- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
Fortinet is a global cybersecurity company that specializes in providing comprehensive network security solutions. Founded in 2000 by Ken Xie and his brother Michael Xie, Fortinet has grown to become one of the leading players in the cybersecurity industry, helping organizations protect their networks, applications, and data from evolving cyber threats.
Fortinet’s product portfolio includes a wide range of cybersecurity solutions designed to protect enterprise networks, cloud environments, endpoints, and communications. Some of the core offerings include:
Fortinet offers a “Security Fabric,” an integrated, end-to-end security architecture that connects various Fortinet products and third-party solutions. This fabric enables seamless communication and data sharing between different components, improving visibility and response times to potential threats.
The heart of Fortinet’s security platform is FortiOS, a robust operating system that powers FortiGate firewalls and other Fortinet devices. It combines advanced security features like intrusion prevention, antivirus, VPN, and web filtering with high-performance capabilities. FortiOS supports both physical and virtual appliances and can be deployed in on-premises, cloud, or hybrid environments.
Fortinet’s FortiGuard Labs provides a global threat intelligence service that helps keep Fortinet’s products up to date with the latest security information. FortiGuard Labs uses machine learning and behavioral analysis to detect new and emerging threats, providing automated updates to Fortinet’s devices for real-time protection.
Fortinet is known for delivering high-performance solutions that scale to meet the needs of organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises. FortiGate firewalls, for example, use Fortinet’s custom FortiASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) hardware, which optimizes the performance of key security features like deep packet inspection and VPN.
As more organizations move their workloads to the cloud, Fortinet has evolved to provide security solutions for cloud and hybrid environments. Its products are compatible with major cloud platforms, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, allowing businesses to extend their security to the cloud.
Fortinet’s offerings cover various aspects of cybersecurity, providing a layered defense strategy. Their solutions protect against threats at the network perimeter, within applications, and across endpoints. Additionally, Fortinet solutions are designed to provide high levels of visibility and control across the entire network, regardless of its size or complexity.
Fortinet has earned a reputation for being a leader in network security, consistently appearing in the top quadrants of analyst reports like Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls. Their solutions are praised for their high-performance and scalability, as well as for their ability to integrate multiple security features into a single platform.
Fortinet operates globally, with a vast network of customers spanning across industries such as finance, healthcare, manufacturing, education, and government. Its solutions are used by organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises, and its services are available in more than 100 countries.
Fortinet offers a robust Fortinet Network Security Expert (NSE) certification program. This program is designed to train and certify professionals in Fortinet technologies and cybersecurity best practices. With various levels of certification, the NSE program helps to build expertise in areas like network security, advanced threat protection, and secure SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN).
Fortinet is a leading cybersecurity company known for its high-performance, scalable, and cost-effective security solutions. It provides a broad portfolio of products that help organizations protect their networks, endpoints, and data from an array of cyber threats. Whether for small businesses or large enterprises, Fortinet’s solutions deliver robust protection with easy integration and centralized management capabilities.
Fortinet is a leading cybersecurity company known for its high-performance network security solutions. There are several reasons why many organizations choose Fortinet for their security needs:
Fortinet offers a broad range of security products, from next-generation firewalls (NGFW) to intrusion prevention systems (IPS), secure Wi-Fi solutions, email security, and endpoint protection. This all-encompassing portfolio helps businesses secure their networks, applications, and data against a wide range of threats.
Fortinet’s FortiGate firewalls are widely recognized for their high performance and scalability. They are designed to provide protection against a wide range of network threats without compromising performance. FortiGate is powered by Fortinet’s custom ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits), which help optimize speed and efficiency.
Fortinet’s Security Fabric integrates multiple security technologies to create a unified and cohesive security environment. This integration helps ensure that all security components work together effectively, providing end-to-end protection across the entire network.
Fortinet leverages its FortiGuard Labs, which provides real-time threat intelligence and automated updates to ensure that its security solutions stay up-to-date with the latest threats. Automated responses and real-time analysis make it easier for organizations to detect and mitigate threats quickly.
Fortinet’s products are highly scalable, making them suitable for organizations of all sizes, from small businesses to large enterprises and service providers. FortiGate firewalls, for example, can scale to support large volumes of traffic and can be deployed in both physical and virtual environments.
Fortinet is known for providing cost-effective solutions without compromising on performance or security features. This makes it an attractive choice for organizations that need enterprise-level protection but are mindful of their budget.
As businesses increasingly adopt cloud technologies, Fortinet provides strong security for hybrid and multi-cloud environments. Fortinet’s solutions are compatible with cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, offering a seamless and secure experience for cloud-based workloads.
Fortinet offers centralized management platforms like FortiManager and FortiAnalyzer that allow IT teams to manage, monitor, and analyze their security infrastructure from a single pane of glass. This simplifies security management, especially in complex, large-scale environments.
Fortinet consistently ranks highly in industry analyst reports, such as the Gartner Magic Quadrant for Network Firewalls and the NSS Labs Security Value Map. This recognition highlights the company’s leadership and innovation in the cybersecurity space.
Fortinet’s solutions are designed to address modern cybersecurity challenges, such as protecting remote workforces, securing IoT devices, and defending against advanced persistent threats (APTs). Their emphasis on next-gen firewall capabilities helps organizations adapt to evolving threat landscapes.
In summary, Fortinet is chosen for its comprehensive, high-performance security solutions, its ability to integrate different aspects of security into a unified system, and its scalability, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes across different industries.





A firewall is a network security device or software that monitors and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. Firewalls are used to establish a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external networks (such as the internet), allowing only authorized traffic to pass through. They are essential for protecting systems and networks from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and malware.
There are several different types of firewalls, each with its specific functionality, strengths, and use cases. Here are the main types:
Each type of firewall serves a different purpose depending on the network requirements and security goals of an organization. For example:
Selecting the right type of firewall depends on factors such as network complexity, performance requirements, and the level of security needed.





Firewall Administrator: As a Firewall Administrator, you can expect a salary package ranging from INR 4-8 lakhs per annum.
Network Security Engineer: As a Network Security Engineer, you can expect a salary package ranging from INR 4-12 lakhs per annum.
Cyber Security Analyst: As a Cyber Security Analyst, you can expect a salary package ranging from INR 5-15 lakhs per annum
Security Consultant: As a Security Consultant, you can expect a salary package ranging from INR 6-20 lakhs per annum.
Next-Generation Security Platform and Architecture
Basic-Terminology
Identify Malware
Firewall Technologies
About Fortinet
Install FortiGate on VMware Workstation
Install FortiGate in GNS3
Install FortiGate on EVE
Introduction and Initial Configuration
FortiGate Dashboard
Initial Working Lab
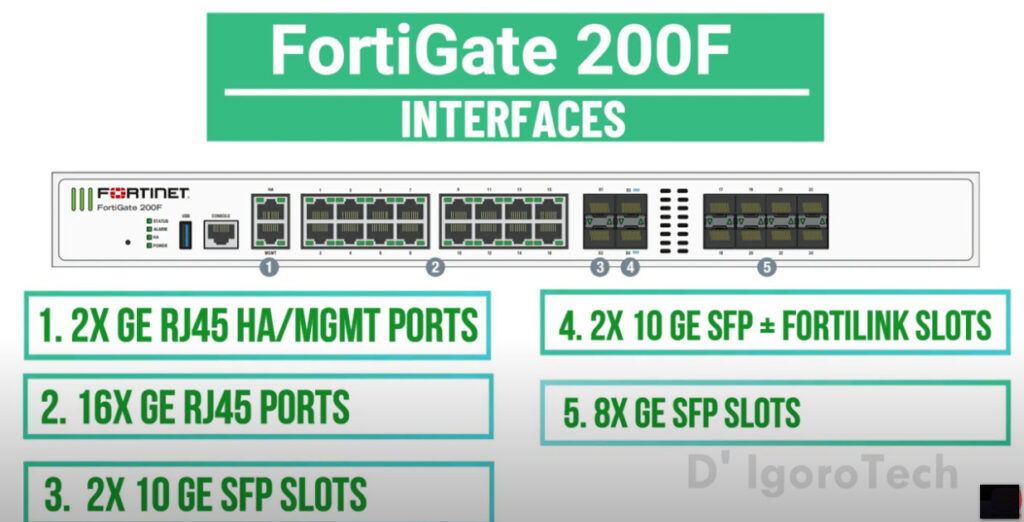
Interfaces
Zone
Virtual Wire Pair
Administrative Access
DNS Server
Routing on Fortinet firewall
Addresses Objects
Services Objects
Static-Policy-Route
RIP
OSPF
Routing Protocols Redistribution
BGP Border Gateway Protocol
Firewall Policies
Policies
Policy-Labs-MAC
Policy-Labs-LocalUser
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT-Basic Network Address Translation
SNAT Lab
DNAT Lab
Policy, Source, Overload NAT Lab
Policy, Source, One-To-One NAT Lab
Policy, Source, Fixed Port Range NAT Lab
Security Profile-Intro
AV-Security Profiles
Web Filter Profiles
DNS Filter Profiles
Application Control Profiles
Intrusion Prevention System Profiles
Inspection Mode
NGFW Modes
FortiGateAD
Passive Authentication AD
Layer 2 firewall
Transparent Mode
Virtual Wire Pairing
Software Switch
Logging and Monitoring
SNMP Access-Lab
Backup and Restore
Configure Syslog in FortiGate Firewall
IPsec VPN
VPN Concept
Site2Site-Policy-Based-VPN
Site-to-Site IPSec Route-Based VPN
Site-to-Site IPSec VPN Template Lab
SSL VPN
Remote Access VPN
Remote Access SSL VPN Web Portal Theory & Lab
High Availability (HA)
What is HA
Active-Passive Lab
Active-Active Lab
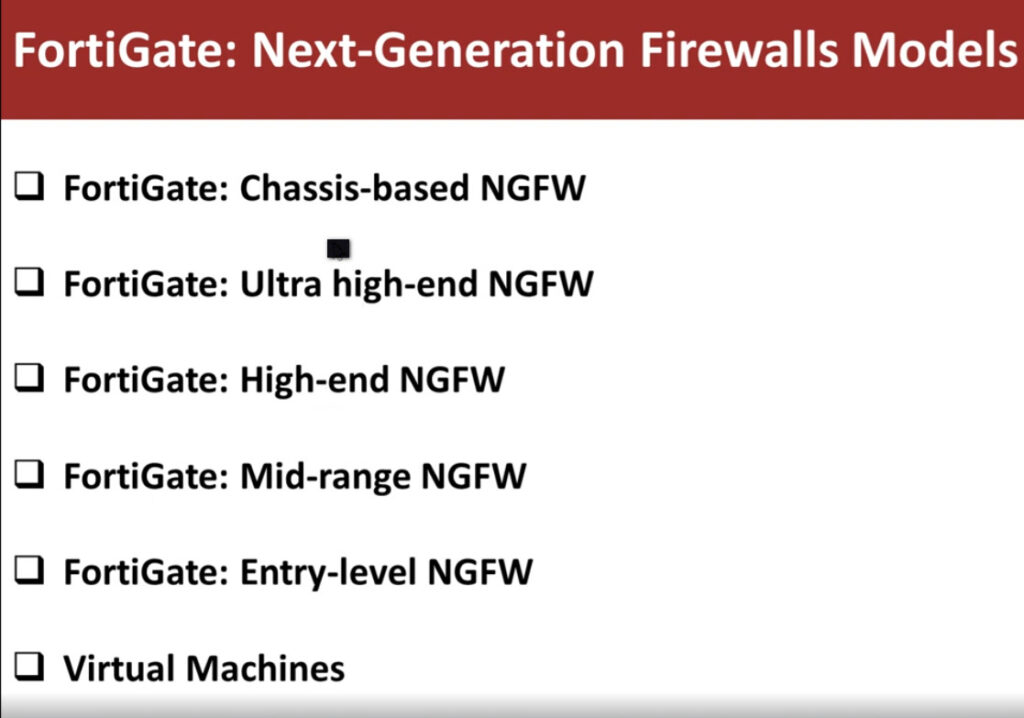
Fortinet offers a wide range of firewalls under its FortiGate series, catering to different network sizes and use cases. These firewalls are used to protect enterprises, data centers, and SMBs (Small and Medium-sized Businesses). The series ranges from entry-level models to high-end enterprise solutions, and they incorporate advanced features like deep packet inspection (DPI), SSL inspection, VPNs, and more.
Here is a breakdown of FortiGate models, from basic to advanced:
These models are ideal for small businesses, branch offices, or smaller network environments. They offer essential security features without the complexity and cost of high-end solutions.
FortiGate 30E/40F/60F:
FortiGate 80F/90E:
These firewalls cater to medium-sized businesses, regional data centers, and more complex security needs. These models offer additional performance, scalability, and more robust security features.
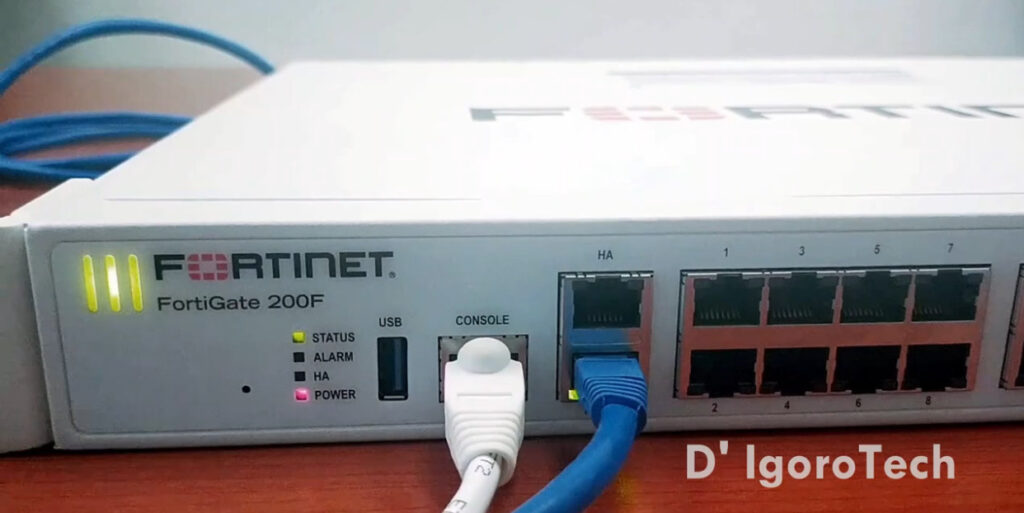
FortiGate 100F/200F/300E:
FortiGate 500E/600E:
These models are designed for large enterprises, data centers, and high-traffic networks that require high throughput, advanced security, and the ability to handle complex, multi-site configurations.
FortiGate 1000D/2000E/3000F:
FortiGate 5000 Series (e.g., FortiGate 5001E, 5003E):
Fortinet also offers virtual firewalls for cloud and virtual environments. These are designed to provide enterprise-grade security without the need for physical hardware.
Choosing the right FortiGate model depends on the size of your organization, the complexity of your network, and your specific security requirements.
FortiGate 90G Data Sheet
2.2 Gbps
FortiGate 80F
900 Mbps
FortiGate 70G
1.3 Gbps
FortiGate 70F
800 Mbps
FortiGate 60F
700 Mbps
FortiGate 50G
1.1 Gbps
FortiGate 40F
600 Mbps
FortiGate 30G
500 Mbps
FortiGate 100F
1 Gbps
FortiGate 120G
2.8 Gbps
FortiGate 200F Data Sheet
3 Gbps
FortiGate 200G
6.4 Gbps
FortiGate 400F
9 Gbps
FortiGate 600F
10.5 Gbps
FortiGate 900G Data Sheet
20 Gbps