- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
What is IP Security (IPSec)
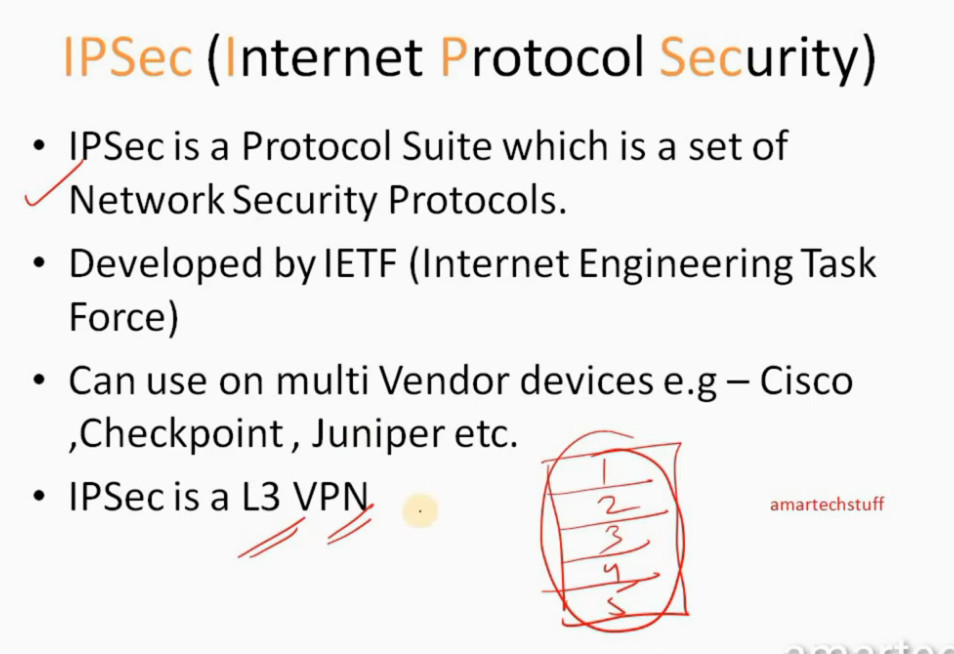
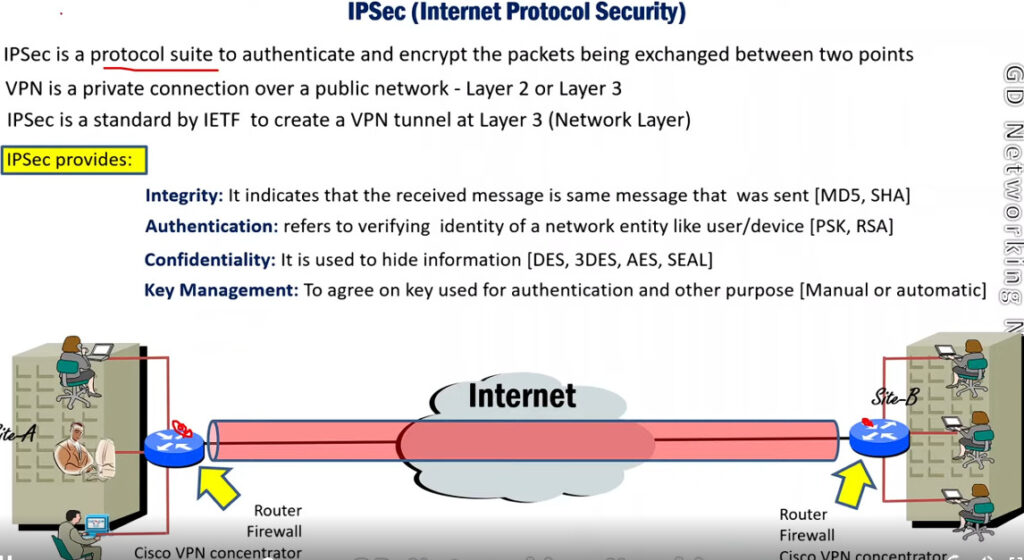
IP Security (IPSec) refers to a collection of communication rules or protocols used to establish secure network connections. Internet Protocol (IP) is the common standard that controls how data is transmitted across the internet. IPSec enhances the protocol security by introducing encryption and authentication. IPSec encrypts data at the source and then decrypts it at the destination. It also verifies the source of the data.
Importance of IPSec
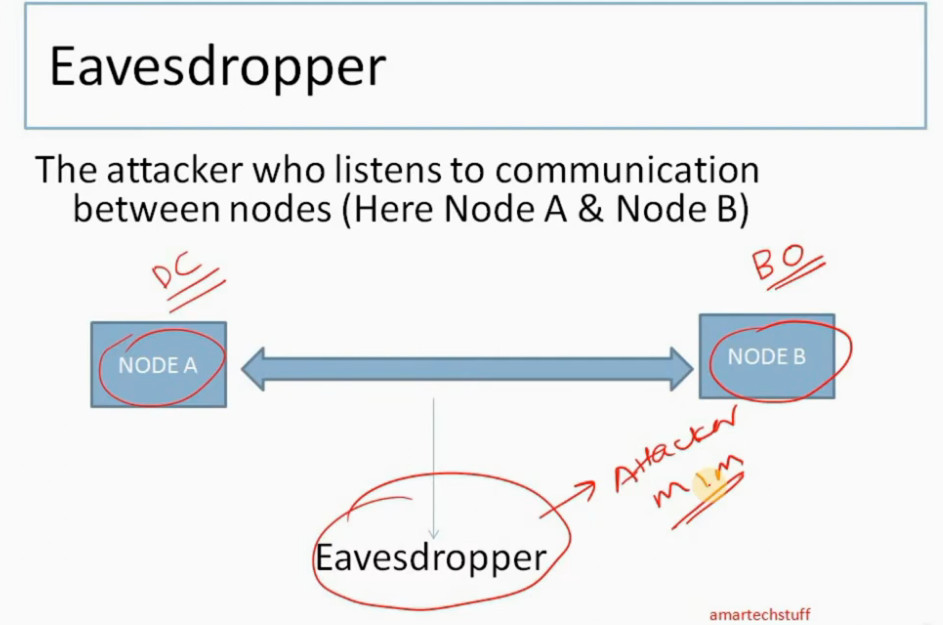
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is important because it helps keep your data safe and secure when you send it over the Internet or any network. Here are some of the important aspects why IPSec is Important:
Features of IPSec
How Does IPSec Work
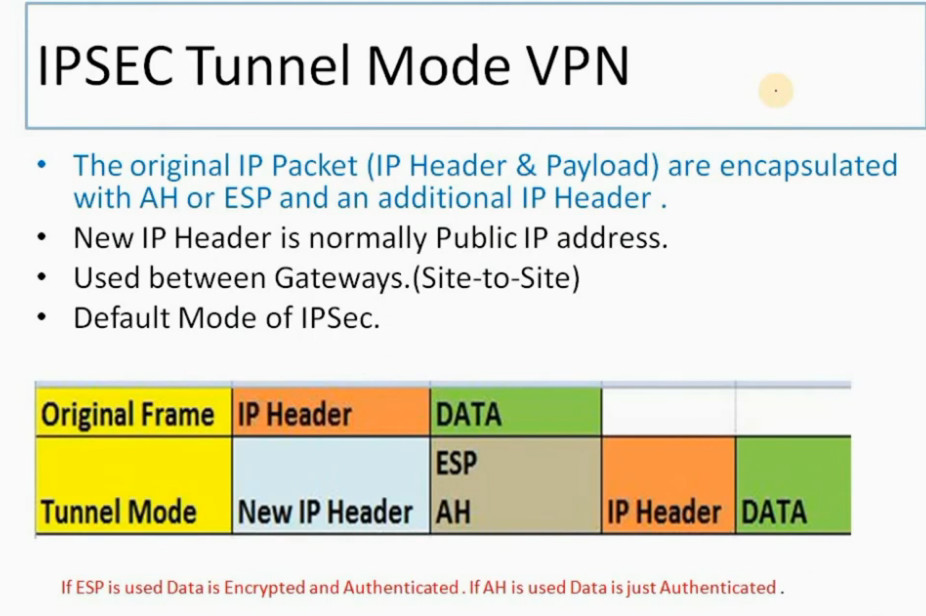
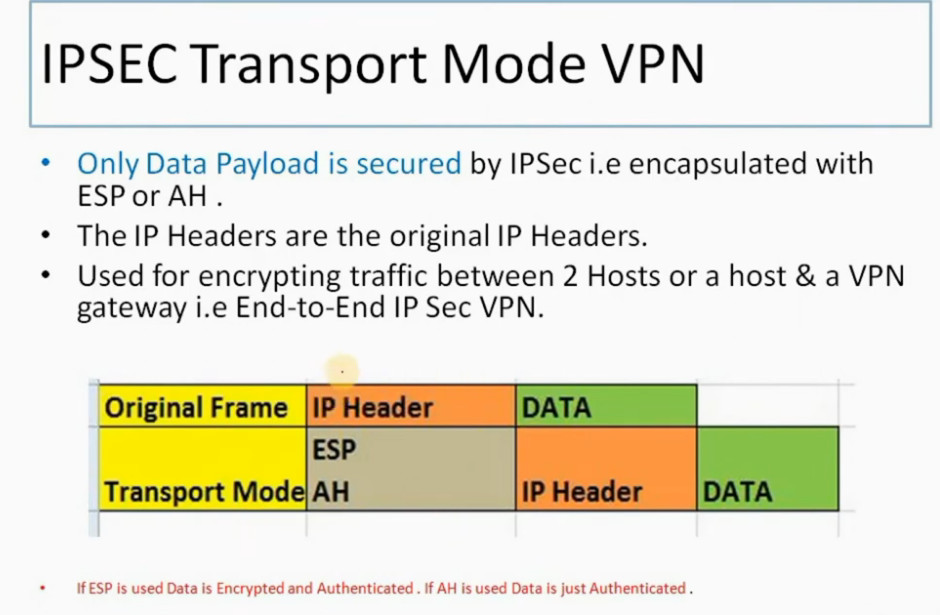
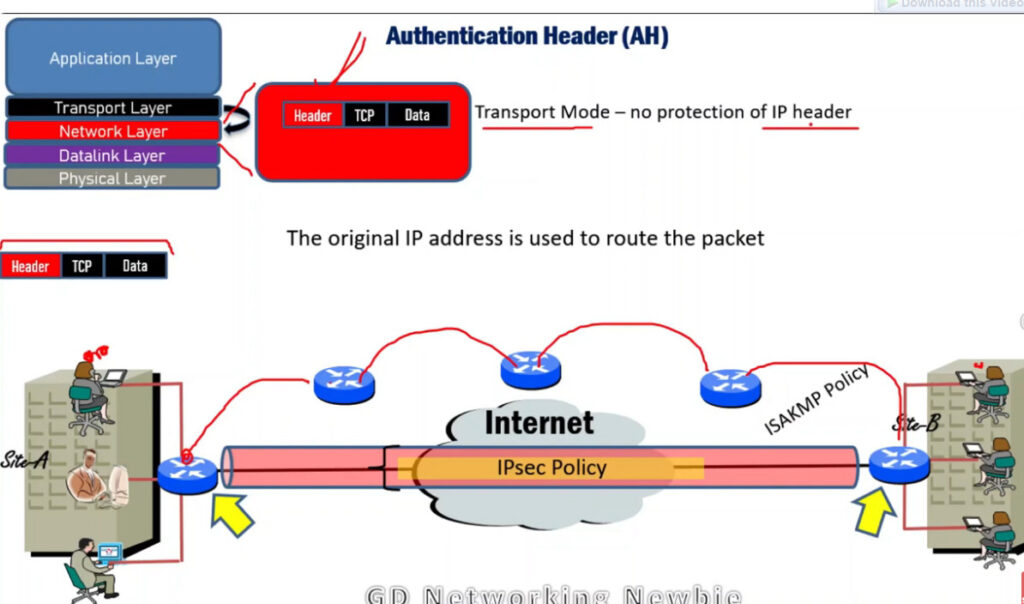
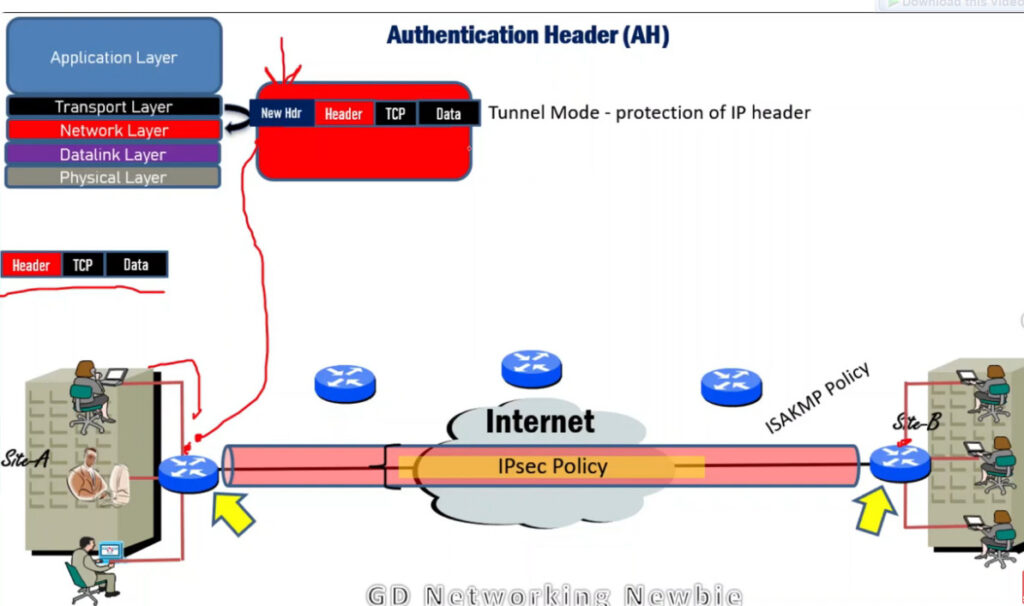
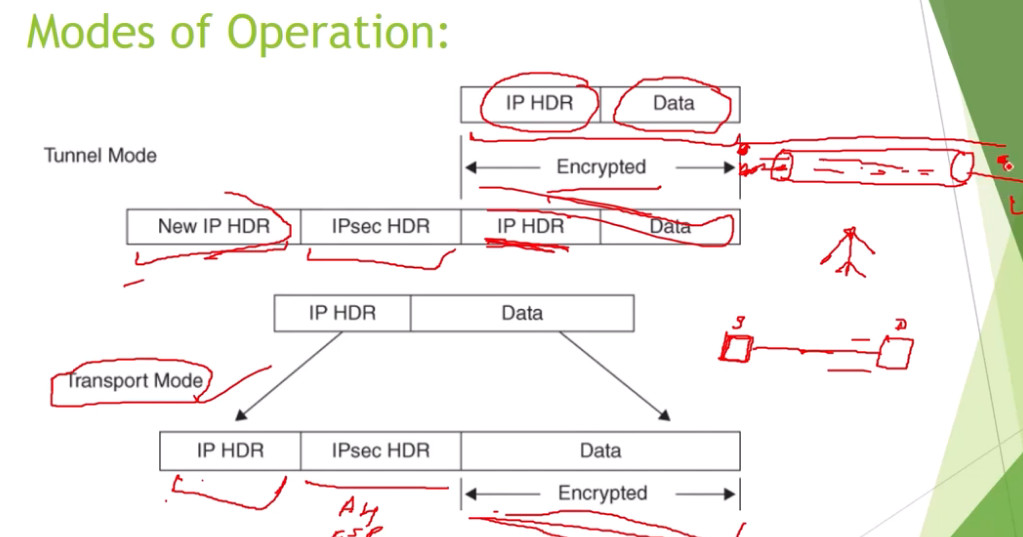
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is used to secure data when it travels over the Internet. IPSec works by creating secure connections between devices, making sure that the information exchanged is kept safe from unauthorized access. IPSec majorly operates in two ways i.e. Transport Mode and Tunnel Mode.
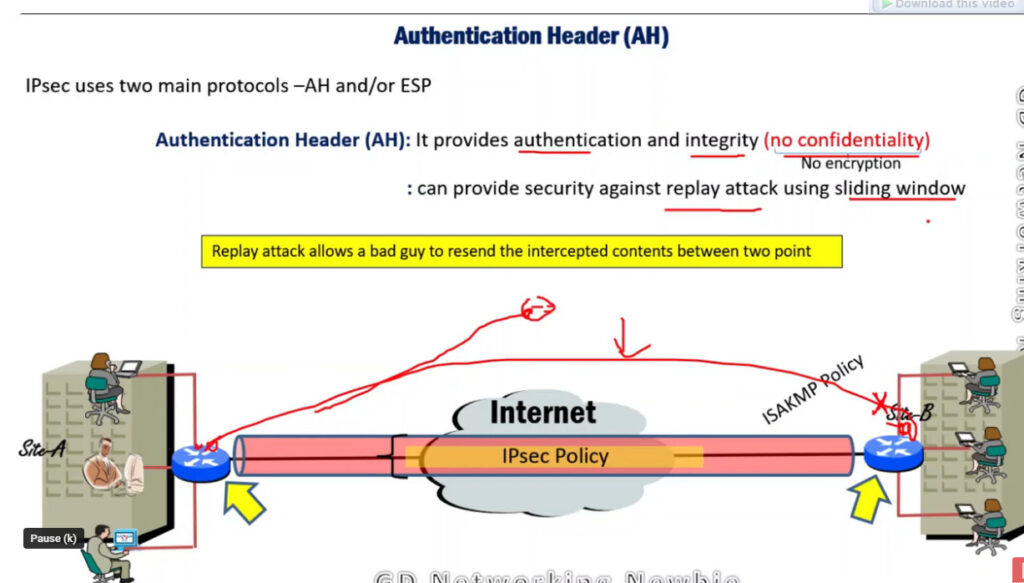
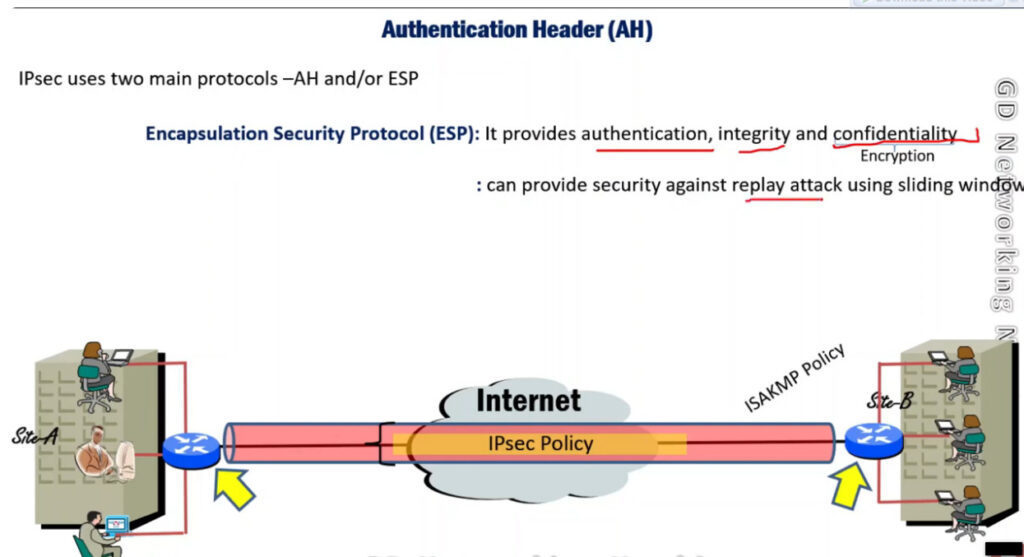
To provide security, IPSec uses two main protocols: AH (Authentication Header) and ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload). Both protocols are very useful as Authentication Header verifies the data that whether it comes from a trusted source and hasn’t been changed, and ESP has the work of performing authentication and also encrypts the data so that it becomes difficult to read.
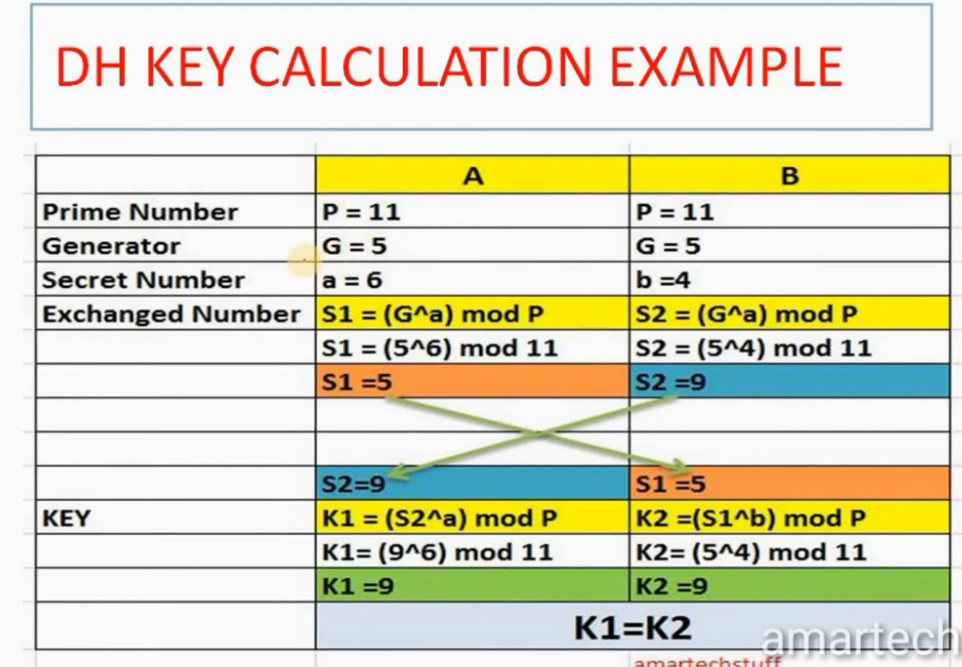
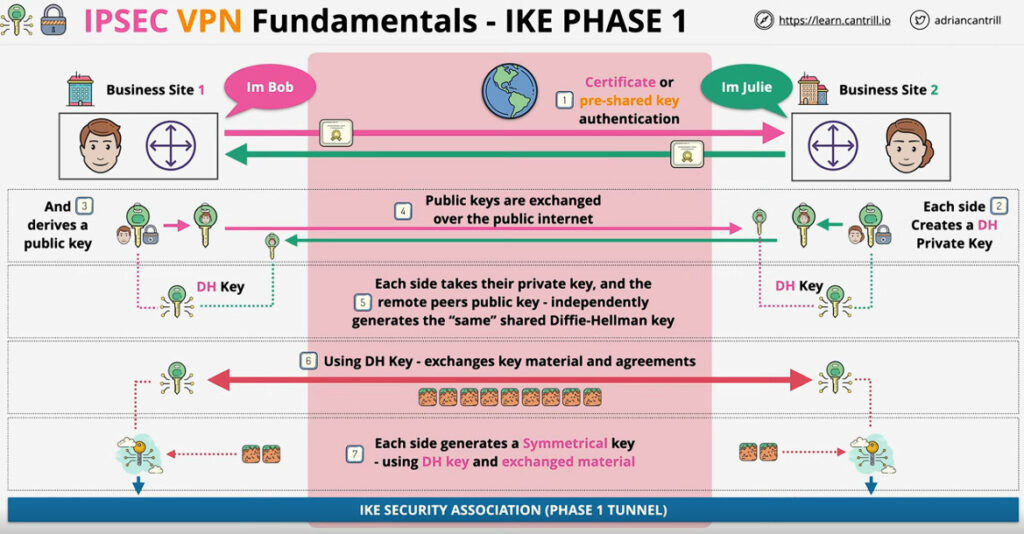
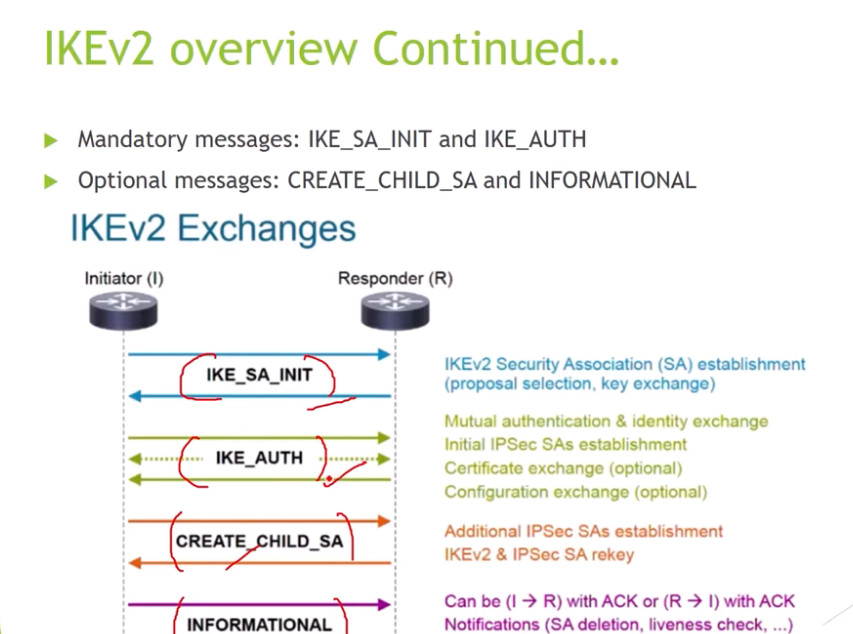
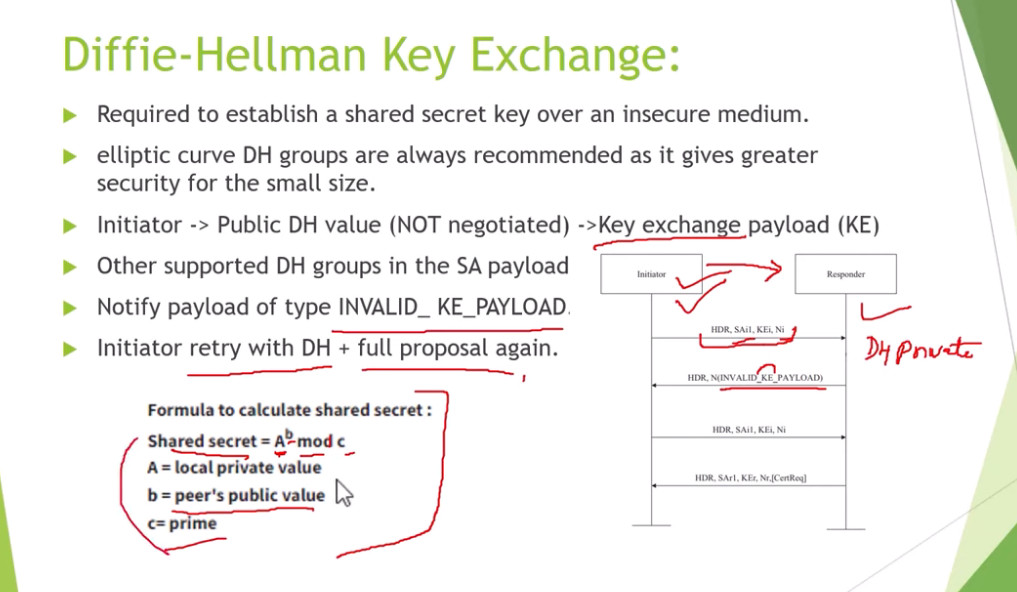
For Encryption, IPSec uses cryptographic keys. It can be created and shared using a process called IKE (Internet Key Exchange), that ensures that both devices have the correct keys to establish a secure connection.
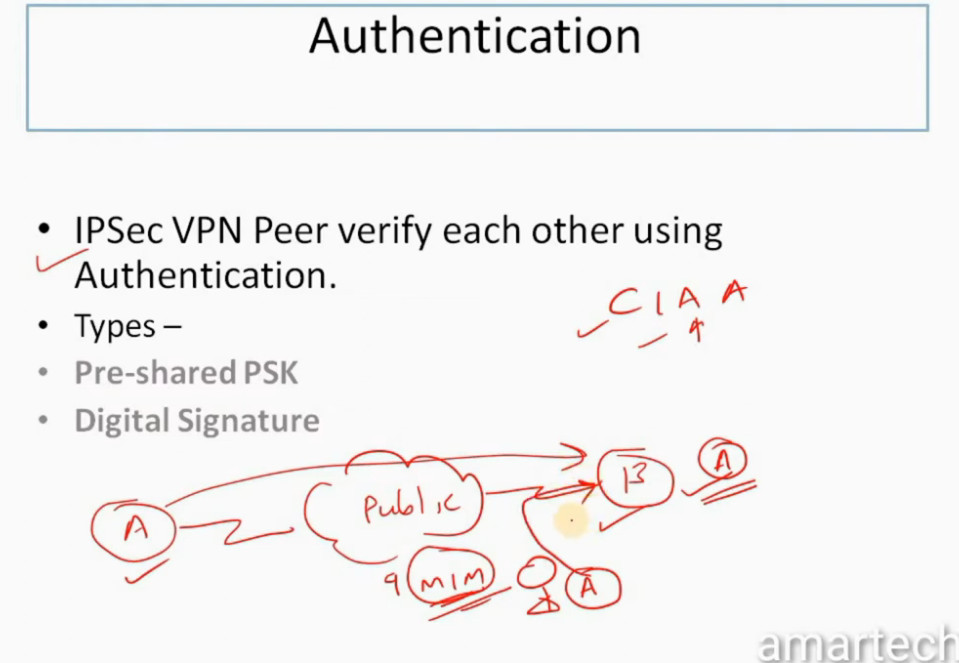
When two devices communicate using IPSec, the devices first initiate the connection by sending a request to each other. After that, they mutually decide on protection of data using passwords or digital certificates. Now, they establish the secure tunnel for communication. Once the tunnel is set up, data can be transmitted safely, as IPSec is encrypting the data and also checking the integrity of the data to ensure that data has not been altered. After the communication is finished, the devices can close the secure connection. In this way, the IPSec works.
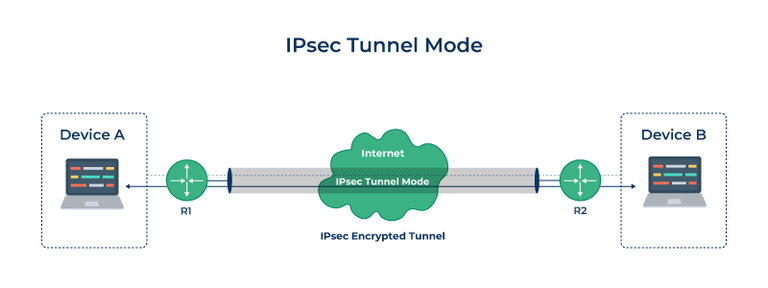
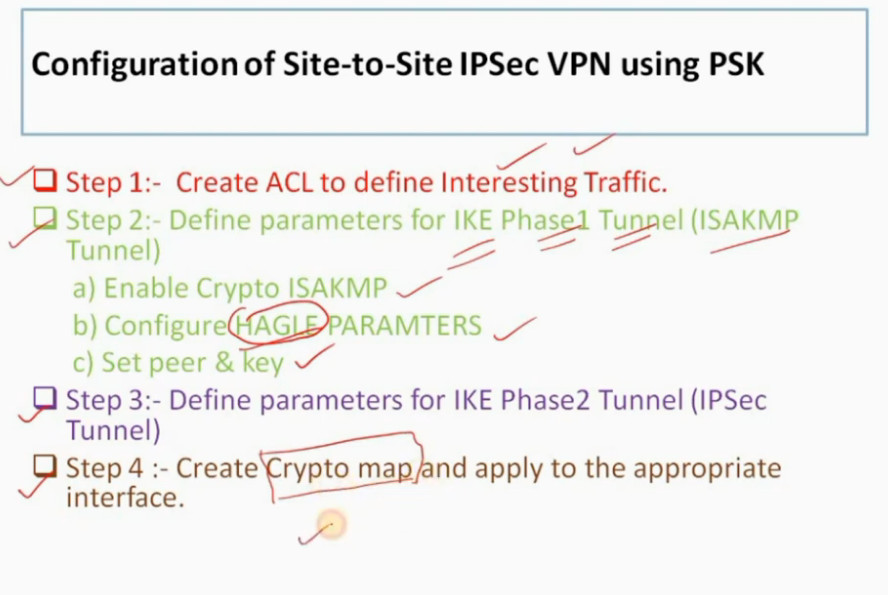
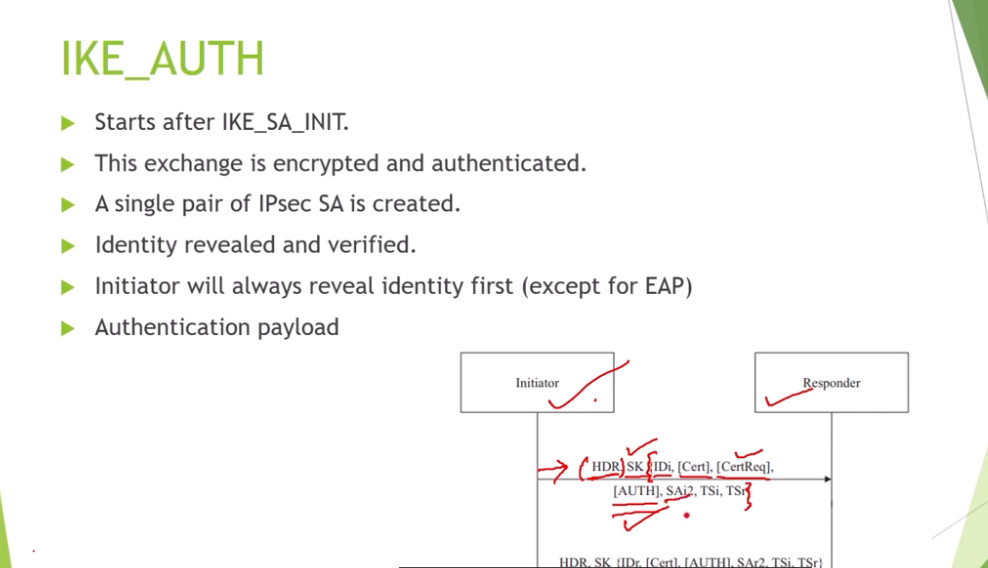
IPSec Connection Establishment Process
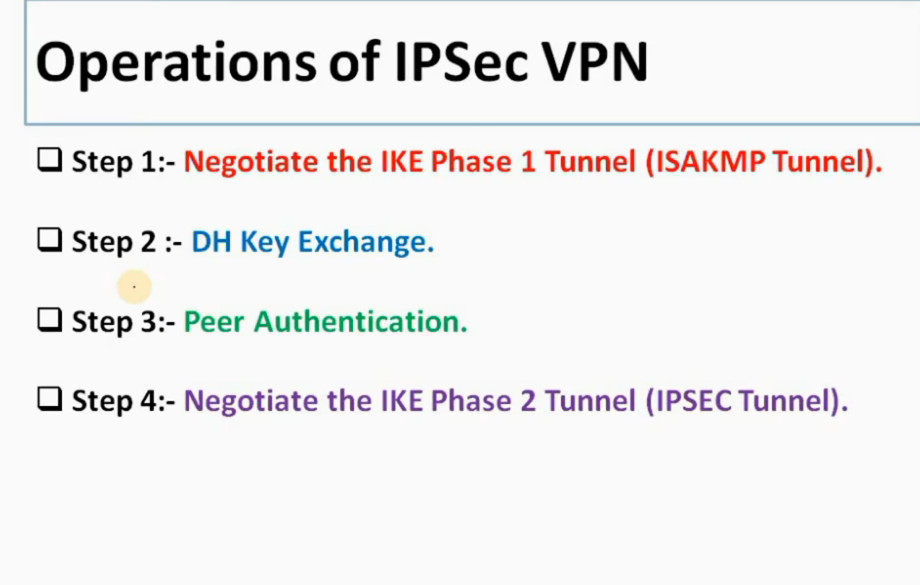
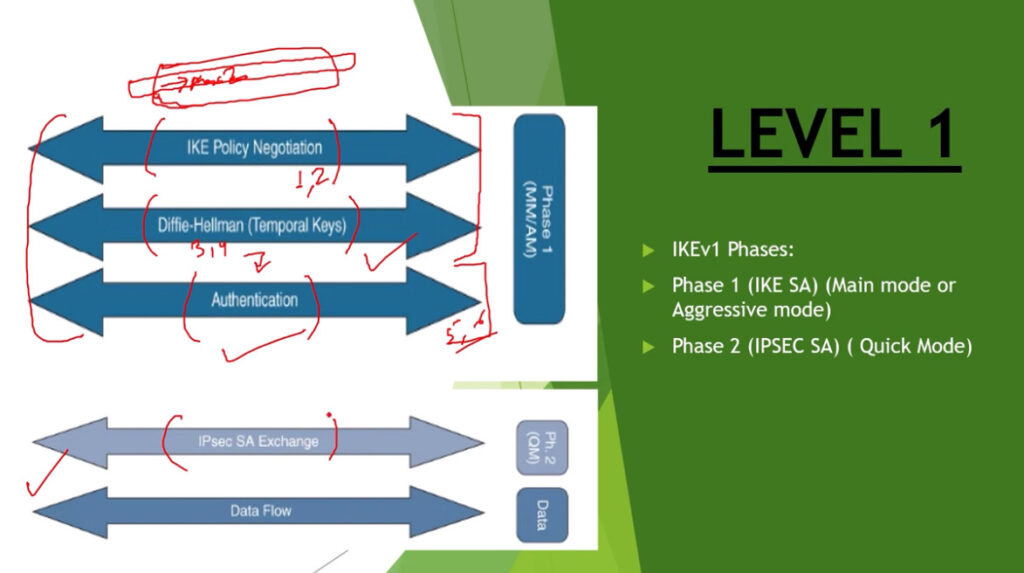
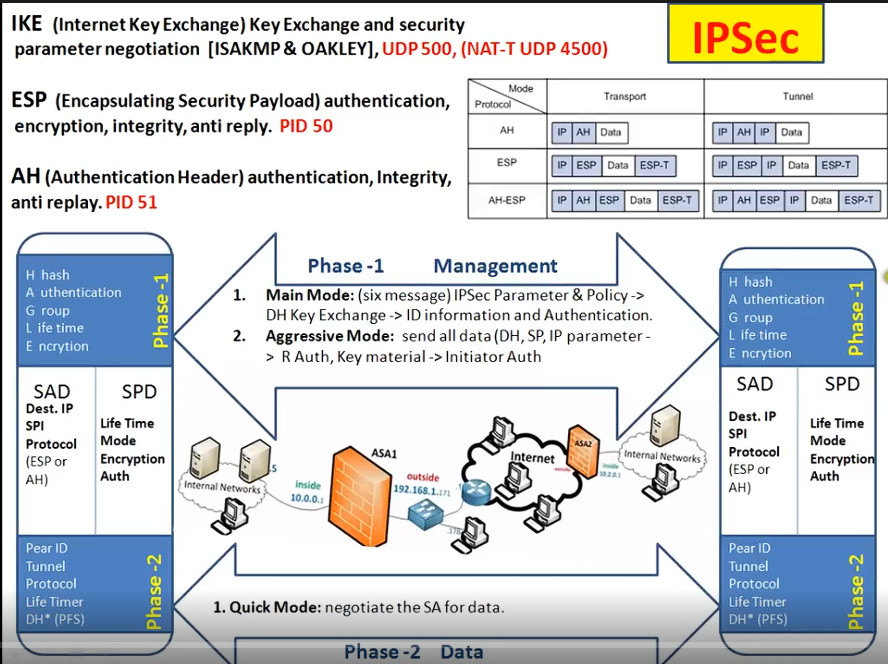
IPSec is a protocol suite used in securing communication using the Internet Protocol such that each packet communicated in the course of a particular session is authenticated and encrypted. The process of establishing an IPSec connection involves two main phases:
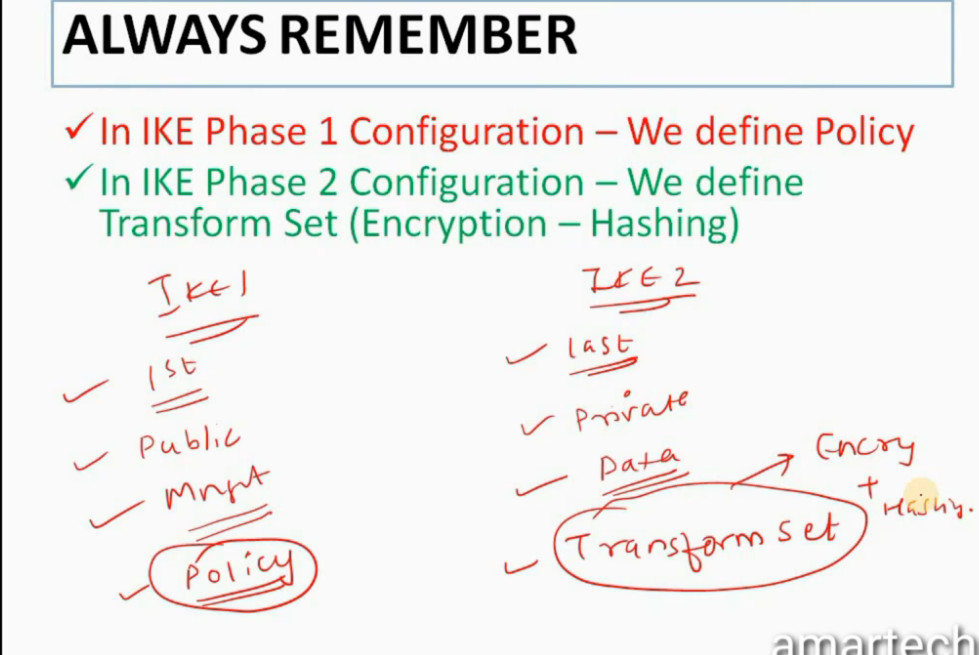
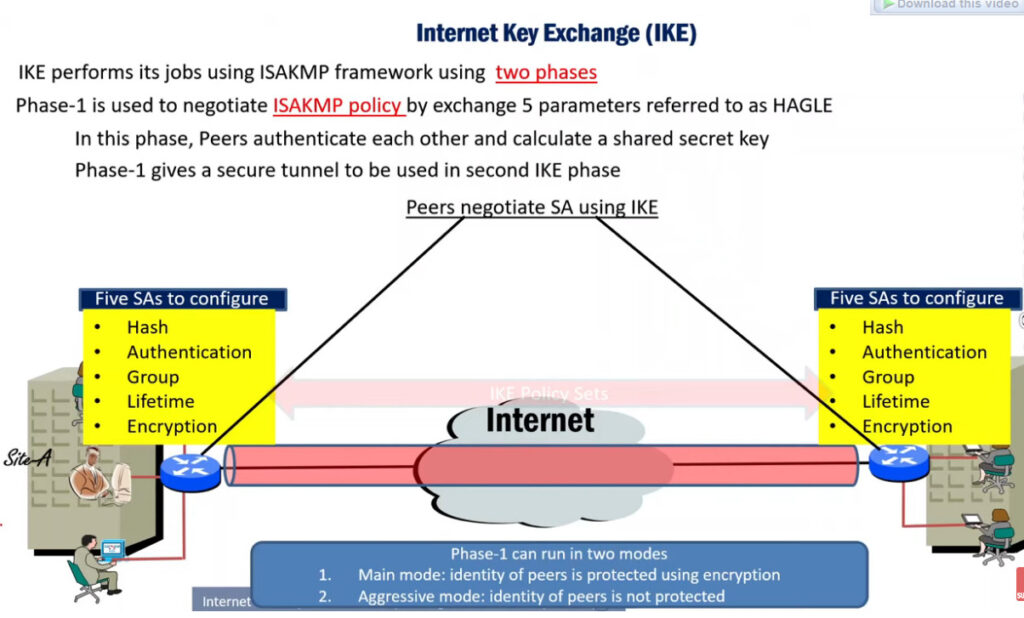
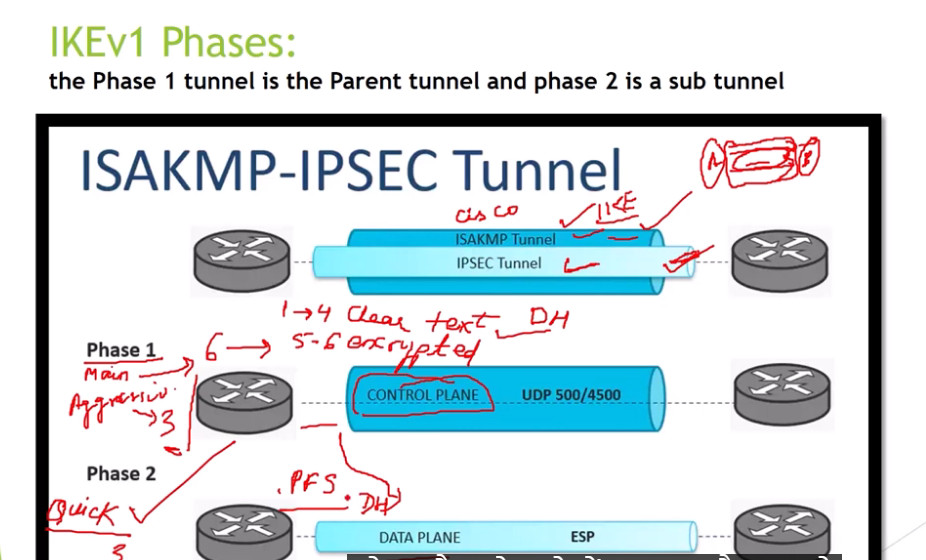
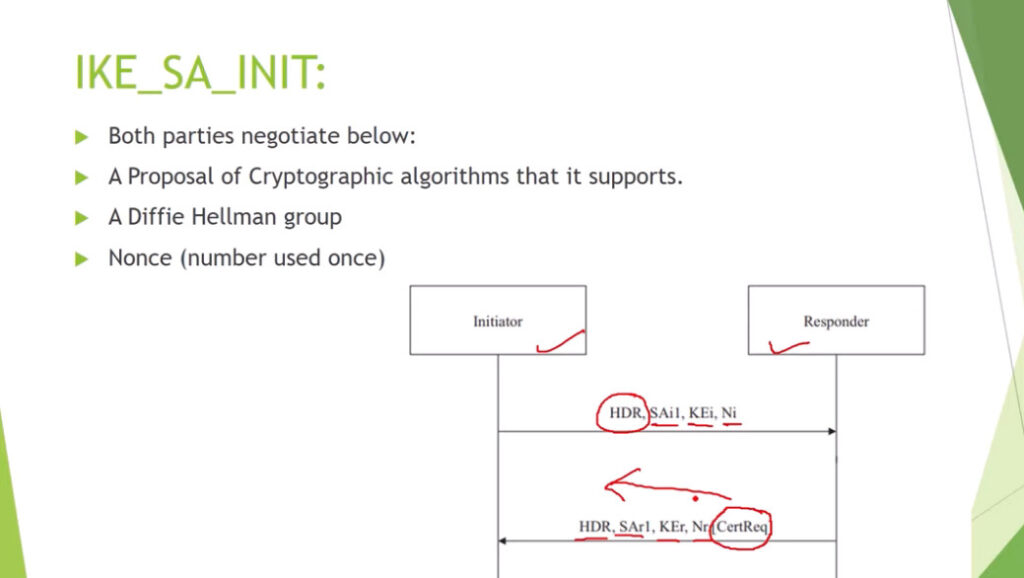
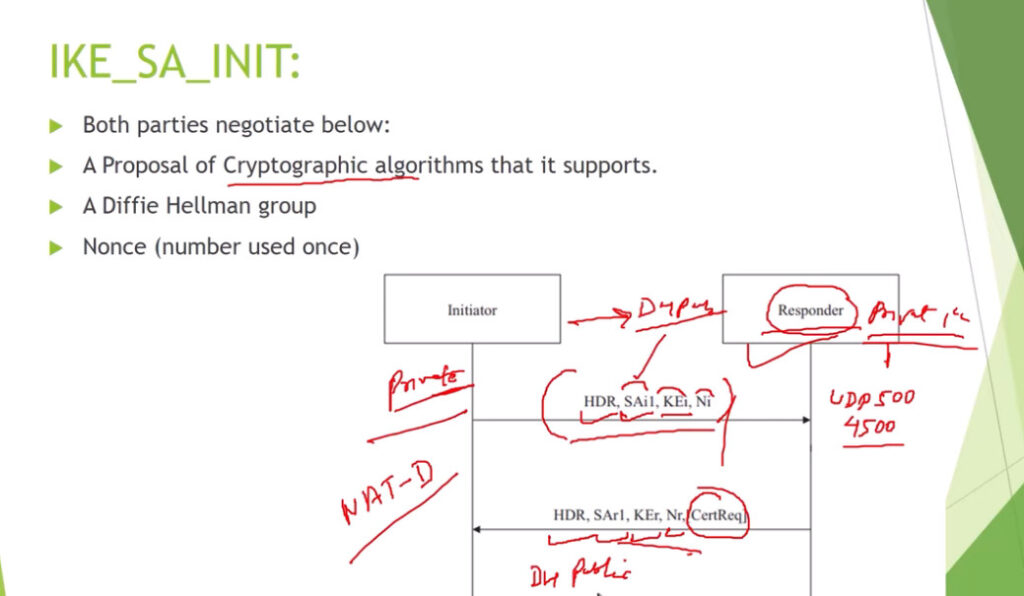
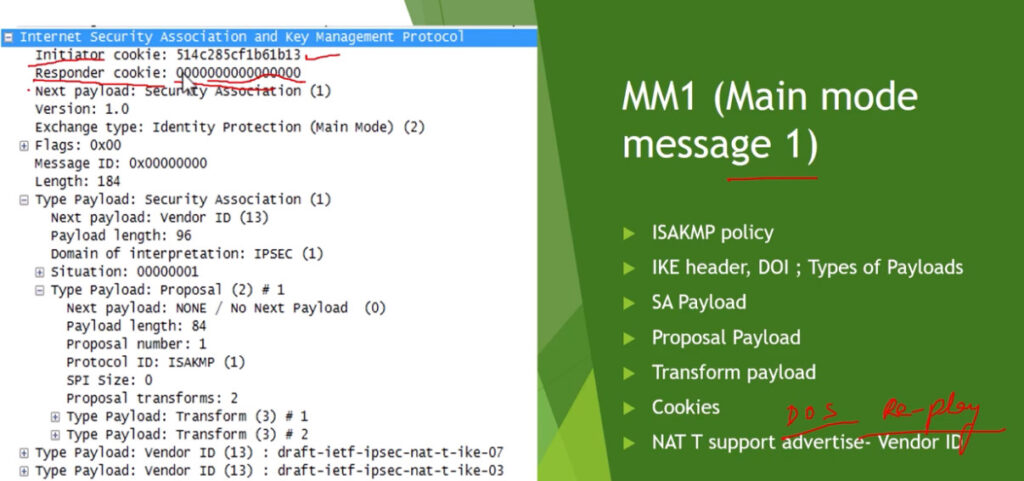
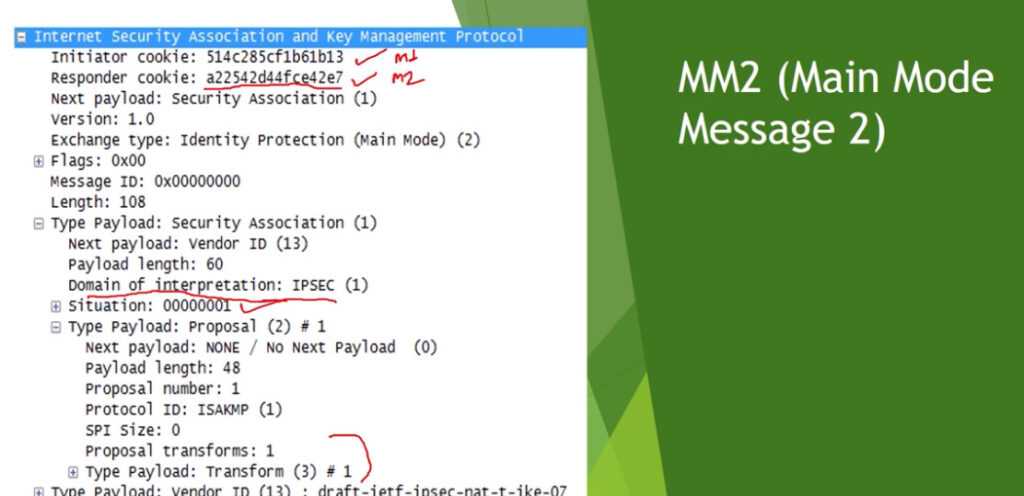
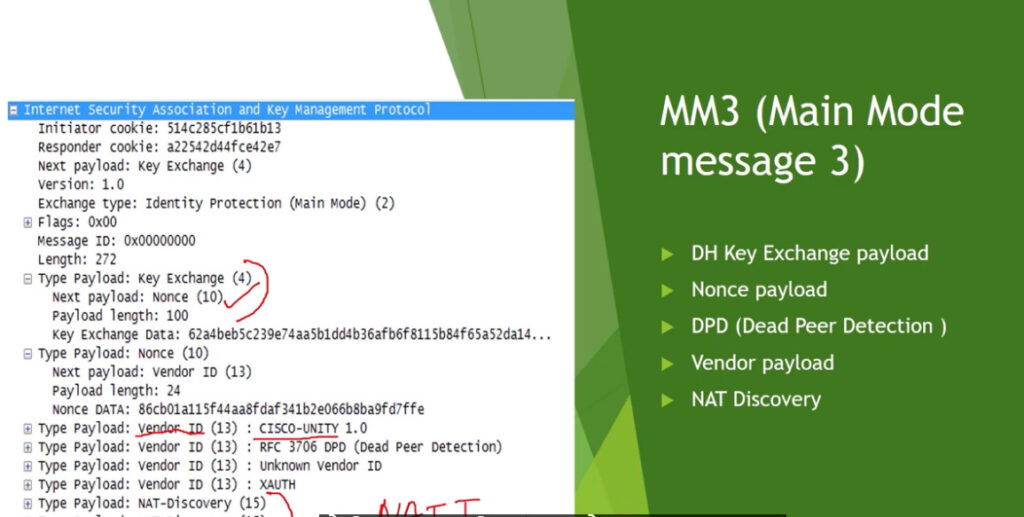
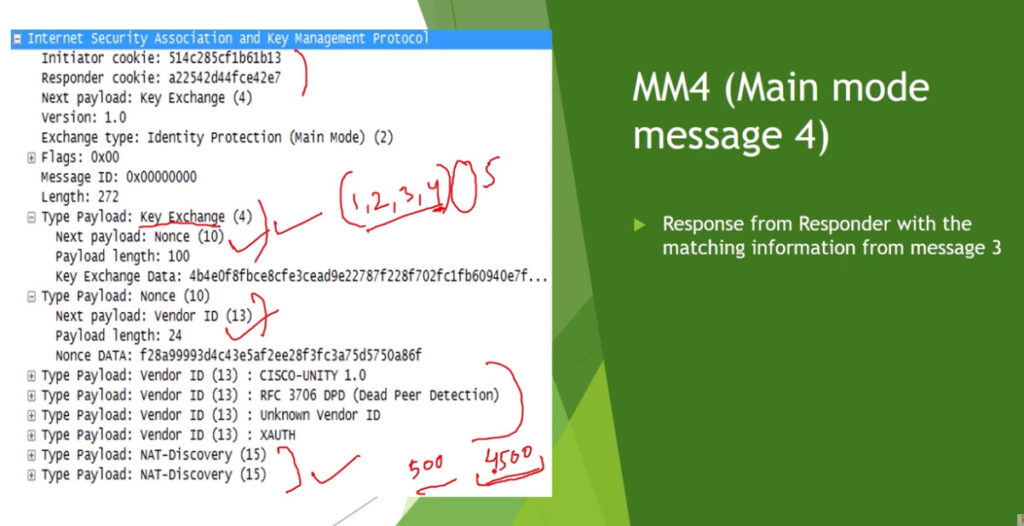
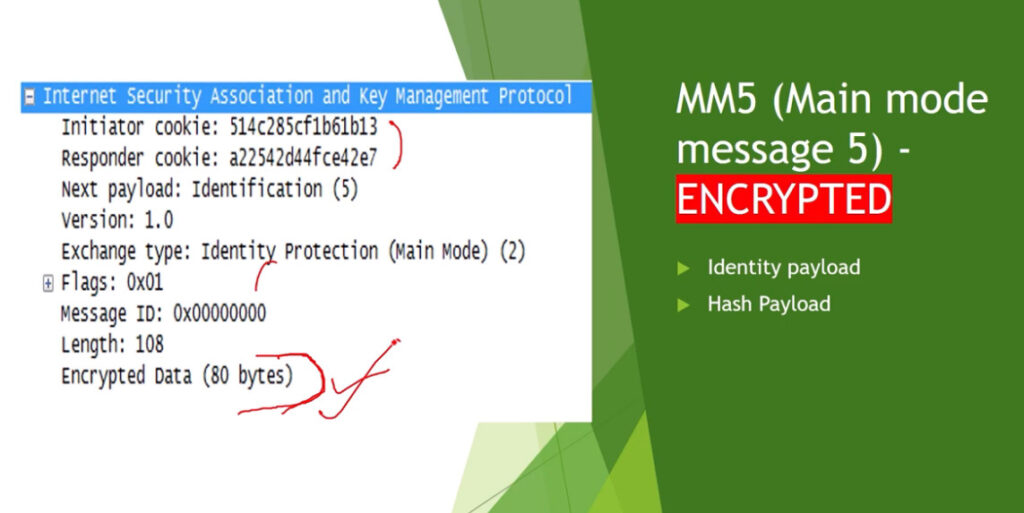
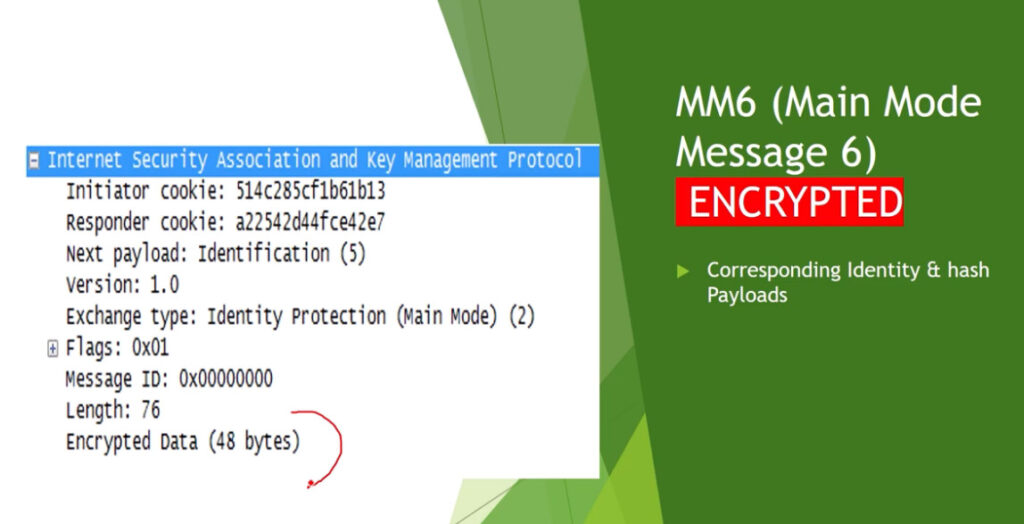
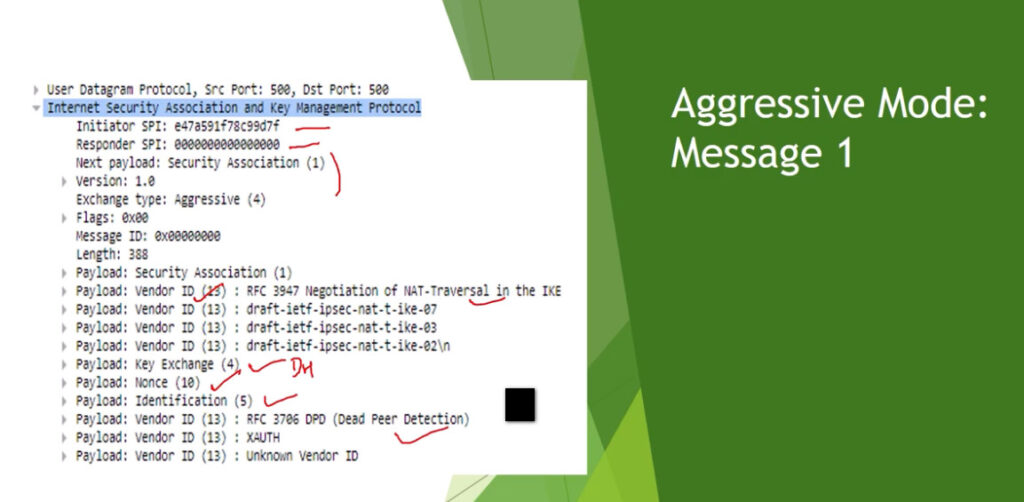
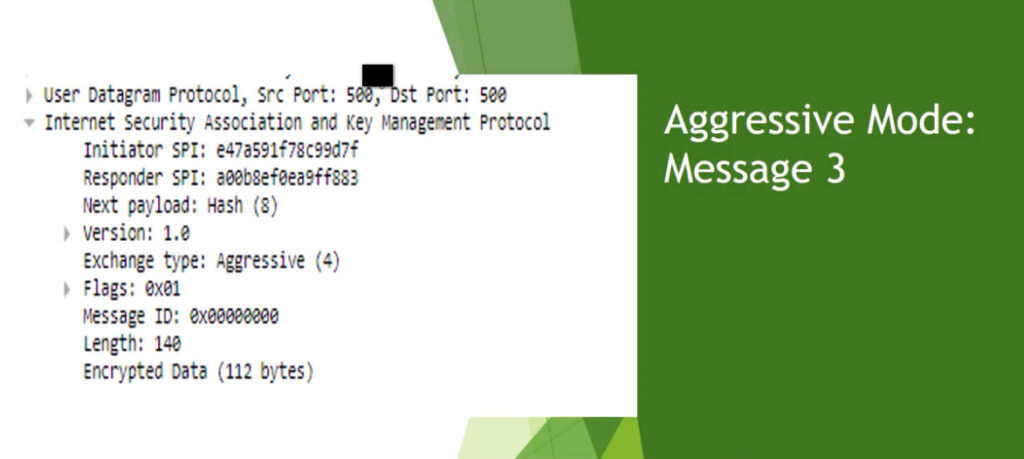
Phase 1: Establishing the IKE (Internet Key Exchange) Tunnel
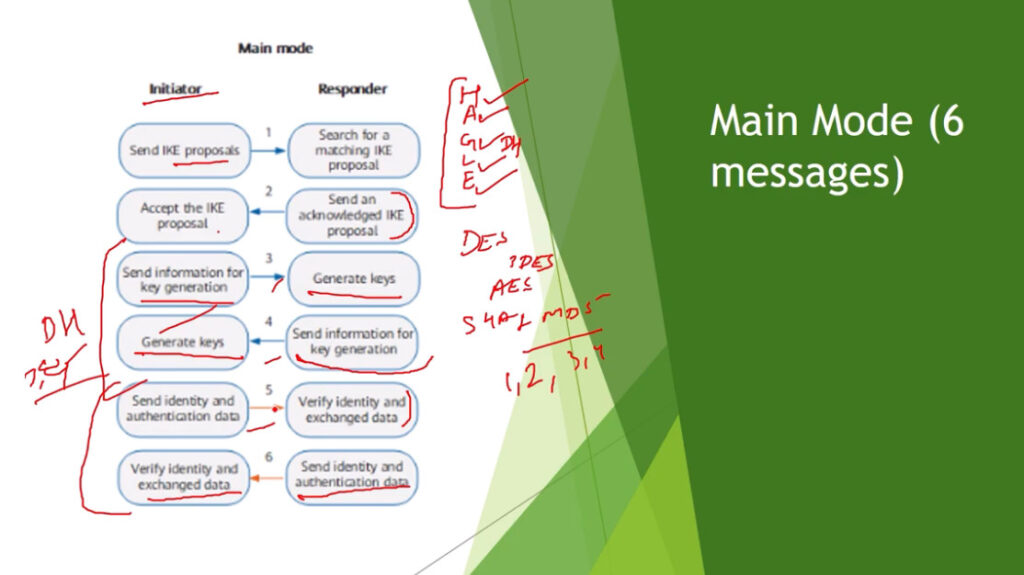
In phase 1, the main aim is to establish the secure channel the IKE tunnel, which is used to further negotiations. Phase 1 can operate in one of two modes:
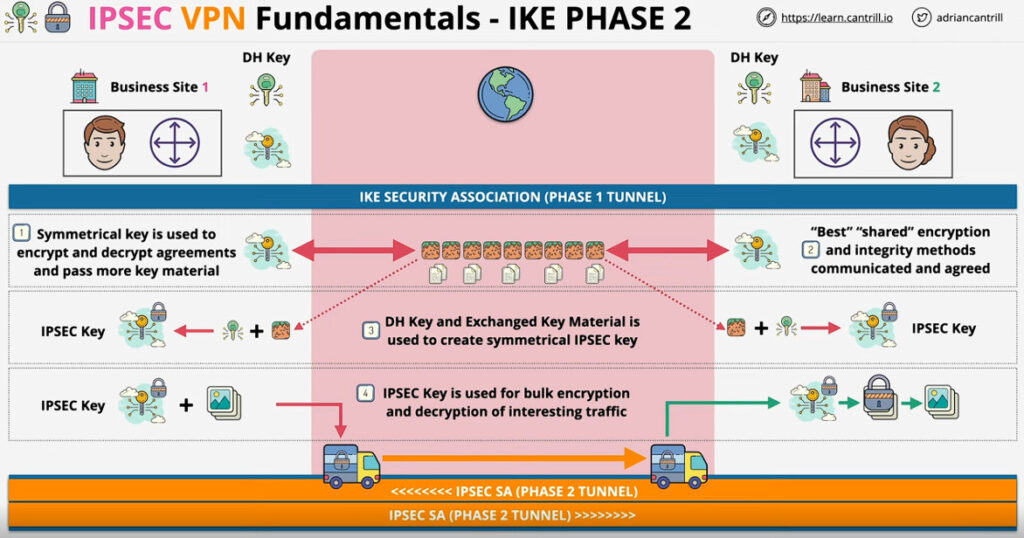
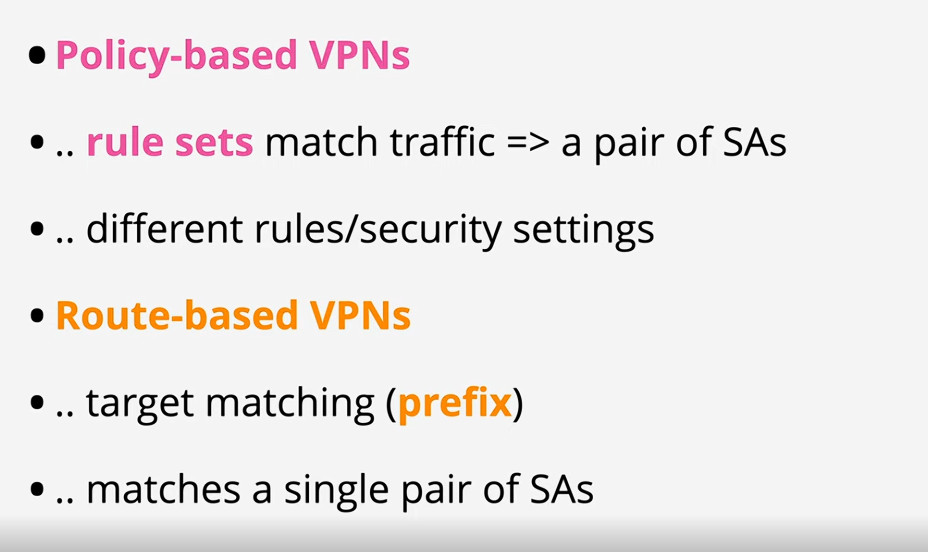
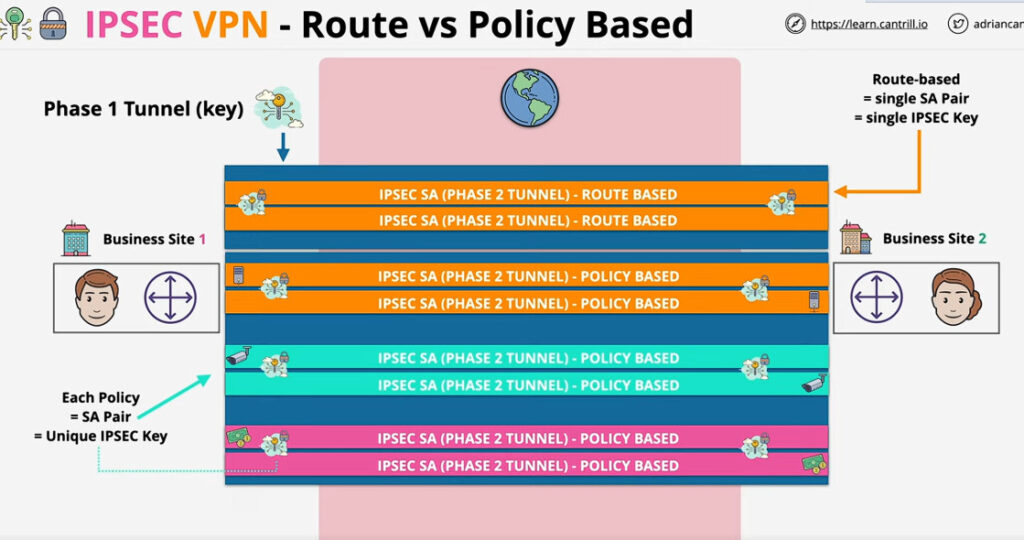
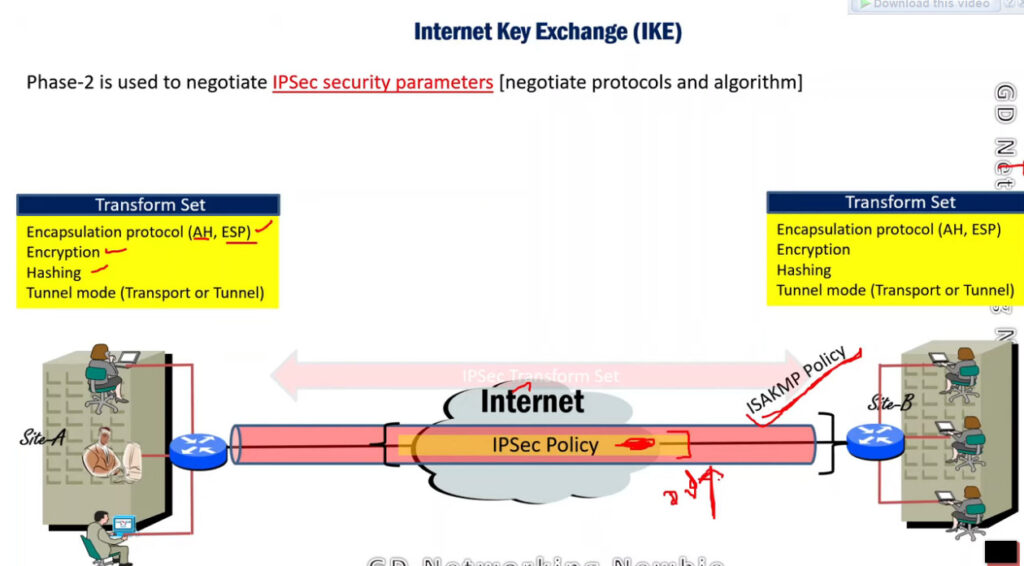
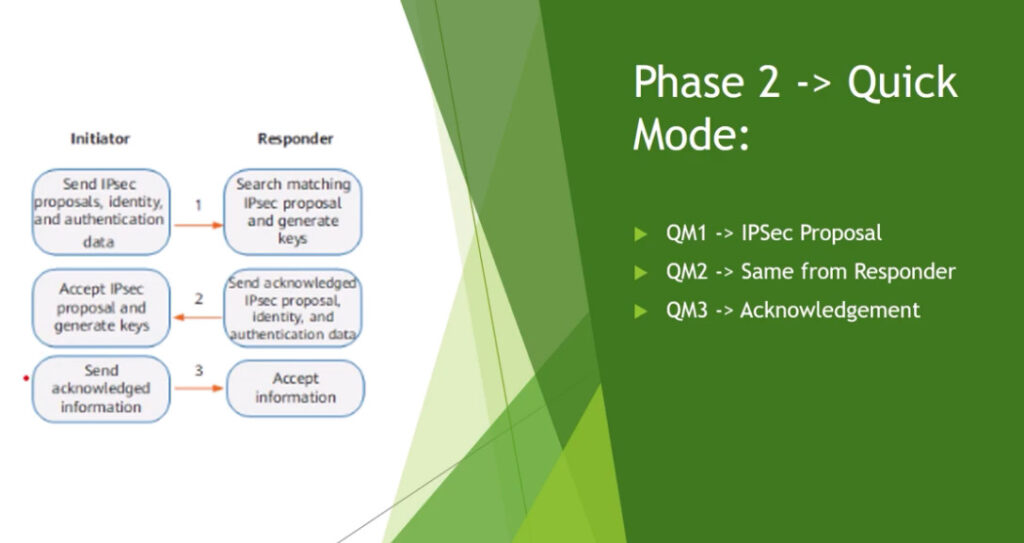
Phase 2: Establishing the IPSec Tunnel
Phase 2 is called Quick Mode and its aim is to negotiate the IPSec Security Associations after the construction of a secure IKE tunnel has been made. There are two modes in Phase 2.
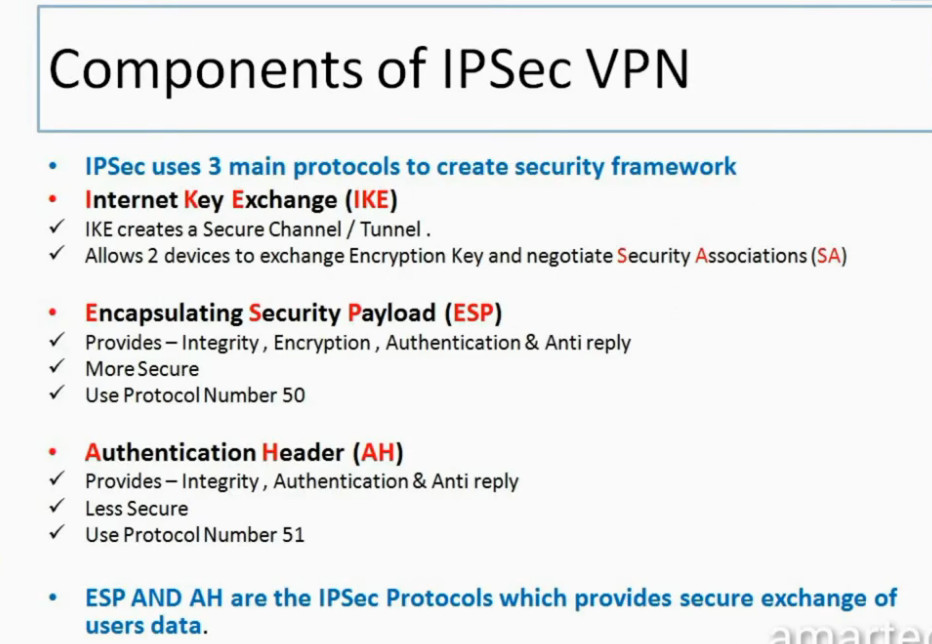
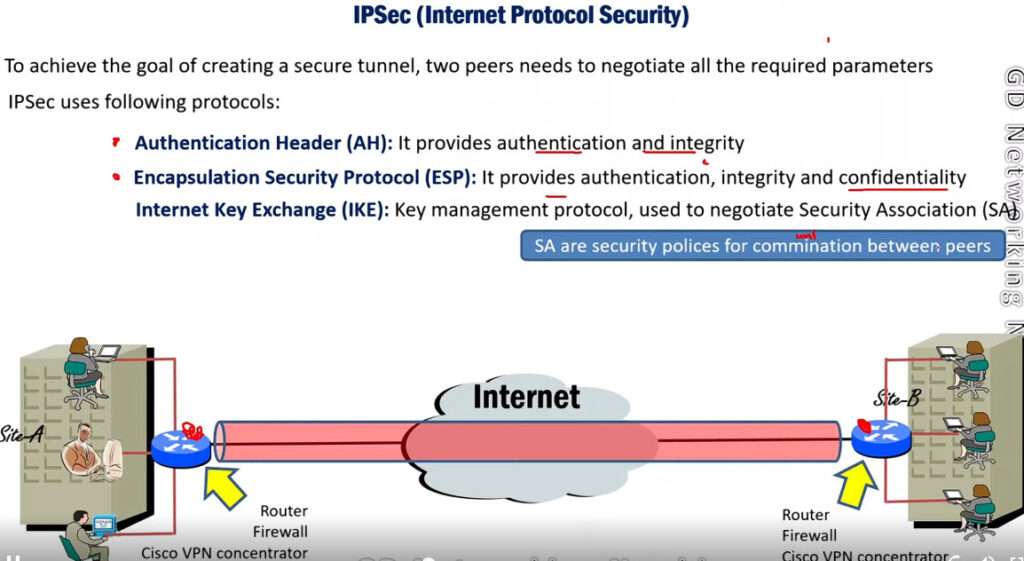
Protocols Used in IPSec
It has the following components:
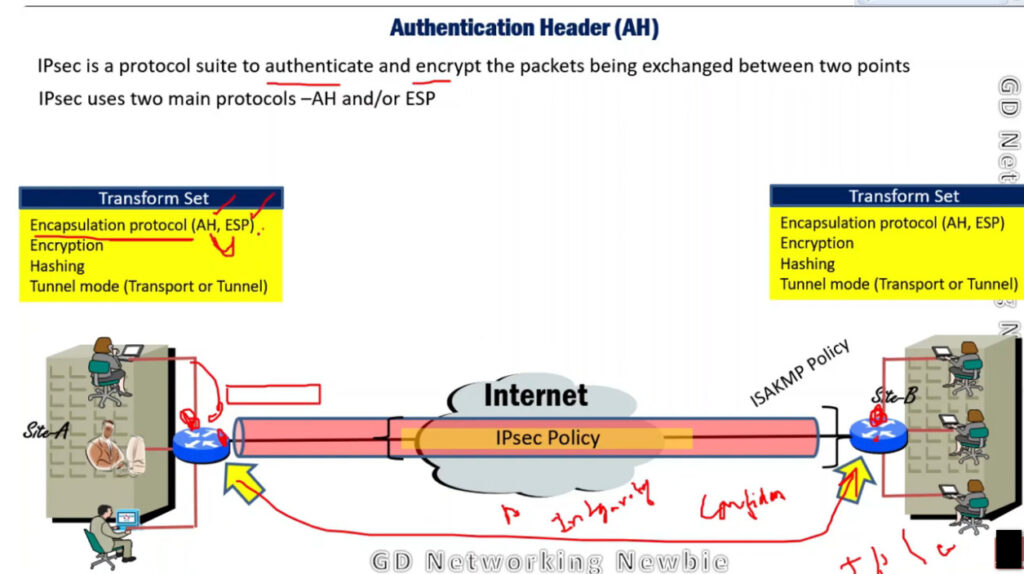
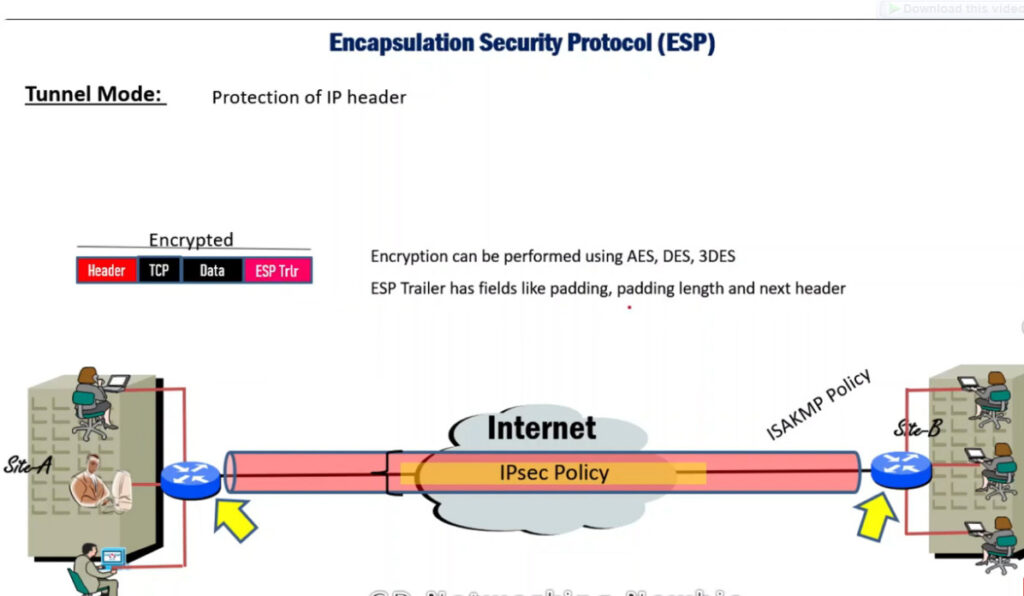
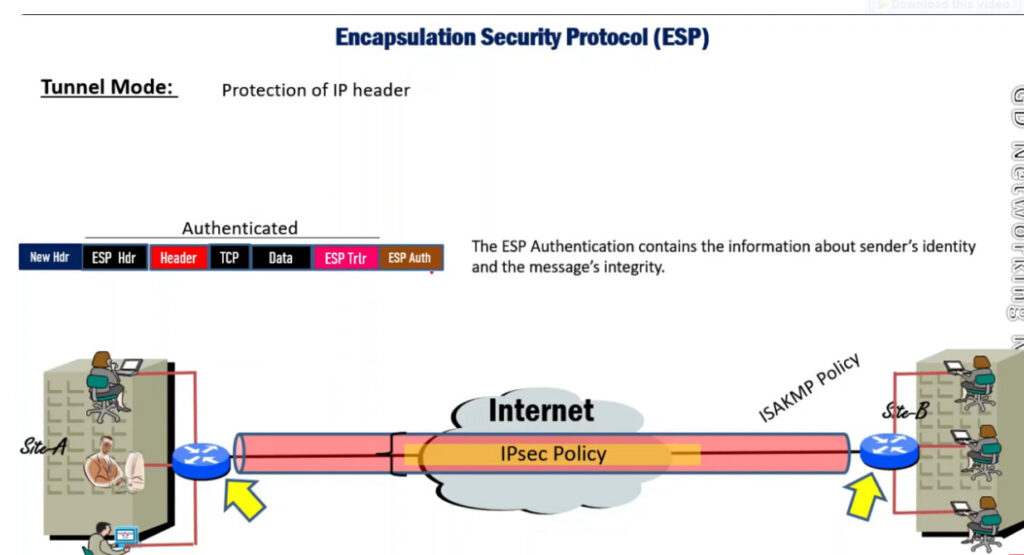
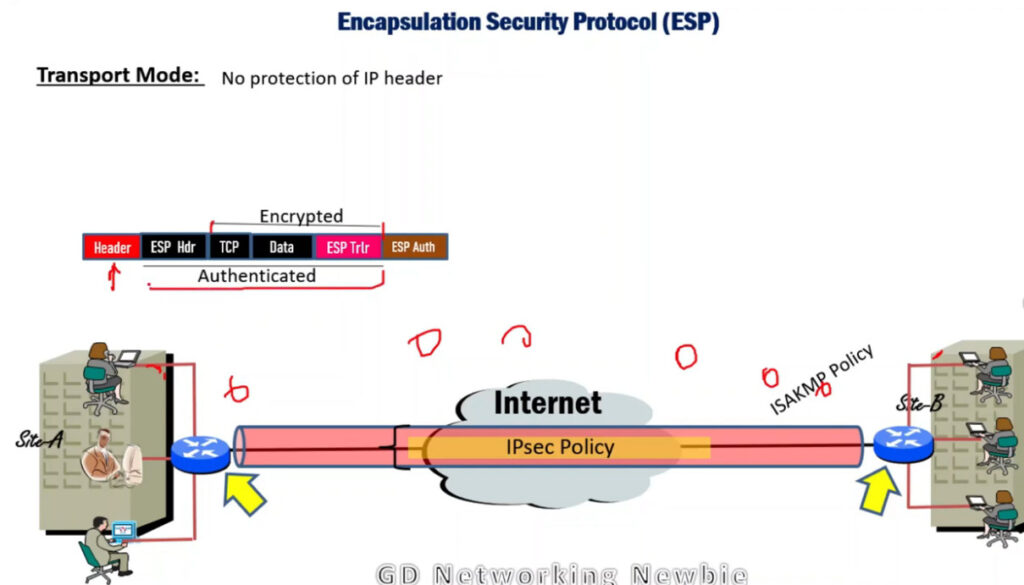
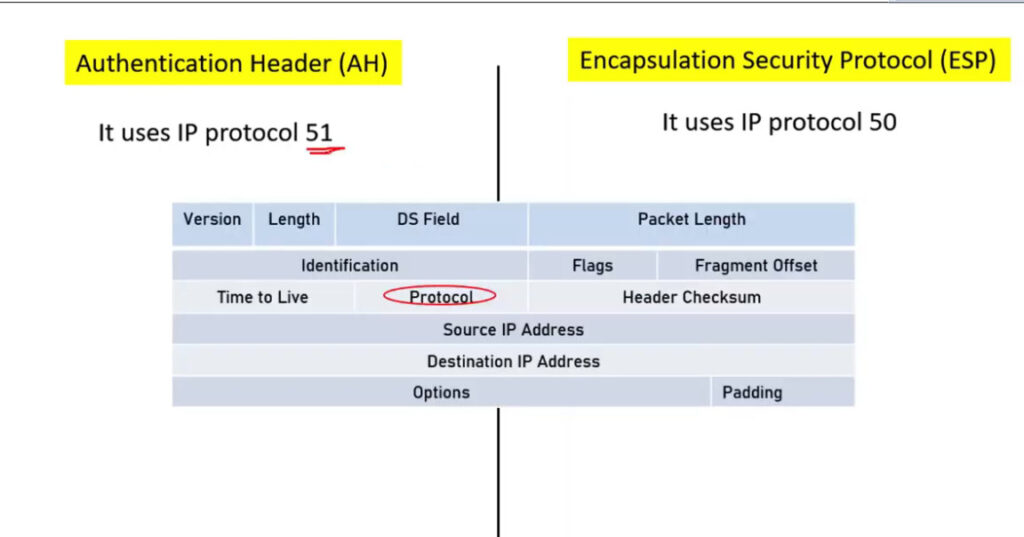
1. Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP): It provides data integrity, encryption, authentication, and anti-replay. It also provides authentication for payload.
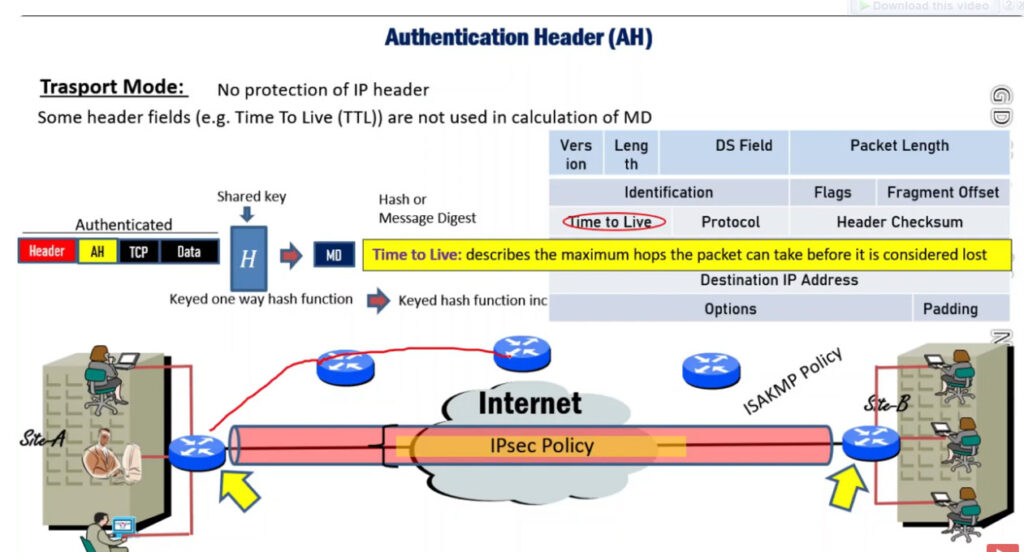
2. Authentication Header (AH): It also provides data integrity, authentication, and anti-replay and it does not provide encryption. The anti-replay protection protects against the unauthorized transmission of packets. It does not protect data confidentiality.
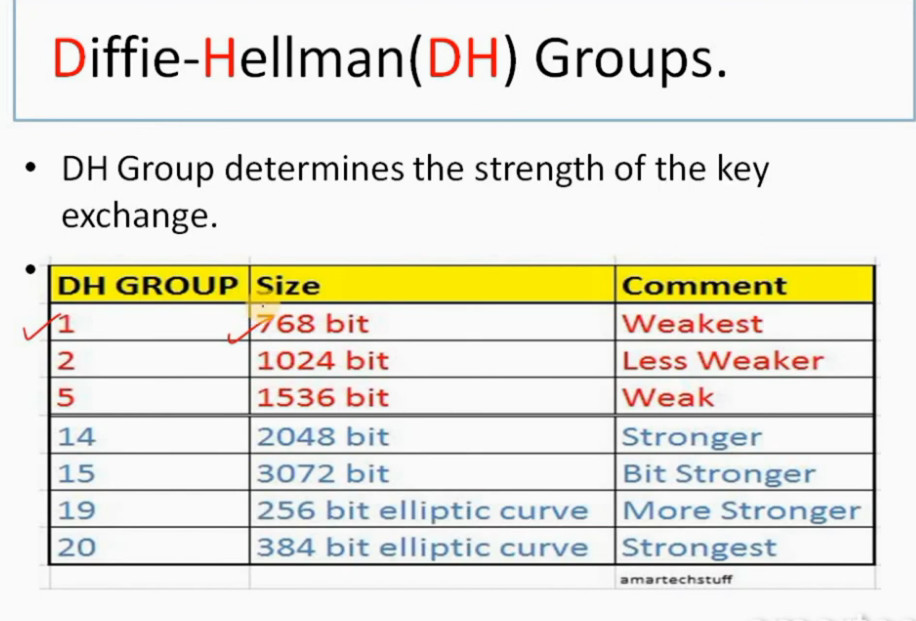
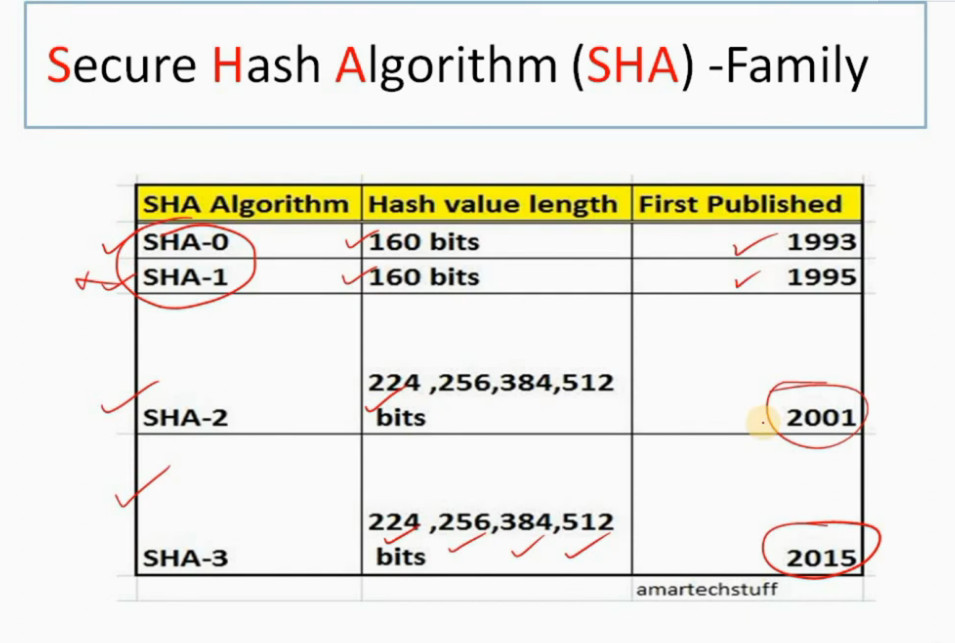
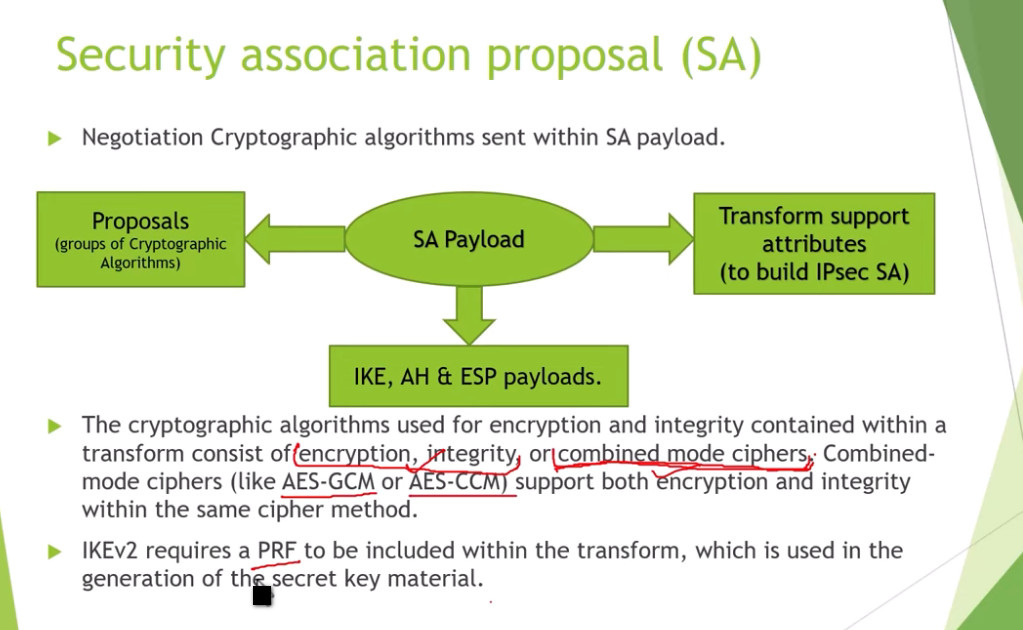
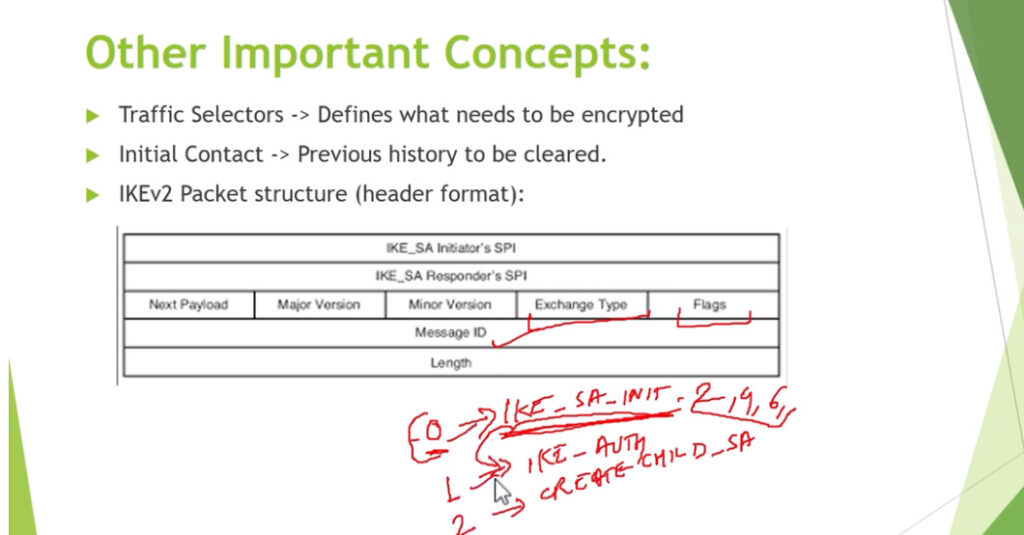
3. Internet Key Exchange (IKE): It is a network security protocol designed to dynamically exchange encryption keys and find a way over Security Association (SA) between 2 devices. The Security Association (SA) establishes shared security attributes between 2 network entities to support secure communication. The Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) and Internet Security Association provides a framework for authentication and key exchange. ISAKMP tells how the setup of the Security Associations (SAs) and how direct connections between two hosts are using IPsec. Internet Key Exchange (IKE) provides message content protection and also an open frame for implementing standard algorithms such as SHA and MD5. The algorithm’s IP sec users produce a unique identifier for each packet. This identifier then allows a device to determine whether a packet has been correct or not. Packets that are not authorized are discarded and not given to the receiver.
IP Security Architecture
IPSec (IP Security) architecture uses two protocols to secure the traffic or data flow. These protocols are
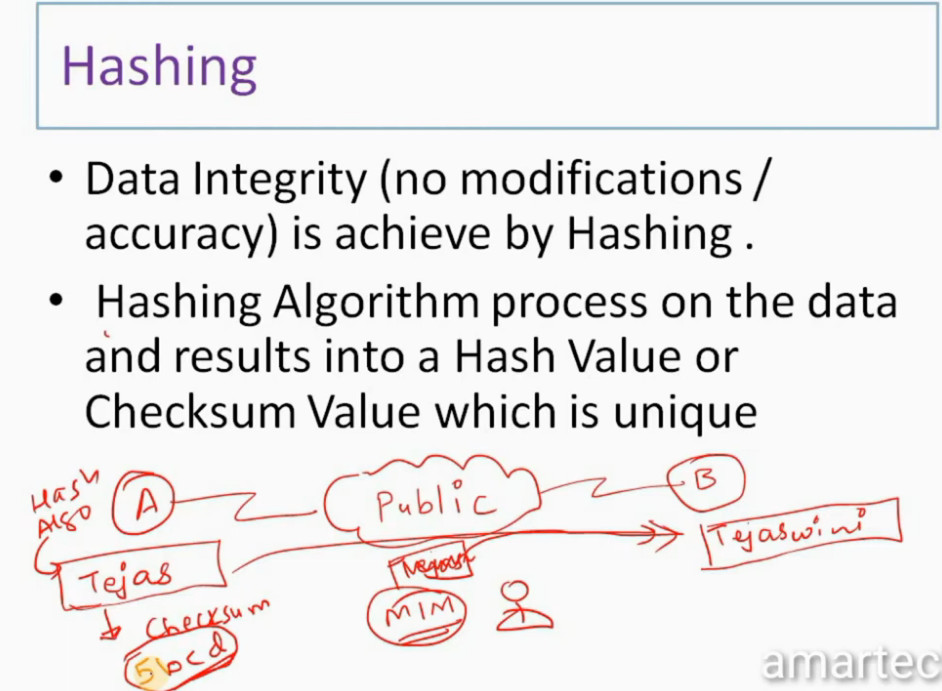
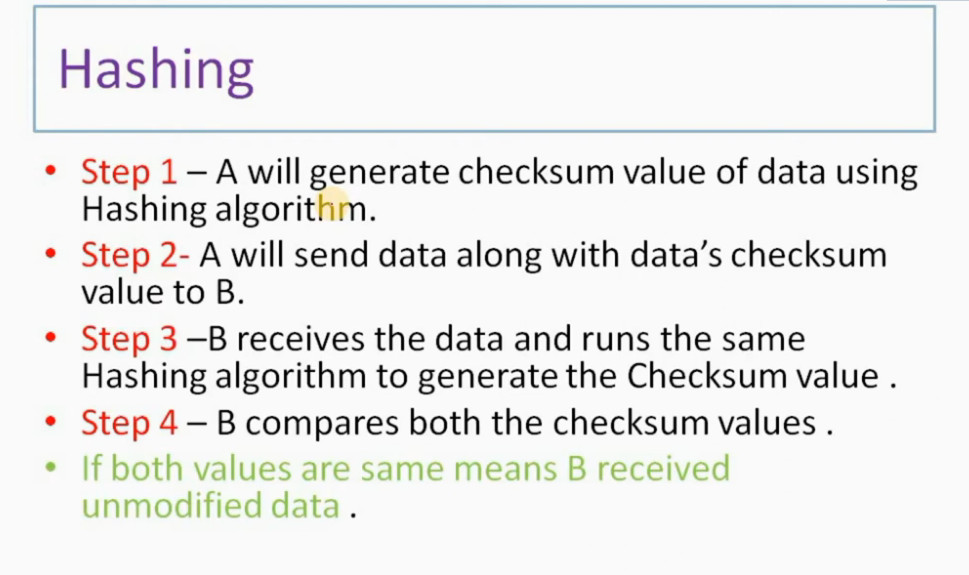
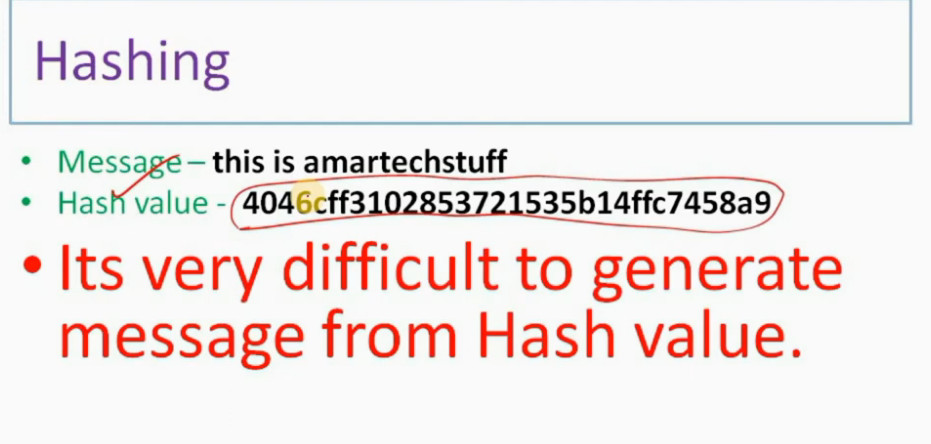
IPSec Architecture includes protocols, algorithms, DOI, and Key Management. All these components are very important in order to provide the three main services such as Confidentiality, Authenticity and Integrity.
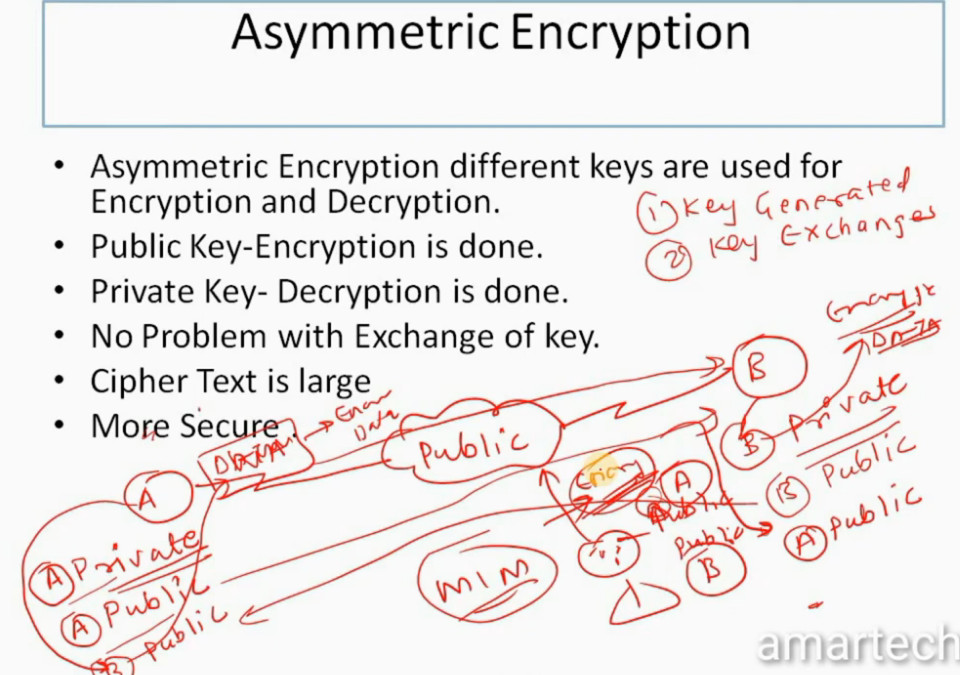
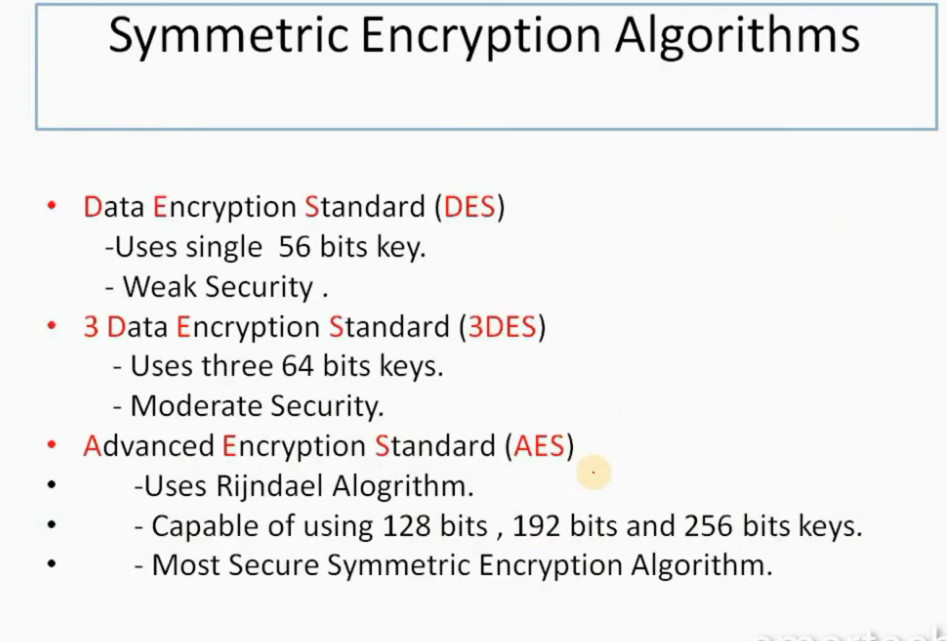
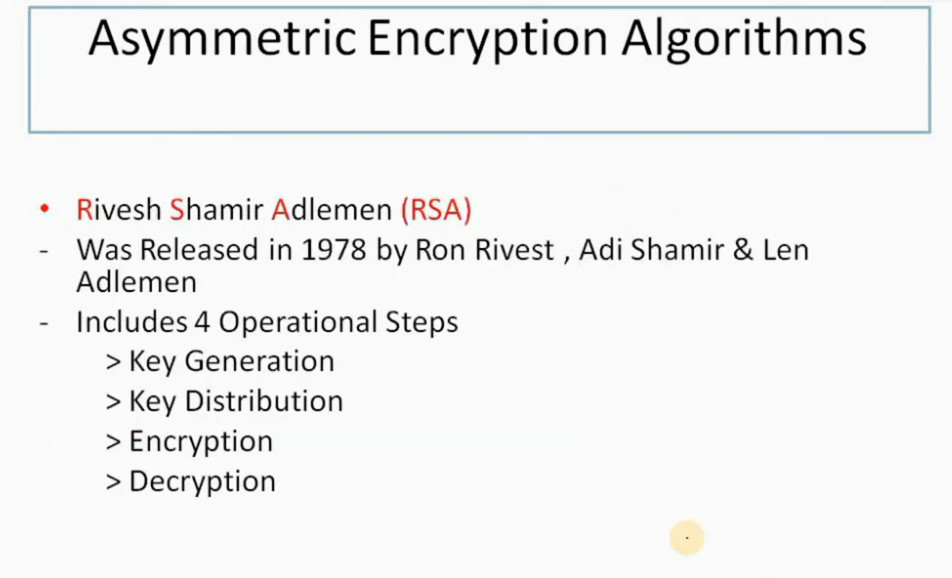
IPSec Encryption
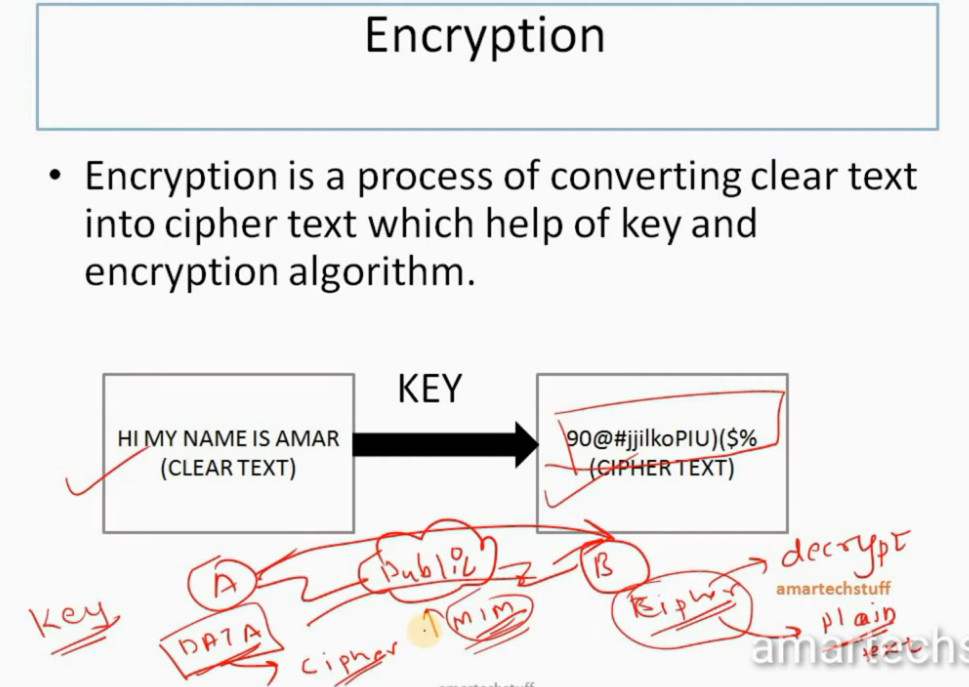
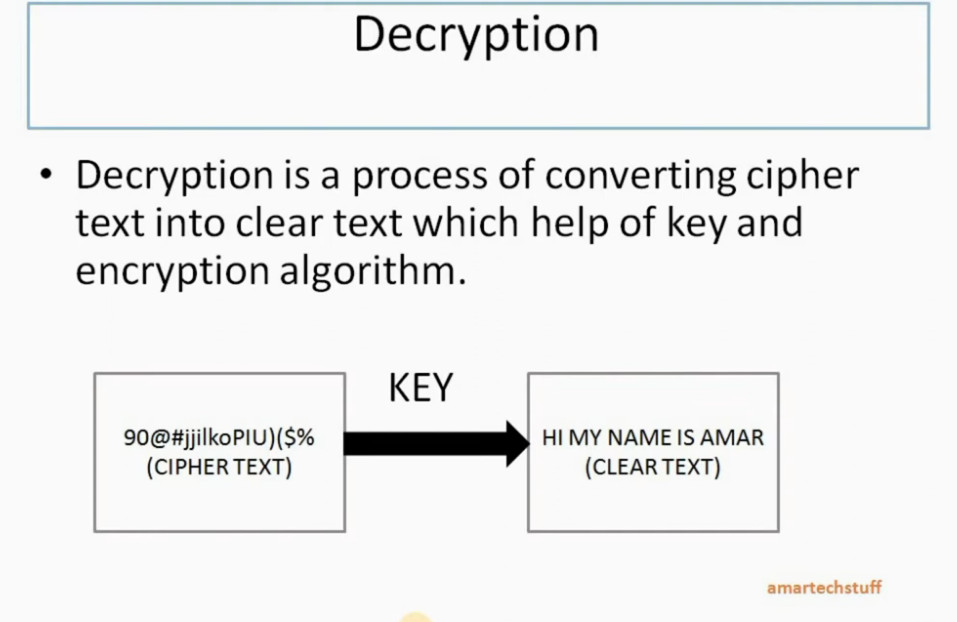
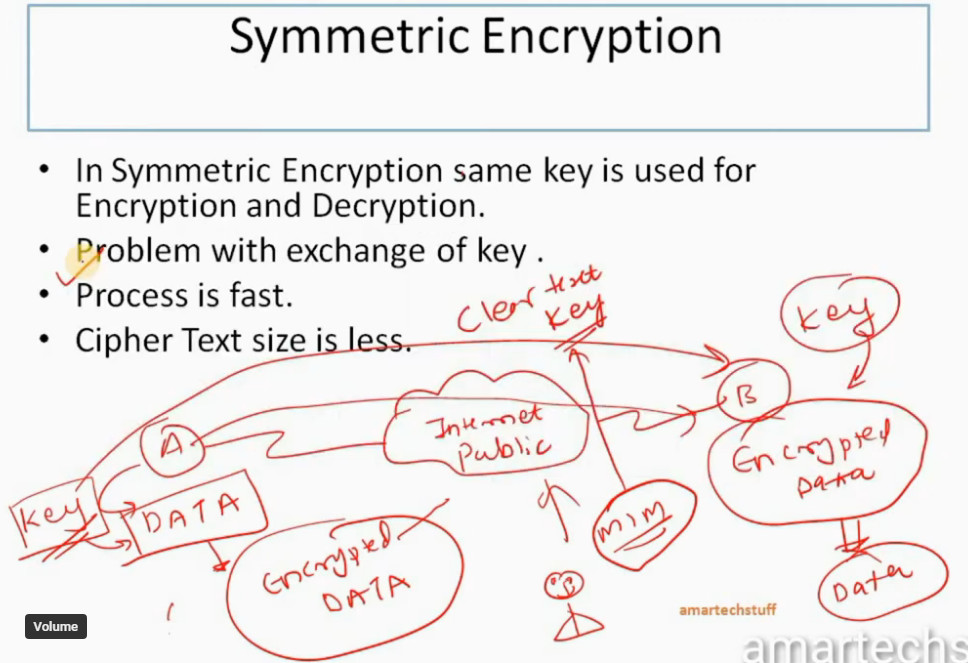
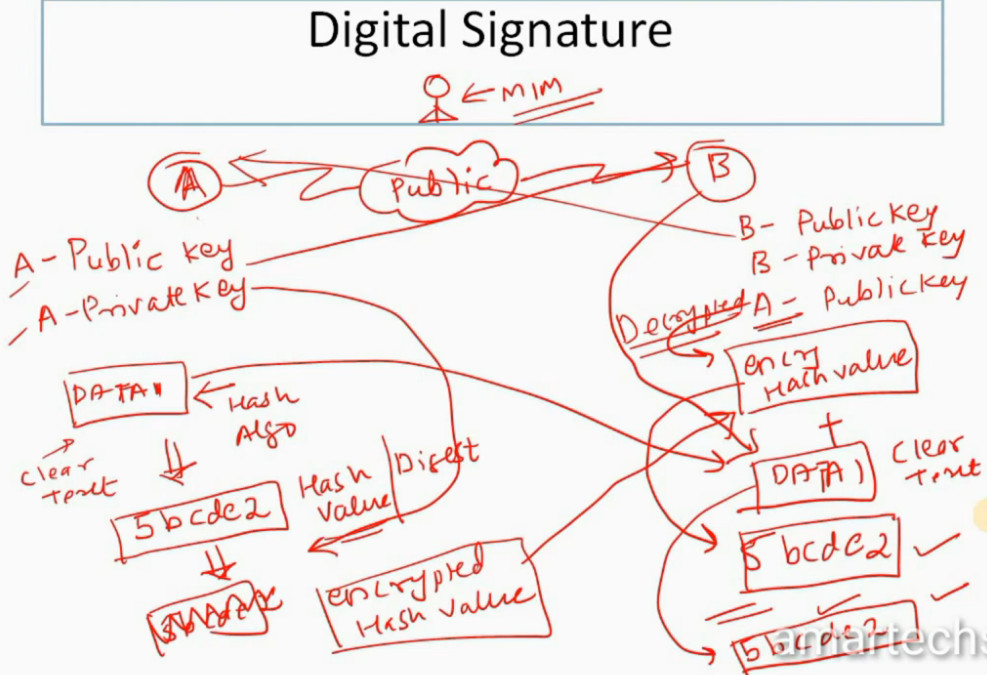
IPSec encryption is a software function that encrypts data to protect it from unauthorized access. An encryption key encrypts data, which must be decrypted. IPSec supports a variety of encryption algorithms, including AES, Triple DES etc. IPSec combines asymmetric and symmetric encryption to provide both speed and security during data transmission. In asymmetric encryption, the encryption key is made public, while the decryption key remains private. Symmetric encryption employs the same public key to encrypt and decrypts data. IPSec builds a secure connection using asymmetric encryption and then switches to symmetric encryption to speed up data transmission.
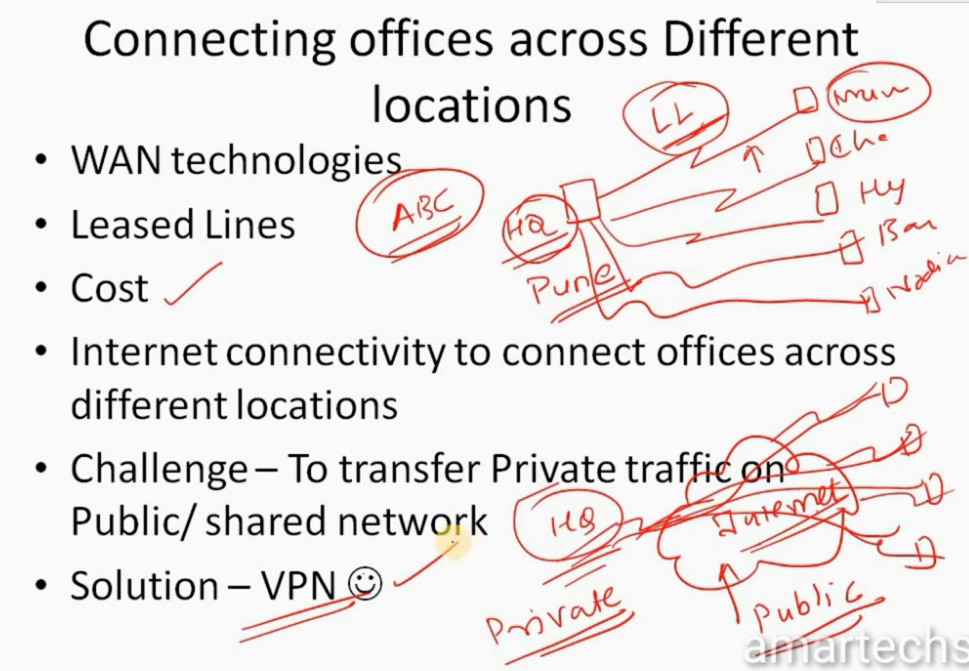
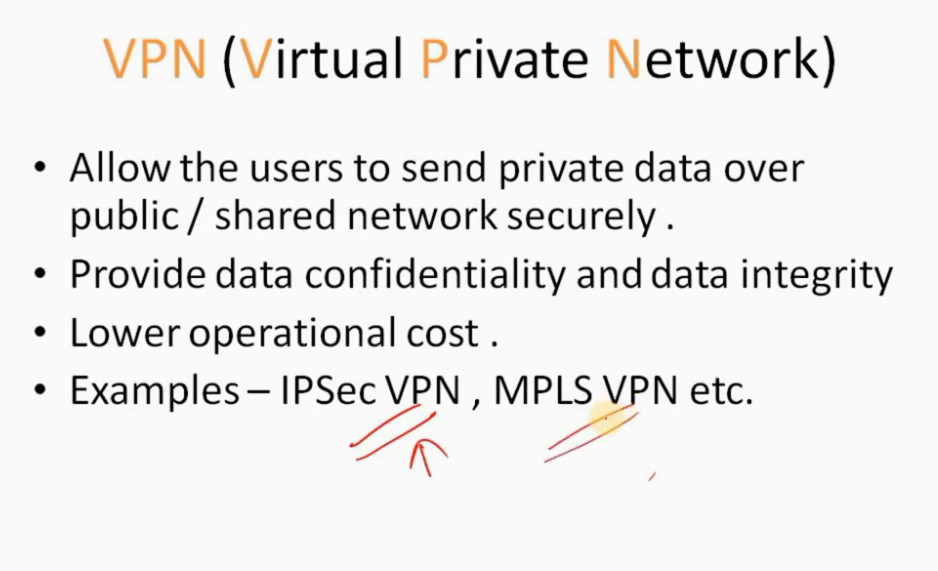
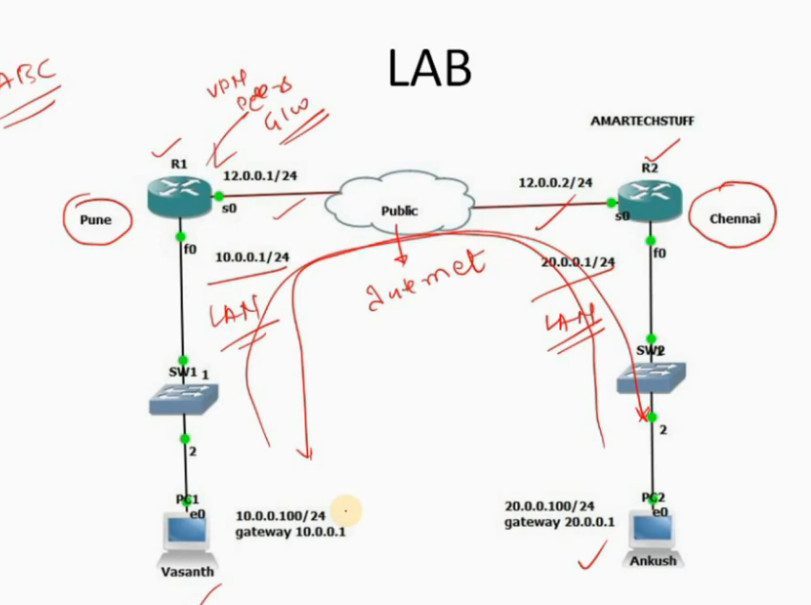
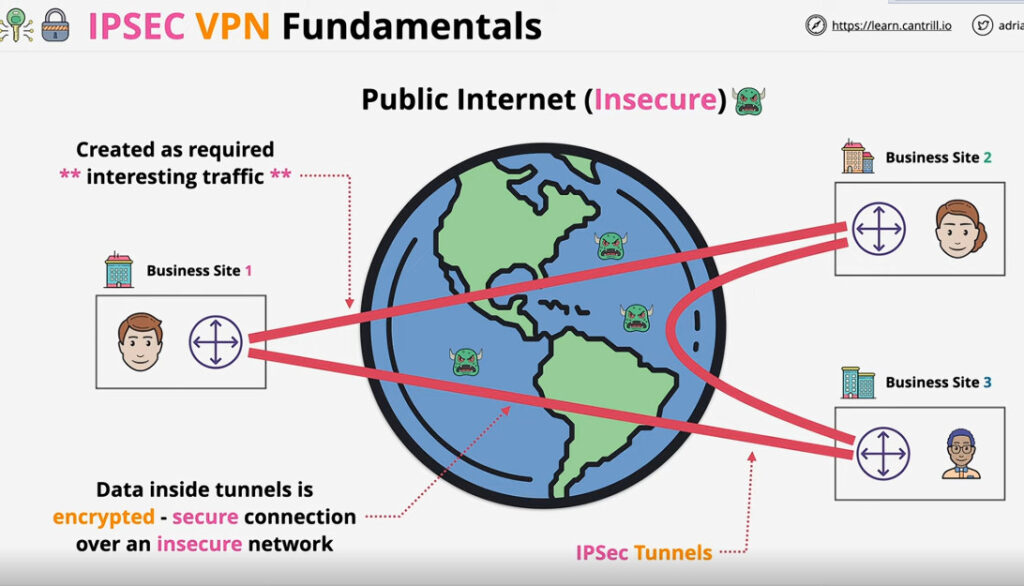
IPSec VPN
VPN(Virtual Private Network) is a networking software that enables users to browse the internet anonymously and securely. An IPSec VPN is a type of VPN software that uses the IPSec protocol to establish encrypted tunnels over the internet. It offers end-to-end encryption, which means that data is broken down at the computer and then collected at the receiving server
Uses of IP Security
Psec can be used to do the following things:
Advantages of IPSec
Disadvantages of IPSec



























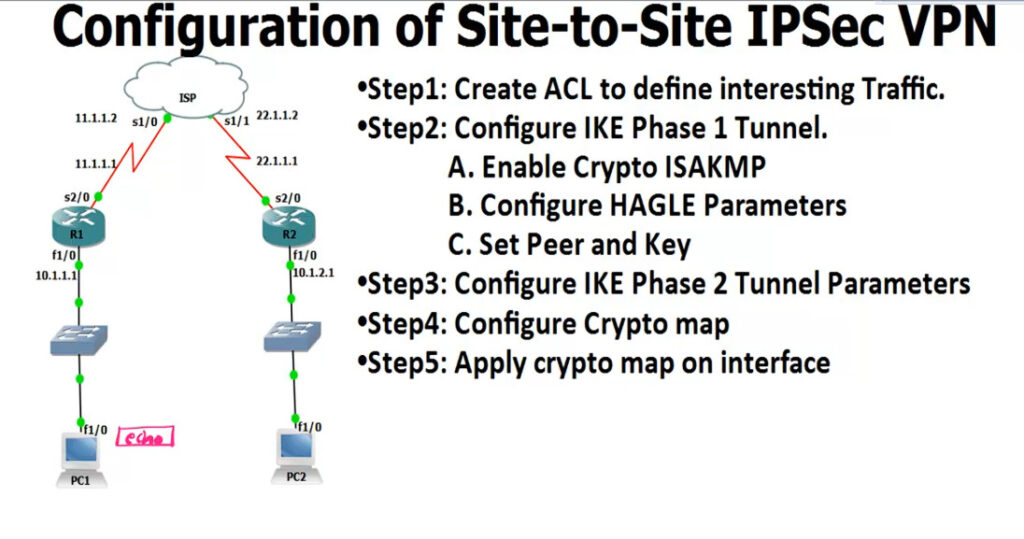
R1
--
access-list 100 permit ip 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255
crypto isakmp enable <Phase 1
crypto isakmp policy 1
encr 3des
hash md5
authentication pre-share
group 2
lifetime 8640
exit
crypto isakmp key 0 HQoffice address 22.1.1.1 <-R2 Public IP
crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac <IPSEC Tunnel Create
crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 12.1.1.1
set transform-set TS
match address 100
interface s2/0 <-Enable IPsec Router Interfaces
crypto map CMAP
ping 12.1.1.10 repeat 10000
IPsec Checking Commnd
---------------------
show crypto isakmp policy <-Checking Policy
show crypto isakmp key <-Checking key
show crypto ipsec transform-set
show crypto map
show crypto isakmp sa <-Checking Phase 1 Status
show crypto ipsec sa <-Checking Phase 2
R2
--
access-list 100 permit ip 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255
crypto isakmp enable
crypto isakmp policy 1
encr 3des
hash md5
authentication pre-share
group 2
lifetime 8640
exit
crypto isakmp key 0 HQoffice address 11.1.1.1 <-R1 Public IP
crypto ipsec transform-set TS esp-3des esp-md5-hmac
crypto map CMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
set peer 12.1.1.1
set transform-set TS
match address 100
interface s2/0
crypto map CMAP