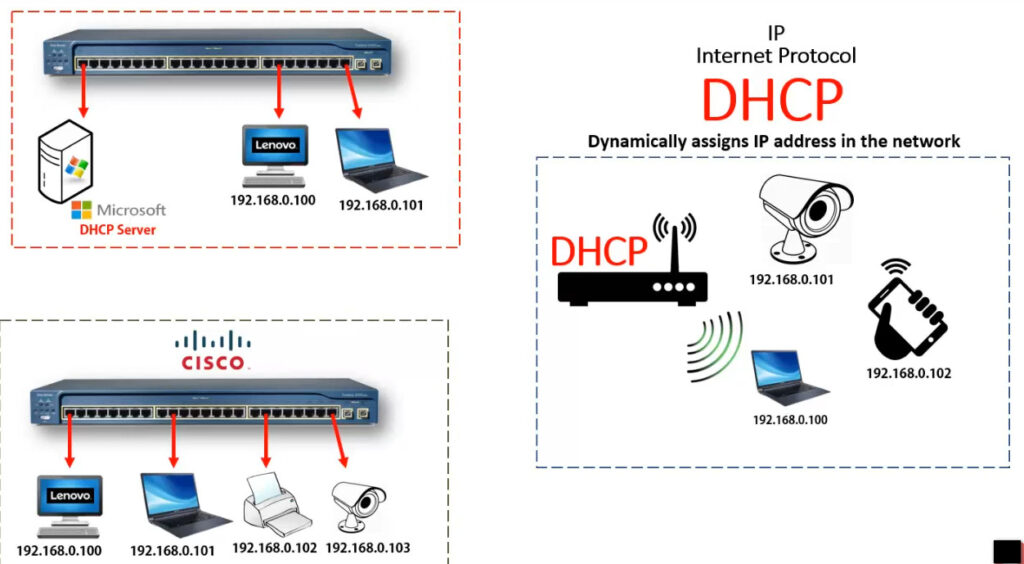
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network protocol that automates the assignment of IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, DNS servers, and other network configurations to devices on a network. Instead of manually assigning IP addresses to each device (static IP addressing), DHCP allows a DHCP server to automatically assign an IP address from a predefined range (called a scope) to any DHCP-enabled device on the network.
How DHCP Works:
Enter Global Configuration Mode:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Define the DHCP Address Pool:
Create a DHCP pool with a name (e.g., LAN-Pool) and specify the IP address range, subnet mask, and other relevant settings.
Router(config)# ip dhcp pool LAN-Pool
Router(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
Router(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.1.1 // Default Gateway IP
Router(dhcp-config)# dns-server 8.8.8.8 // DNS Server IP (optional)
Router(dhcp-config)# domain-name example.com // Domain name (optional)
Exclude IP Addresses (Optional):
It’s a good practice to reserve specific IP addresses (e.g., for servers, printers, or other devices) so they are not assigned dynamically by the DHCP server.
Use the ip dhcp excluded-address command:
Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.20
This excludes the IP range 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.20 from being assigned dynamically.
Verify DHCP Configuration:
To check the status of your DHCP server and the assigned IP addresses, use the following command:
Router# show ip dhcp binding
This shows the IP address leases that have been assigned to clients.
2. DHCP Configuration on a Cisco Switch:
In general, Cisco switches do not act as DHCP servers by default (unless they are Layer 3 switches or have additional services configured). However, you can configure a Layer 3 switch to act as a DHCP server or simply configure a switch to relay DHCP requests (using the ip helper-address command).
a) Configuring a Cisco Layer 3 Switch as a DHCP Server:
If you’re using a Layer 3 switch and want to configure it as a DHCP server, the process is very similar to configuring a router. Here’s an example:
Enter Global Configuration Mode:
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Define the DHCP Address Pool:
Switch(config)# ip dhcp pool VLAN10
Switch(dhcp-config)# network 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0
Switch(dhcp-config)# default-router 192.168.10.1
Switch(dhcp-config)# dns-server 8.8.8.8
Exclude IP Addresses:
Switch(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.10.1 192.168.10.10
Configure VLAN Interface:
The switch needs an IP address for the VLAN interface (SVI) to communicate with devices in that VLAN:
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Verify DHCP Configuration:
Switch# show ip dhcp binding
Switch# show ip dhcp pool
b) Configuring a Layer 2 Switch to Relay DHCP Requests:
In some cases, a Layer 2 switch (which doesn’t route traffic between different subnets) can relay DHCP requests from clients to a DHCP server on another network. This is done using the ip helper-address command, which forwards the DHCP requests to a specified DHCP server.
Enter Global Configuration Mode:
Switch> enable
Switch# configure terminal
Configure the Switch’s VLAN Interface (if needed):
If you want to configure the switch to be part of a VLAN (e.g., VLAN 10), configure the interface for that VLAN:
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.2 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Configure the ip helper-address Command:
Point the switch to the IP address of the DHCP server (assuming the DHCP server is located on a different subnet):
Switch(config)# interface vlan 10
Switch(config-if)# ip helper-address 192.168.1.1 // IP of the DHCP server
Verify Configuration:
To check the forwarding of DHCP requests, you can use the following:
Switch# show ip interface vlan 10
Conclusion:
Router as DHCP Server: If you’re using a Cisco router to assign IP addresses, you can configure the DHCP pool and set up exclusions to avoid assigning certain IPs.
Switch as DHCP Server: If you’re using a Layer 3 switch, it can act as a DHCP server, similar to a router.
Layer 2 Switch: A Layer 2 switch can forward DHCP requests to a DHCP server on a different network by using the ip helper-address command.
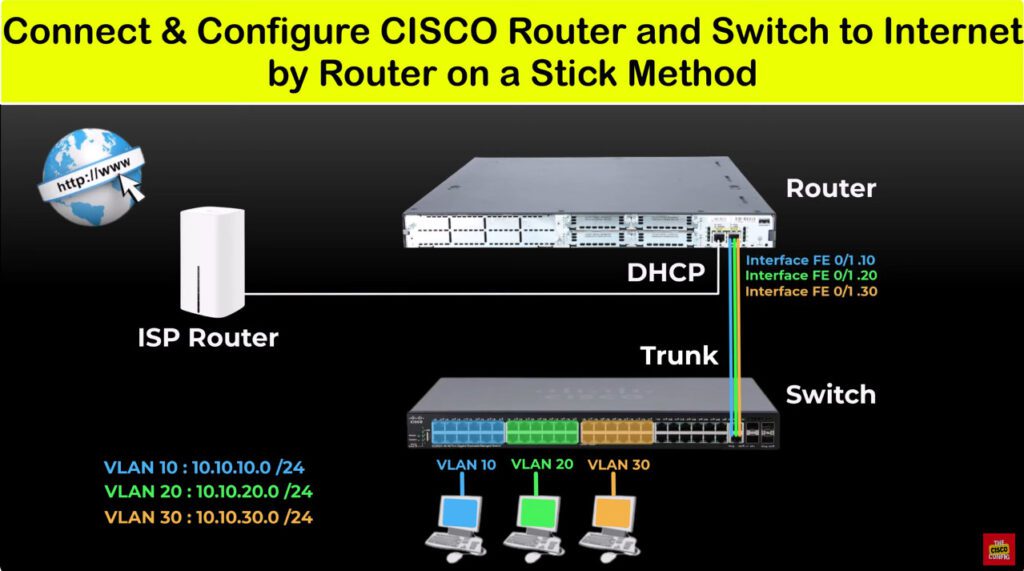
VLAN DHCP Configuartion
config t
ip dhcp pool 10 <For VLAN 10>
network 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0
default router 10.10.10.1
dns-server 8.8.8.8
exit
config t
ip dhcp pool 20
network 10.10.20.0 255.255.255.0
default router 10.10.20.1
dns-server 8.8.8.8
exit
config t
ip dhcp pool 30
network 10.10.30.0 255.255.255.0
default router 10.10.30.1
dns-server 8.8.8.8
exit