- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B

What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding is a technique used to enable external devices to connect to services on a private network by redirecting network traffic from a router’s public IP address to a specific internal IP address and port. This is essential for services that require direct access, such as gaming, remote desktop applications, and web hosting.
Purpose of Port Forwarding
Access Services: Allows external users to access applications running on a device in a local network.Improve Connectivity: Enhances the ability of devices to communicate over the internet, especially for gaming and VoIP applications.- Hosting: Enables hosting of servers (like game servers or web servers) that can be accessed from outside the local network.
Common Uses
1. Online Gaming: Many multiplayer games require specific ports to be open for players to connect to game servers.
2. Remote Access: Services like Remote Desktop, FTP servers, and security cameras often need port forwarding to be accessible over the internet.
3.Web Hosting: If you want to host a website from a local machine, port forwarding is essential to direct traffic to the correct device.
How to Set Up Port Forwarding
1. Determine Your Internal IP Address:
Find the IP address of the device you want to forward traffic to. This can usually be found in the network settings of the device.
2. Log into Your Router:
– Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
– Enter your router’s admin credentials.
3. Navigate to the Port Forwarding Section:
– Look for options like “Port Forwarding,” “Virtual Server,” or “NAT/QoS” in the router settings.
4. Add a Port Forwarding Rule:
– External Port: The port on which the router listens for incoming traffic.
– Internal IP Address: The IP address of the device you’re forwarding to.
– Internal Port: The port on the device that will handle the incoming traffic (often the same as the external port).
– Protocol: Choose TCP, UDP, or both, depending on the application’s requirements.
5. Save and Test:
– Save your changes and restart your router if necessary.
– Use an external network (like mobile data) to test if you can access the service.
Important Considerations
– Security Risks: Port forwarding can expose your devices to potential attacks. Always ensure that:
– Services are secured with strong passwords.
– Software is up-to-date.
– Only necessary ports are forwarded.
– Static IP Address: It’s advisable to assign a static IP address to the device you’re forwarding to, to prevent IP address changes that could break the forwarding rules.
– Firewall Configuration: Ensure that any firewalls on your router or device are configured to allow traffic through the forwarded ports.
– ISP Restrictions: Some Internet Service Providers may block certain ports or restrict port forwarding; check with your ISP if you encounter issues.
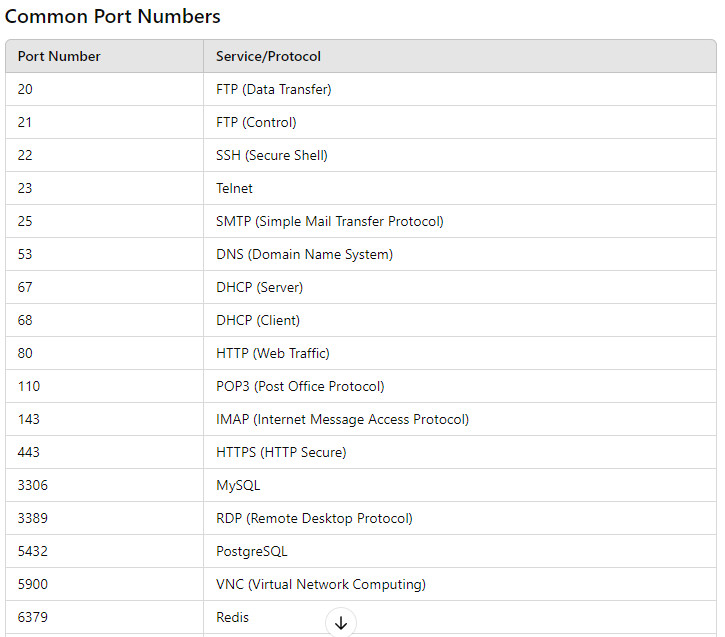
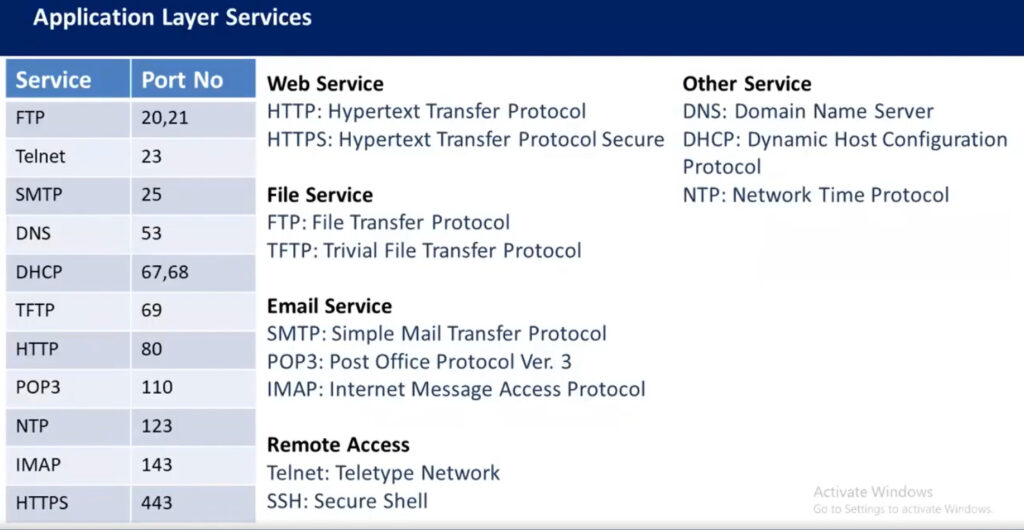
Network Port No
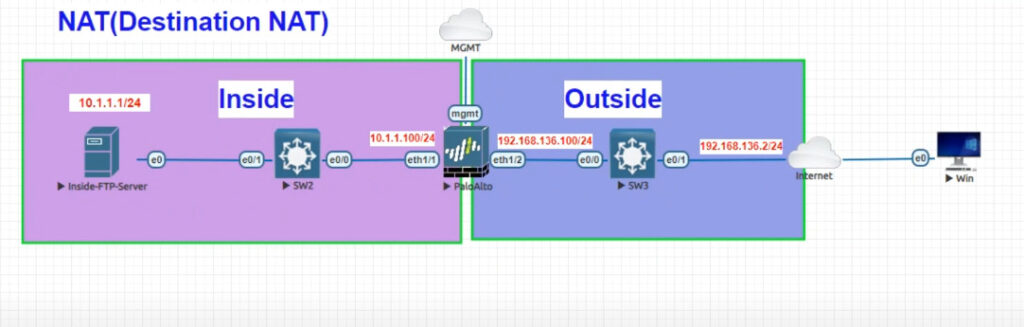
Configuring port forwarding on a Palo Alto Networks firewall involves setting up a NAT (Network Address Translation) rule and a security policy. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
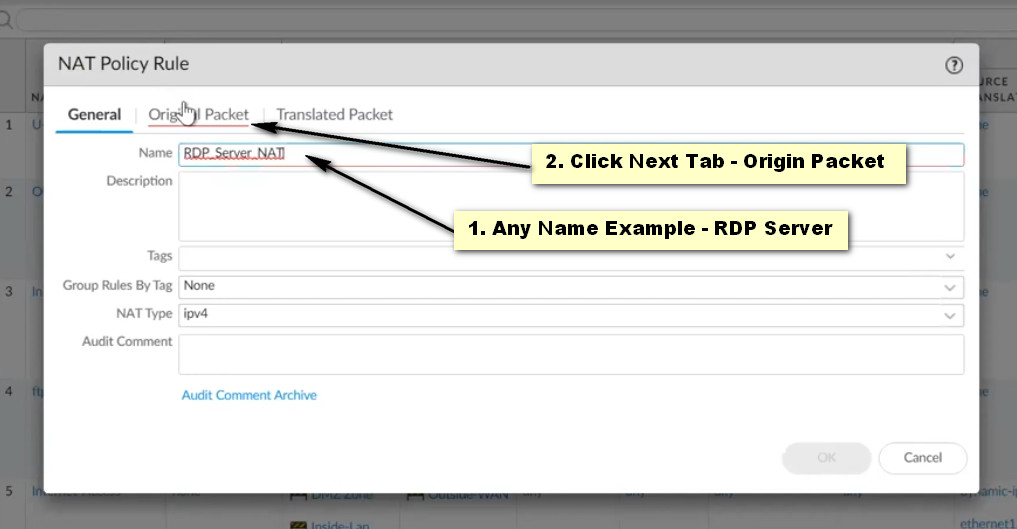
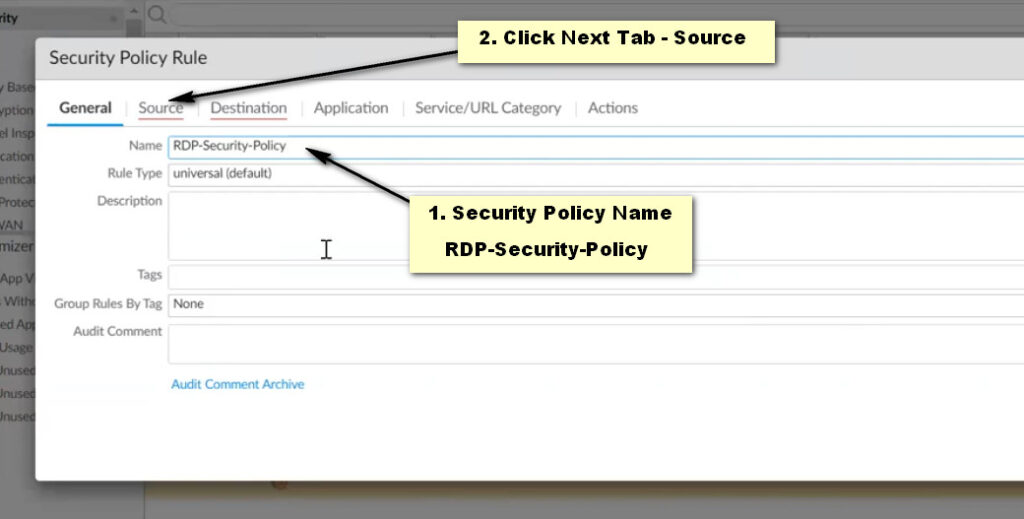
General Tab:
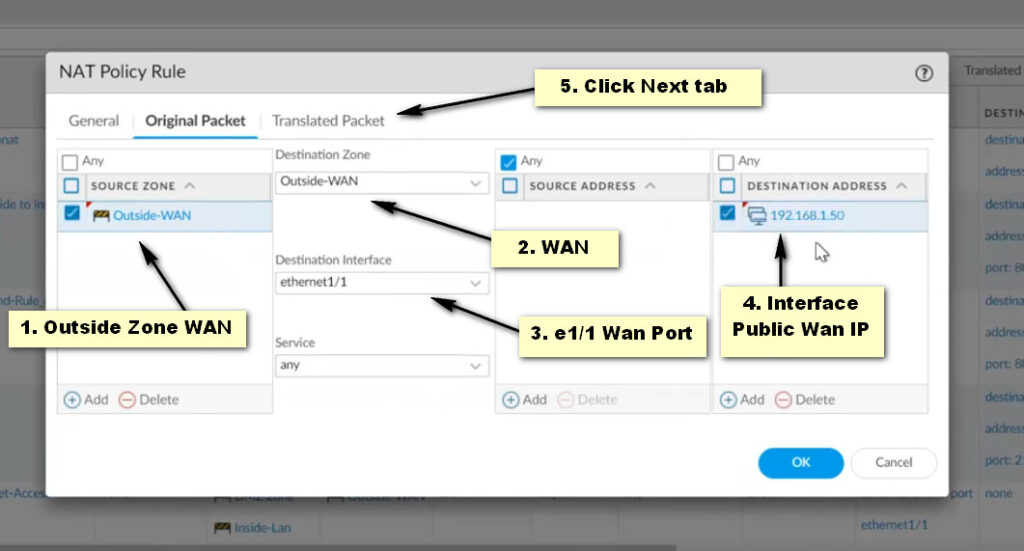
Original Packet Tab:
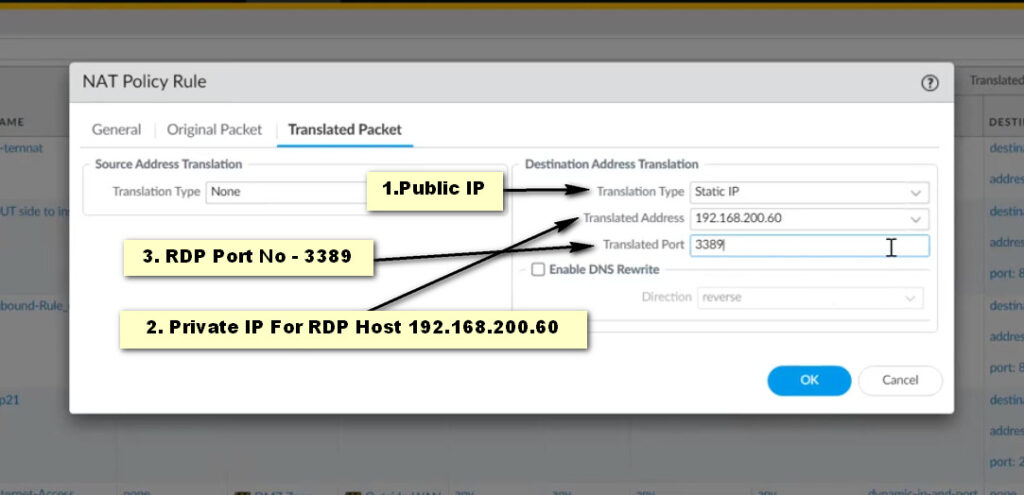
Translated Packet Tab:
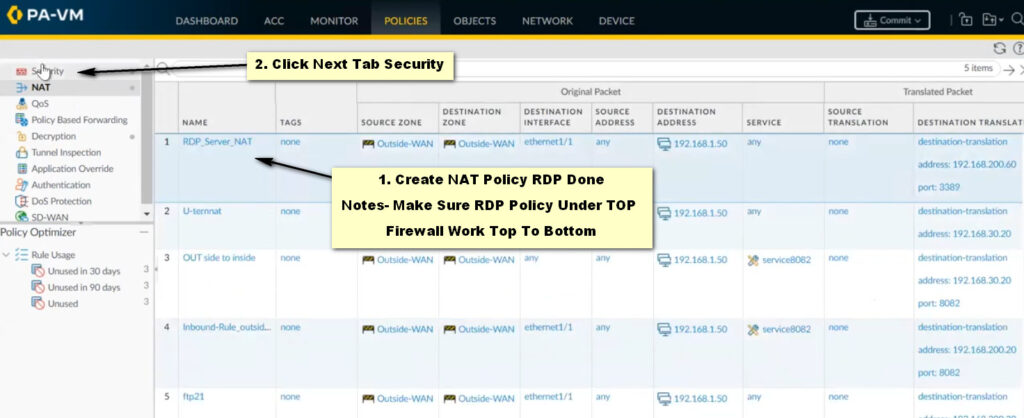
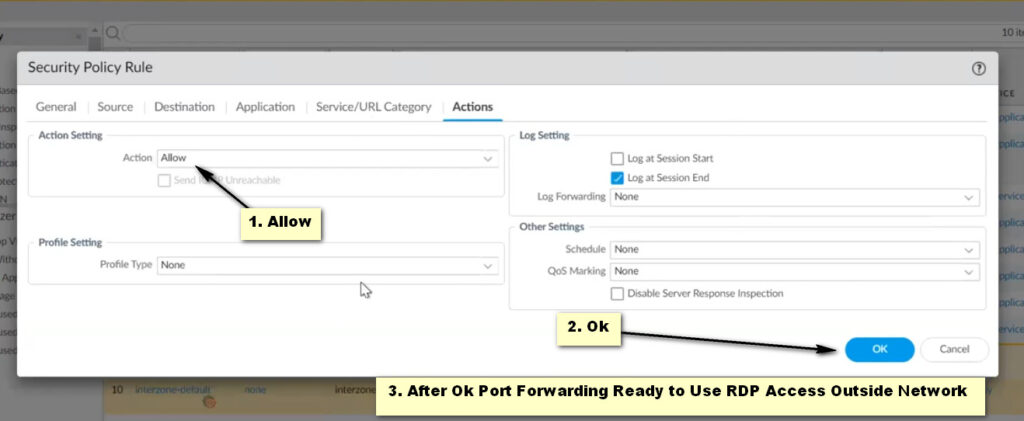
Actions Tab:
Click OK to save the NAT rule.
General Tab:
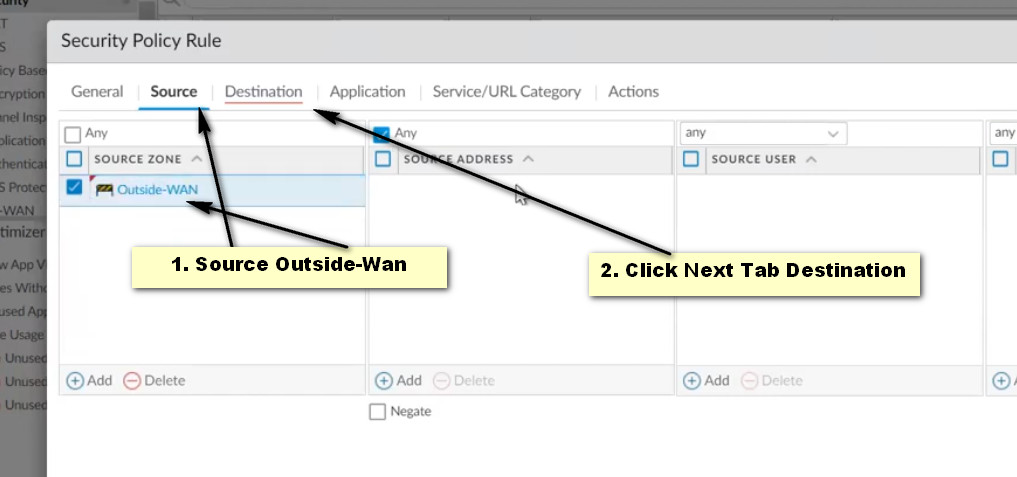
Source Tab:
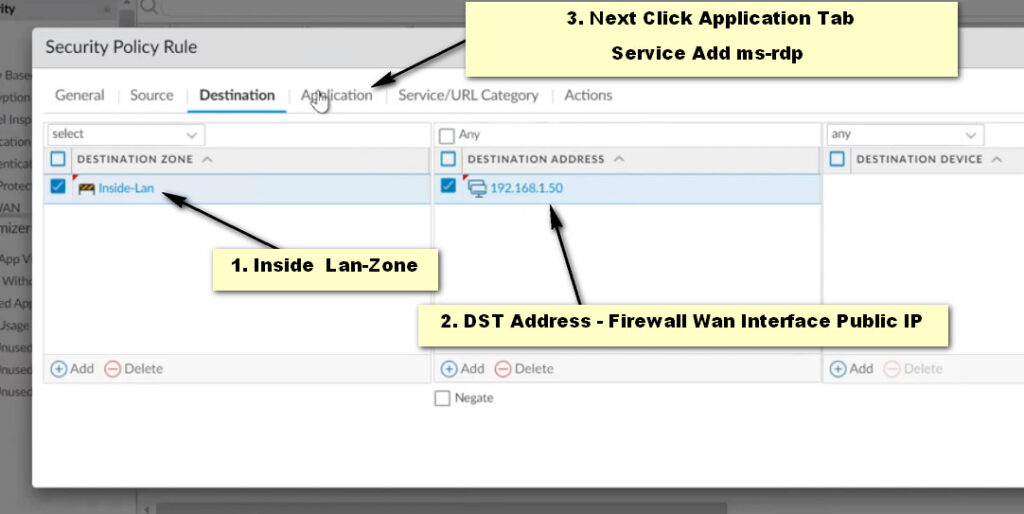
Destination Tab:
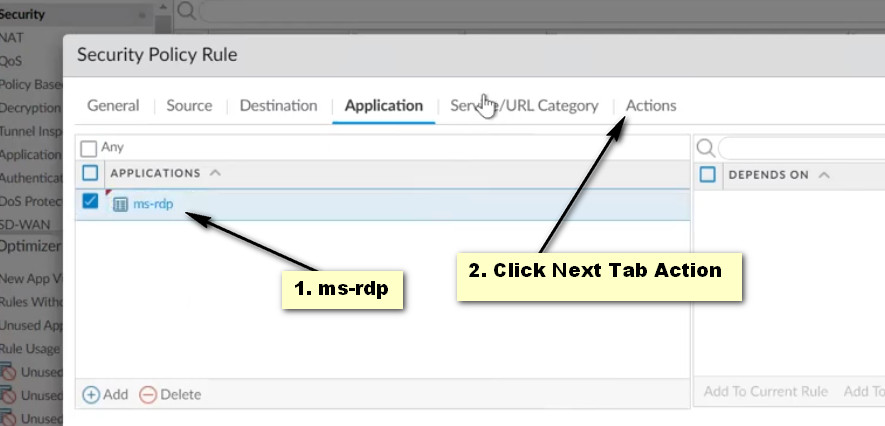
Application Tab:
Service/URL Category Tab:
Action Tab:
Click OK to save the security policy.