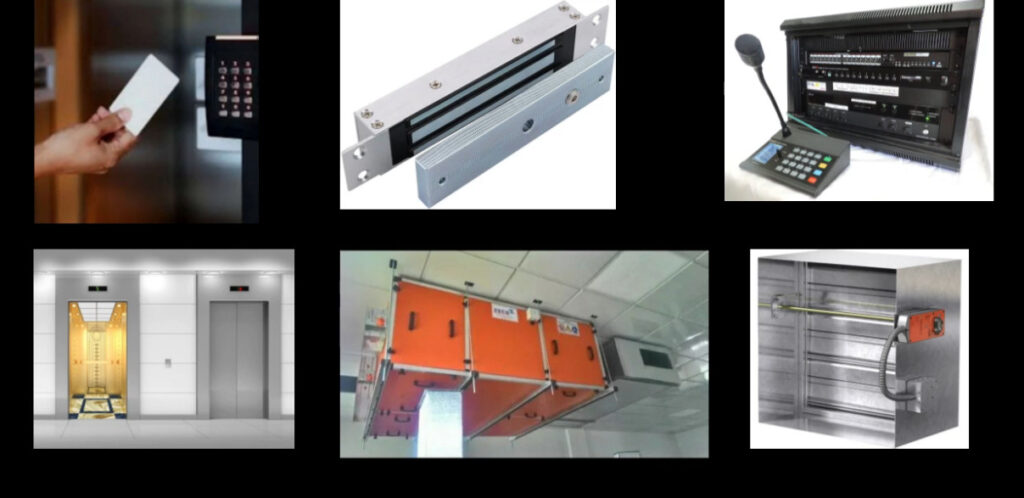
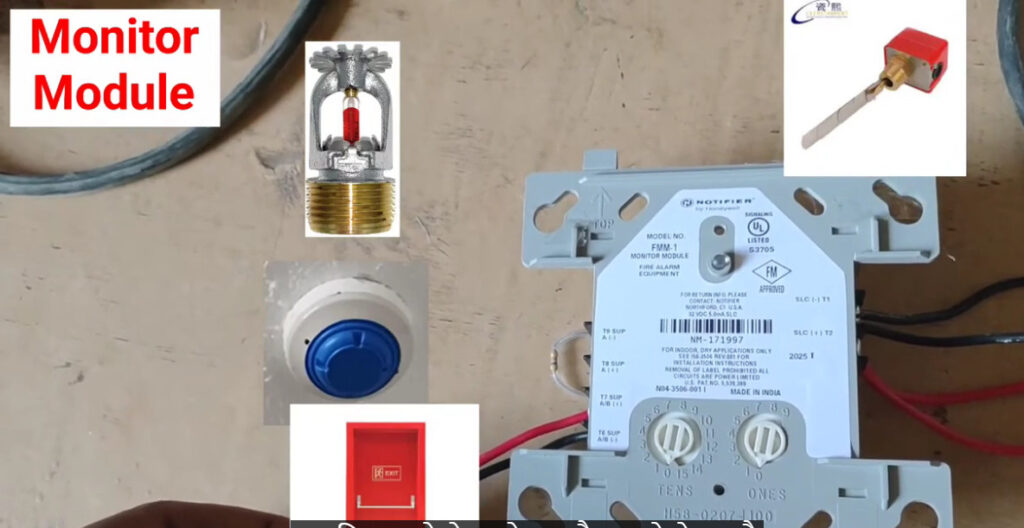
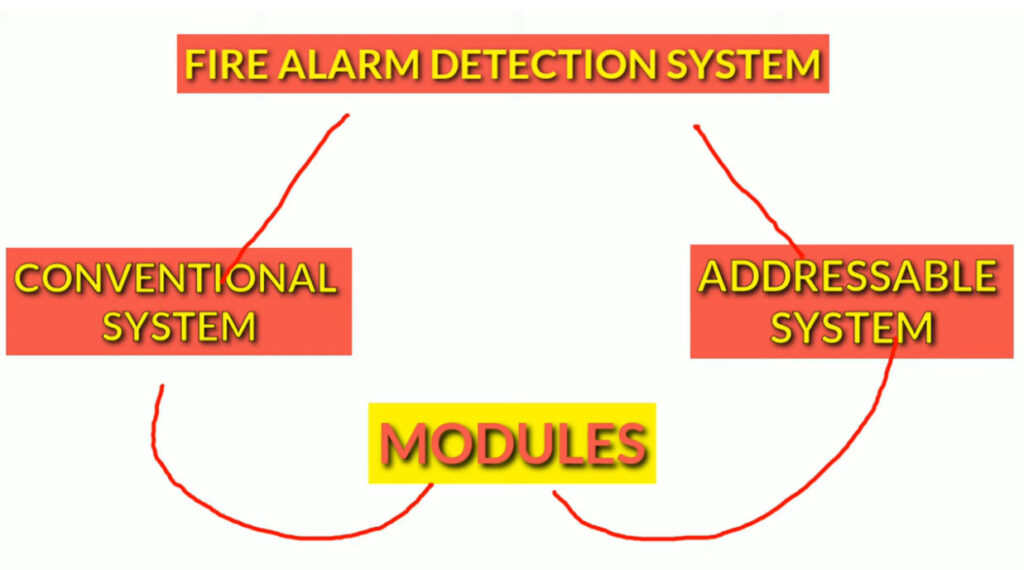
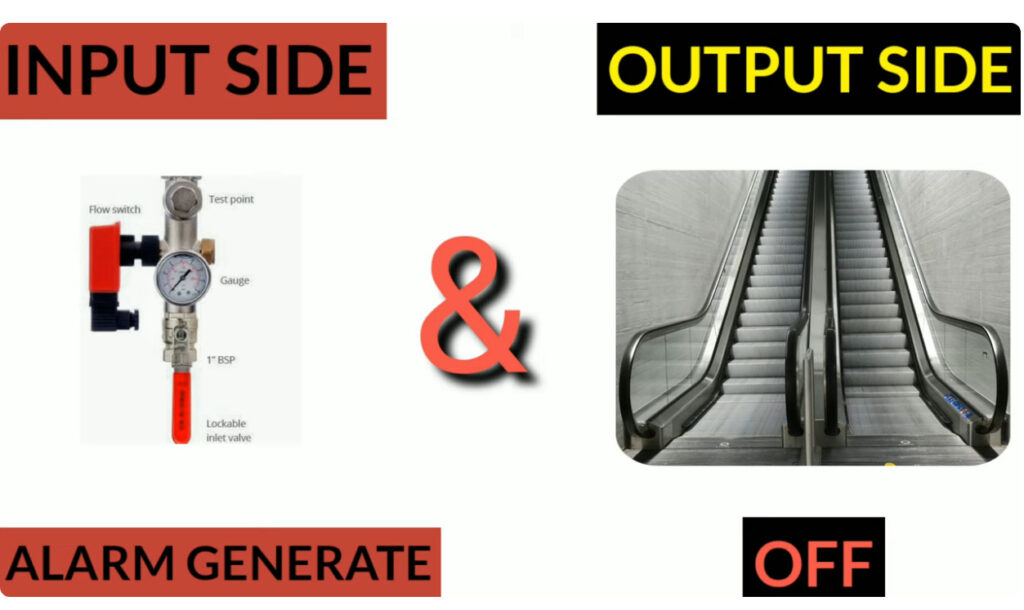
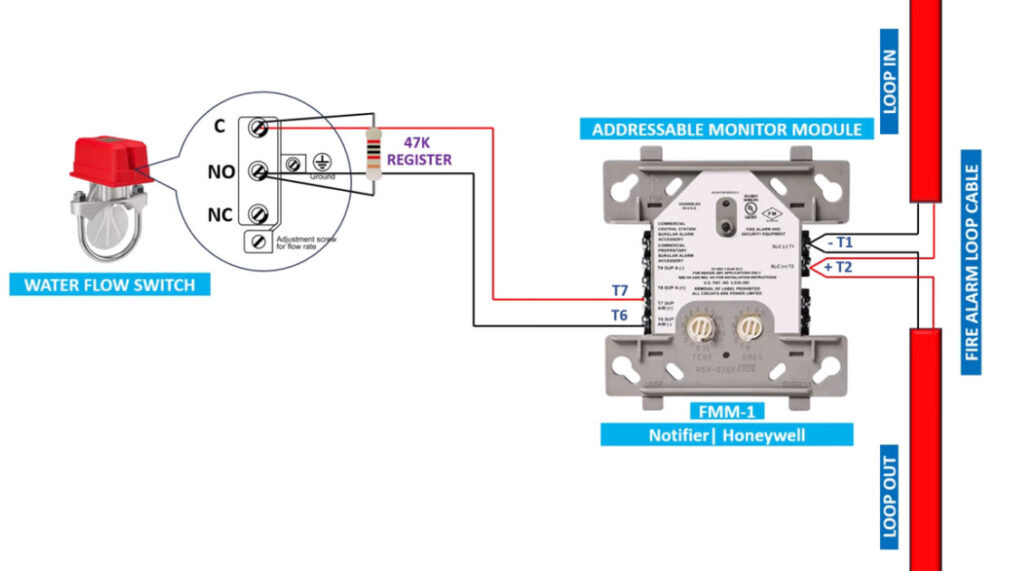
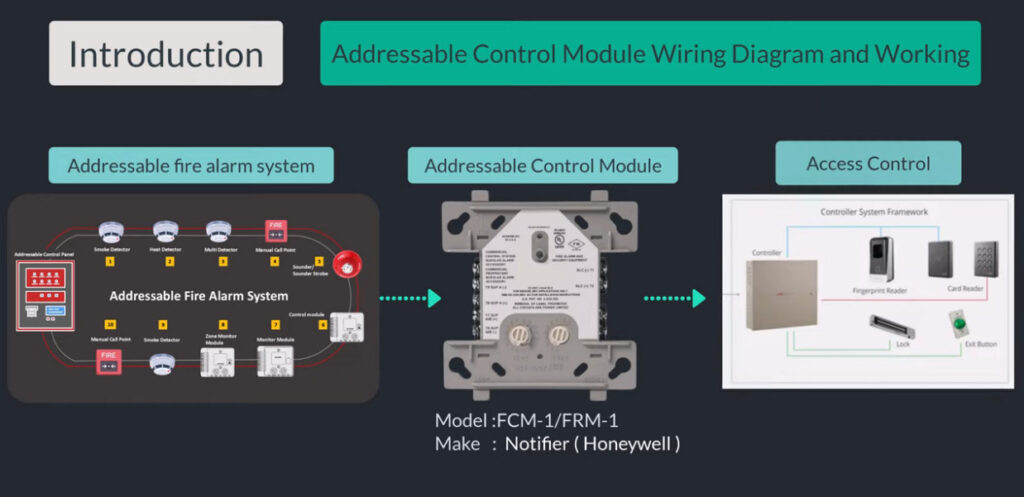
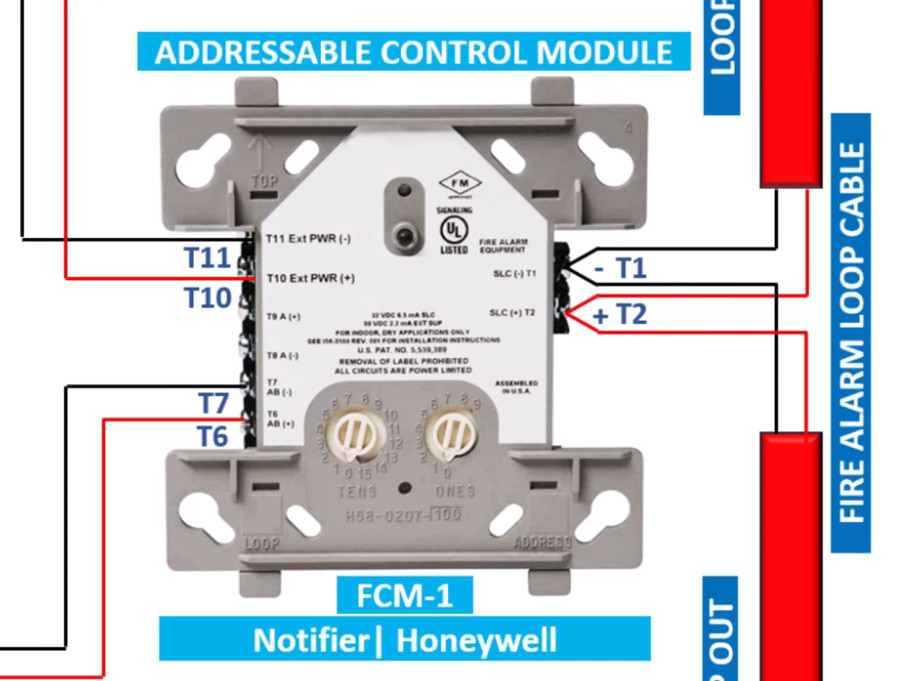
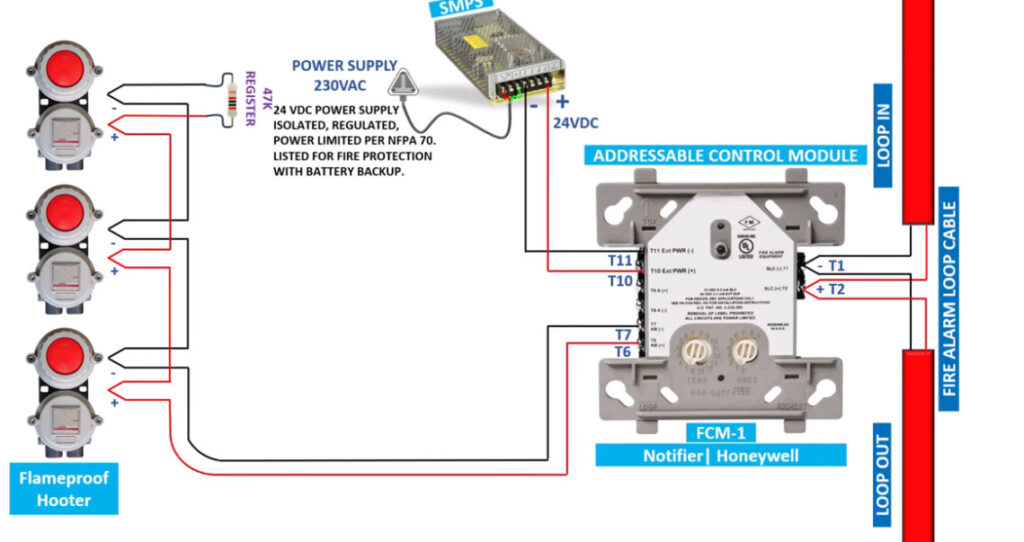
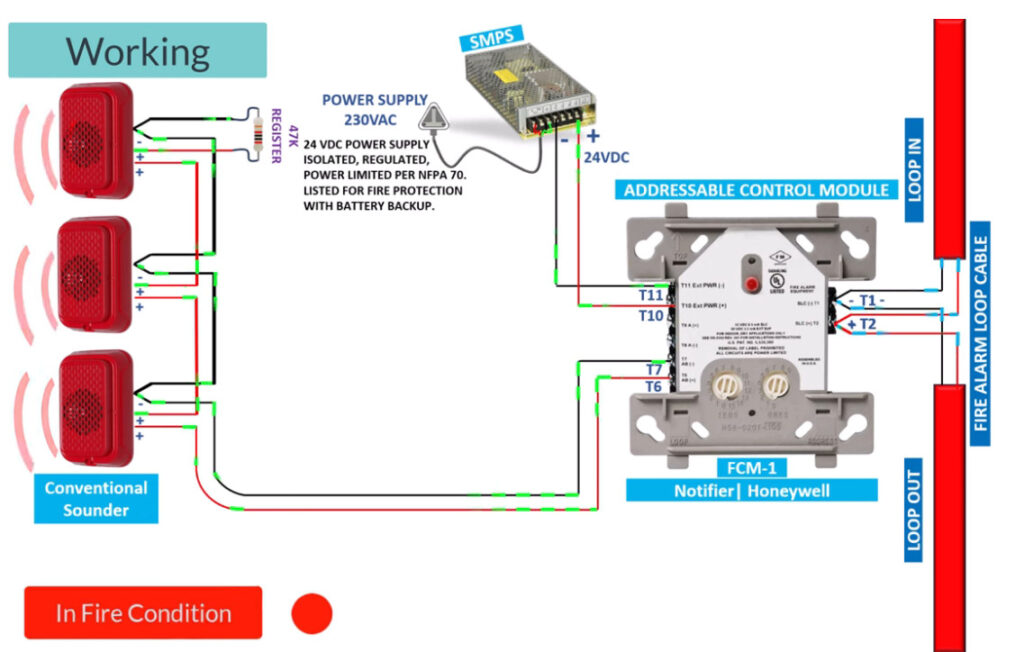
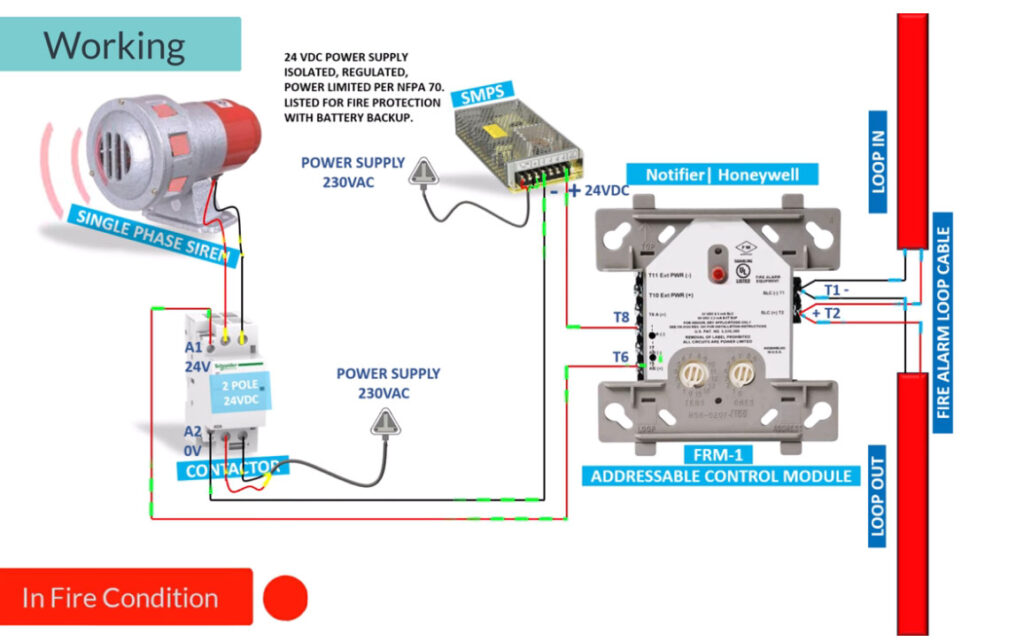
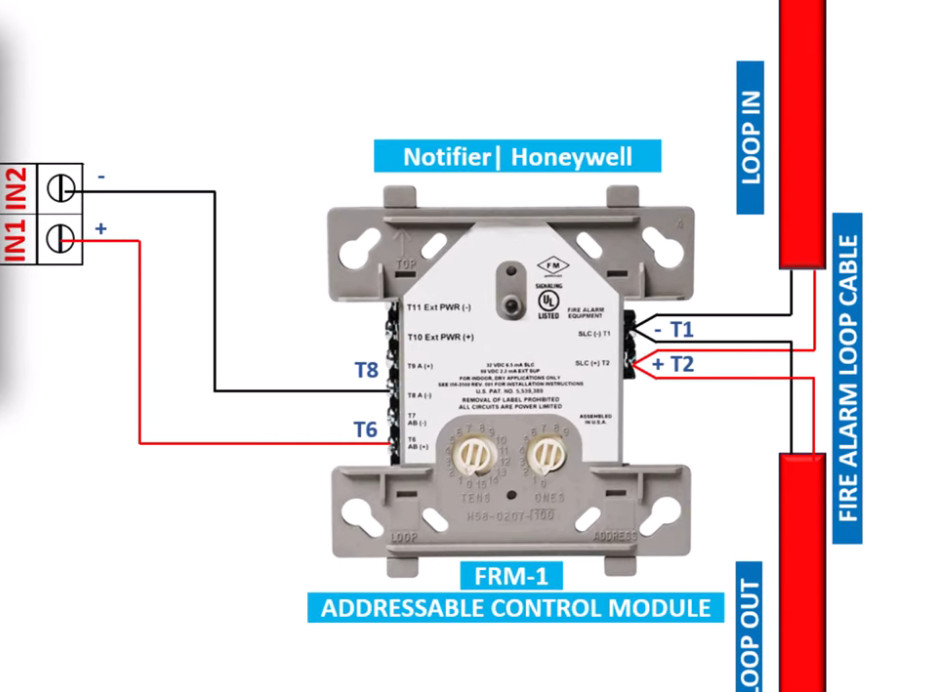
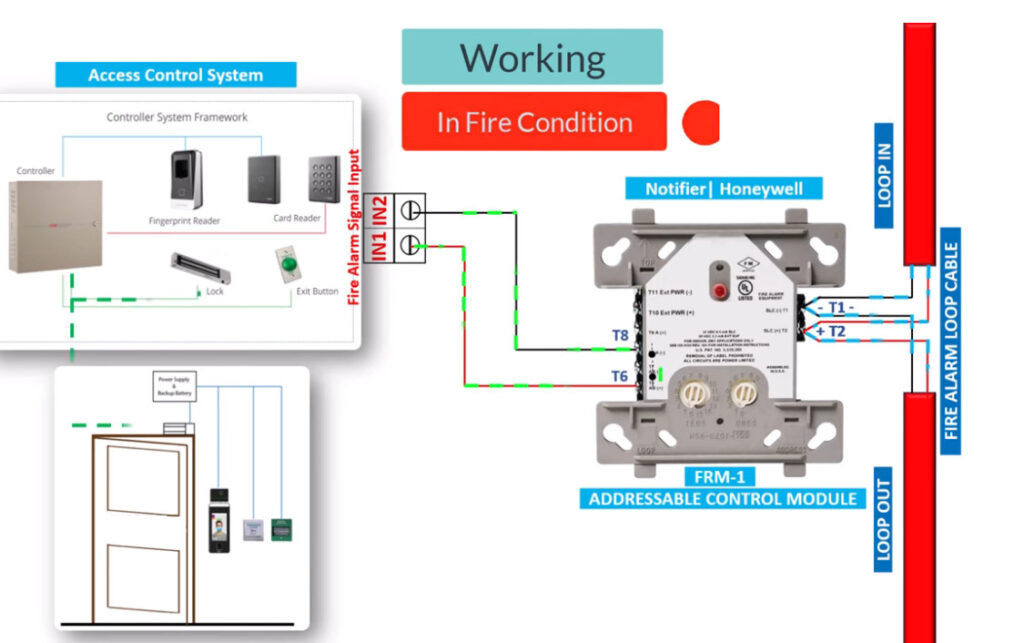
Fire alarm systems consist of various fire alarm modules that perform distinct functions, allowing for comprehensive fire detection, alarm signaling, and emergency response. These modules are interconnected within a fire alarm system to enhance its performance, reliability, and adaptability. Below is an overview of the common fire alarm modules used in both conventional and addressable fire alarm systems:
1. Control Panel (Main Fire Alarm Control Panel)
- Function: The central hub of the fire alarm system that monitors and controls all connected modules. It receives signals from detectors and other components, processes the data, and activates alarms or other systems based on the situation.
- Features:
- Displays system status, fire events, and trouble signals.
- Can be programmed for different detection zones, evacuation plans, and system maintenance.
- May include interfaces for remote monitoring or connection to other building systems (e.g., HVAC).
2. Smoke Detectors
- Function: Detect the presence of smoke in the air, signaling the potential for fire.
- Types:
- Ionization Smoke Detectors: Best for fast-flaming fires.
- Photoelectric Smoke Detectors: Better for detecting smoldering fires.
- Combined Smoke Detectors: Use both ionization and photoelectric technologies.
- In Addressable Systems: Each detector is assigned a unique address, allowing for precise identification of the location of the detected fire.
3. Heat Detectors
- Function: Detect rapid temperature changes or exceed a preset temperature threshold.
- Types:
- Fixed-Temperature Heat Detectors: Trigger when the temperature rises above a set level.
- Rate-of-Rise Heat Detectors: Detect rapid increases in temperature.
- Use: Common in areas where smoke detection may not be effective (e.g., kitchens, boiler rooms).
4. Manual Call Points (MCP)
- Function: Allow individuals to manually trigger the fire alarm system in case of a fire emergency.
- Operation: Typically involves breaking a glass or pressing a button to activate the alarm.
- Locations: Installed near exits, hallways, and high-traffic areas where people can quickly trigger the alarm in case of a fire.
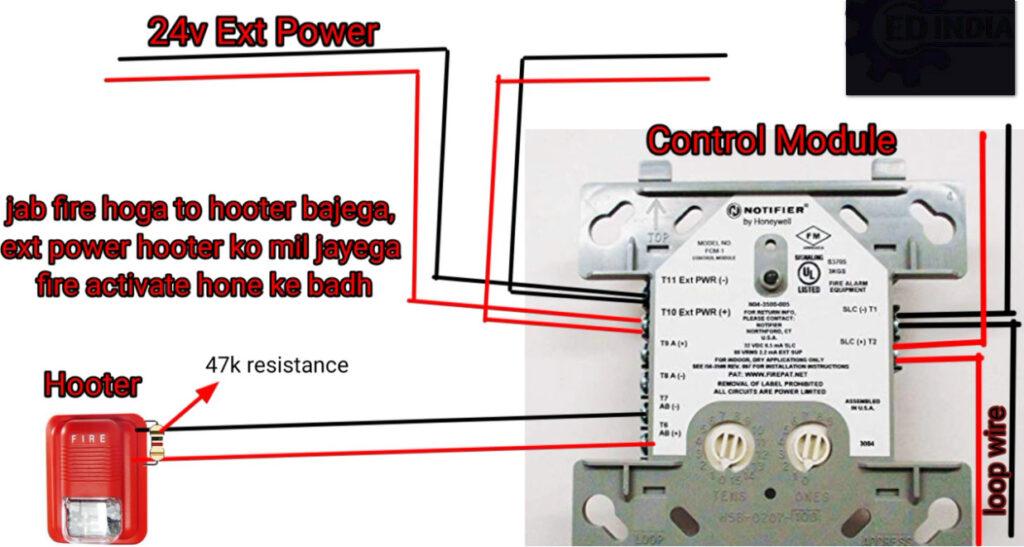
5. Sounders (Alarm Sounders)
- Function: Emit an audible sound to alert building occupants of a fire emergency.
- Types:
- Electronic Sounders: Produce various tones and volume levels.
- Mechanical Sounders: Produce a specific mechanical sound (e.g., bells or horns).
- In Addressable Systems: These sounders are often linked to specific zones, so they can be activated independently depending on the alarm’s location.
6. Visual Indicators (Strobes or Flashing Lights)
- Function: Provide a visual indication of an alarm, especially for people who are hearing-impaired.
- Types:
- Strobe Lights: Flash at a high intensity to attract attention.
- Location: Installed in areas where people might not hear the alarm sound, such as in noisy environments or for individuals with hearing impairments.
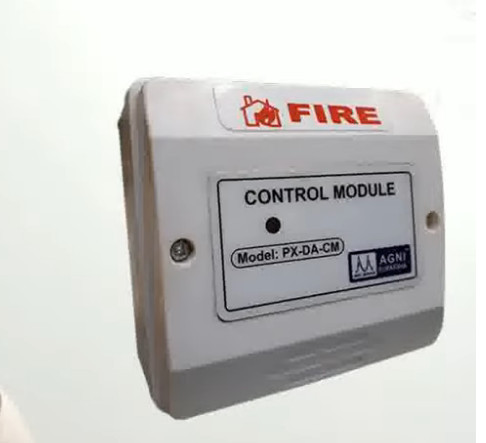
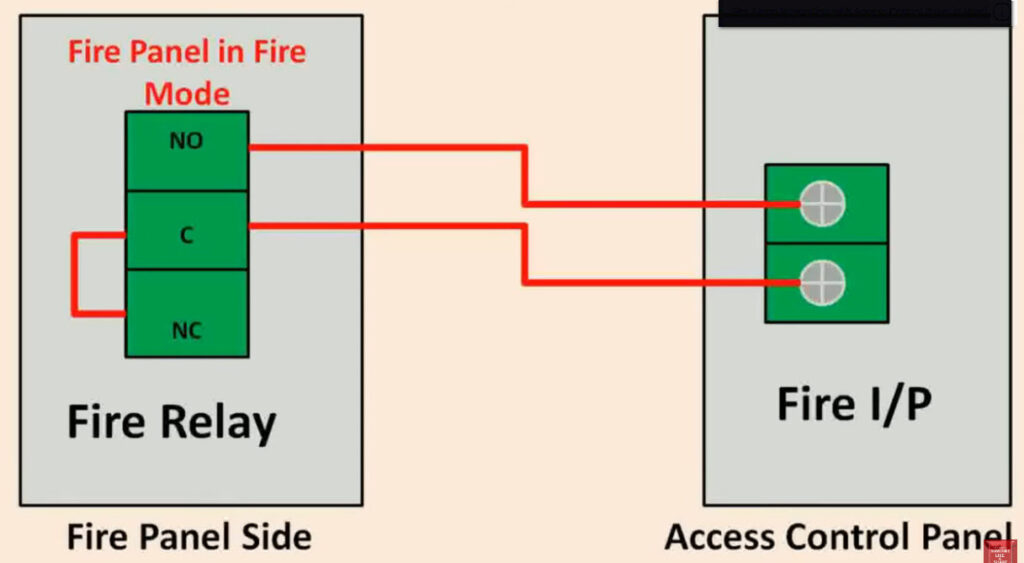
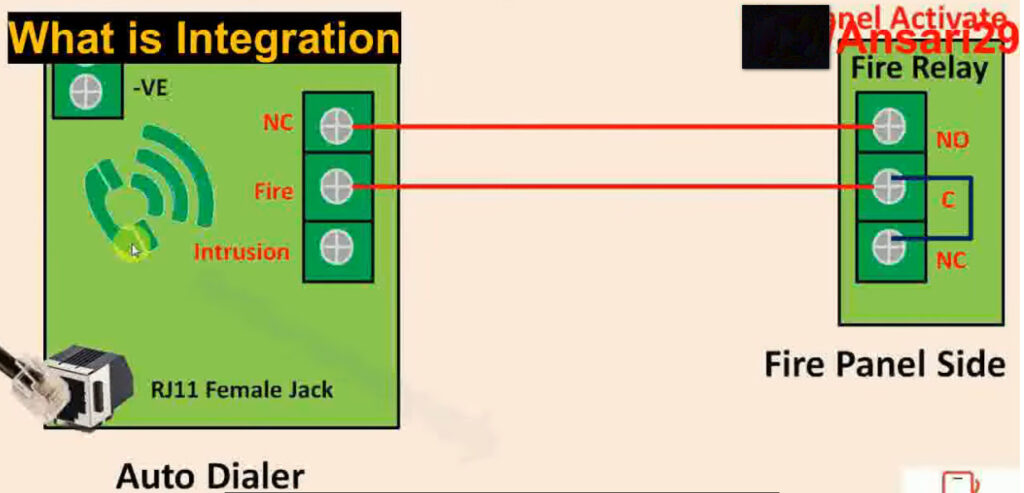
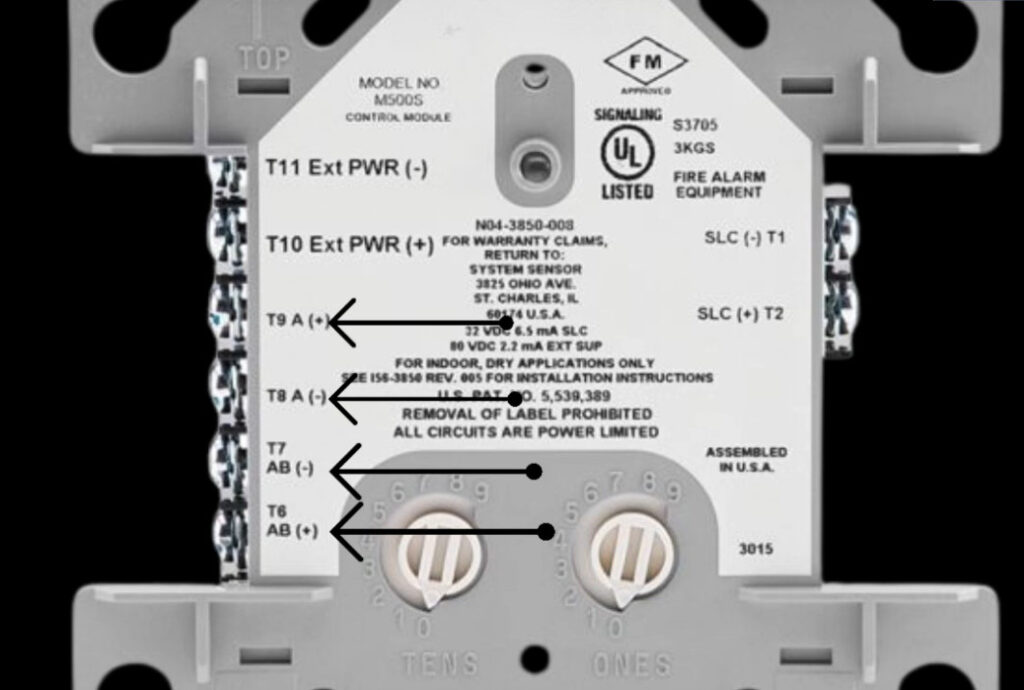
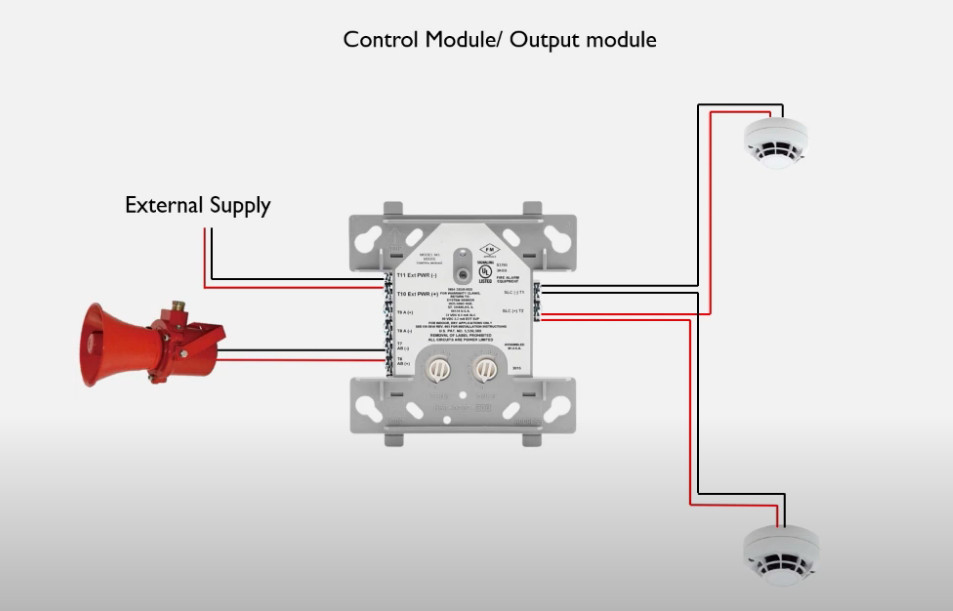
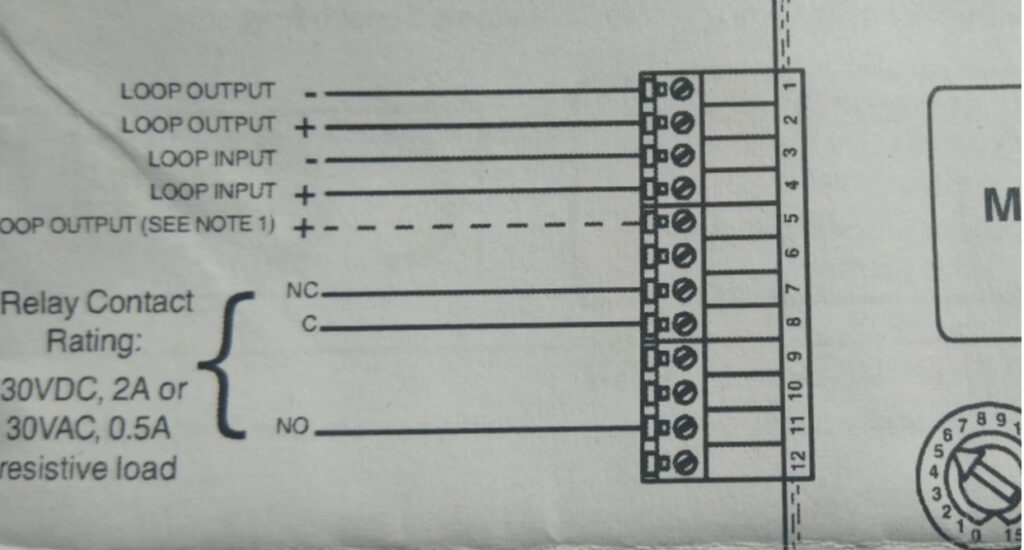
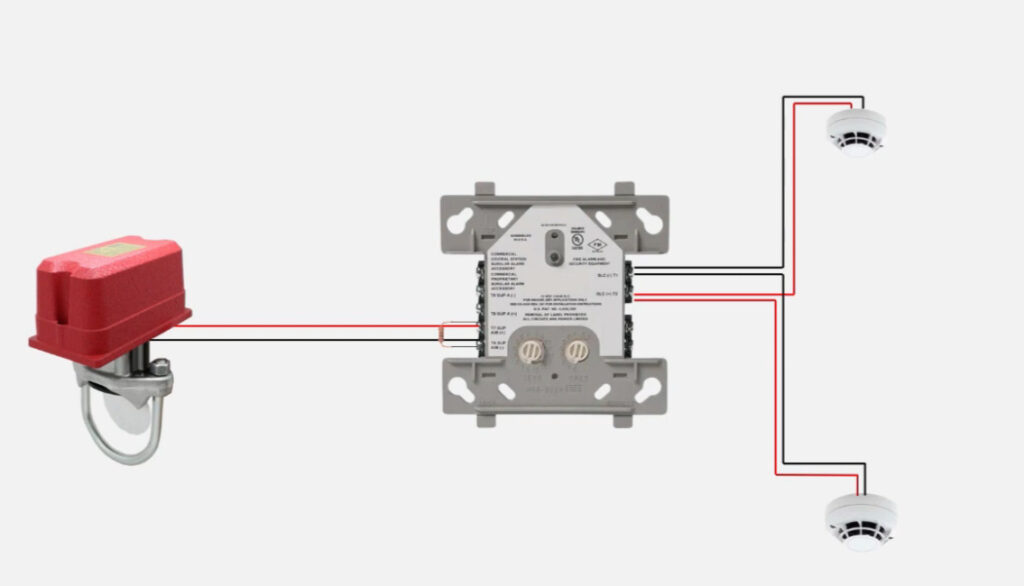
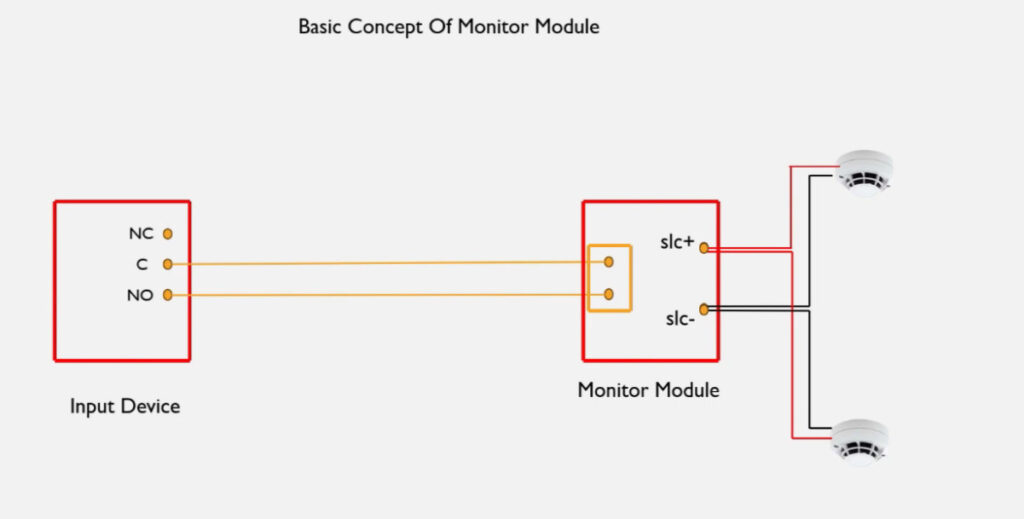
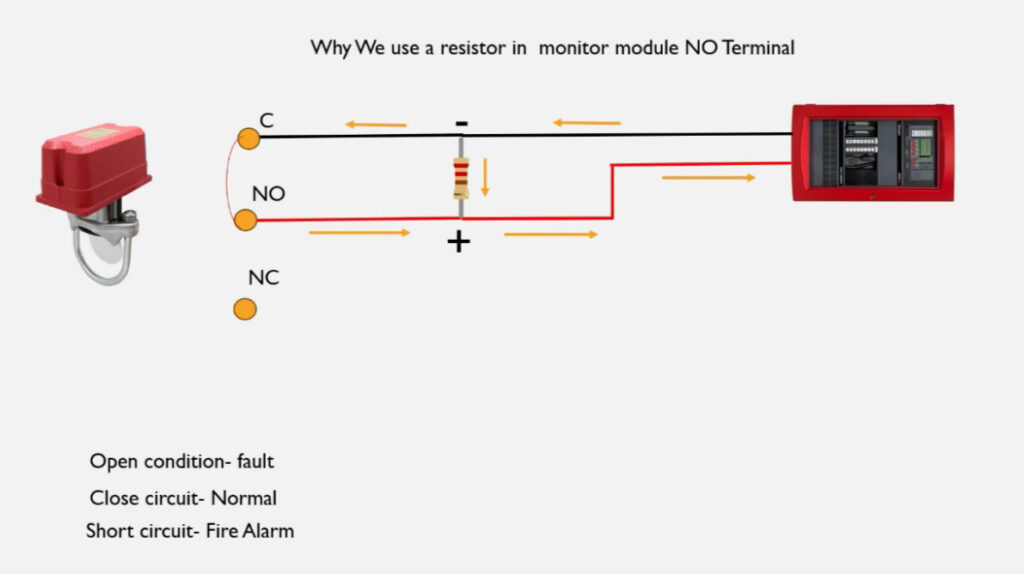
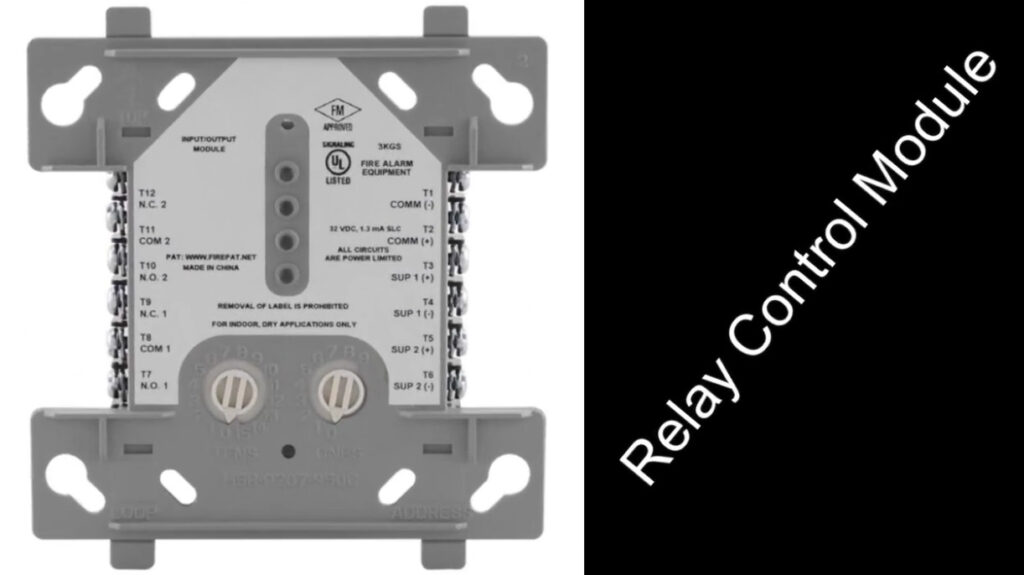
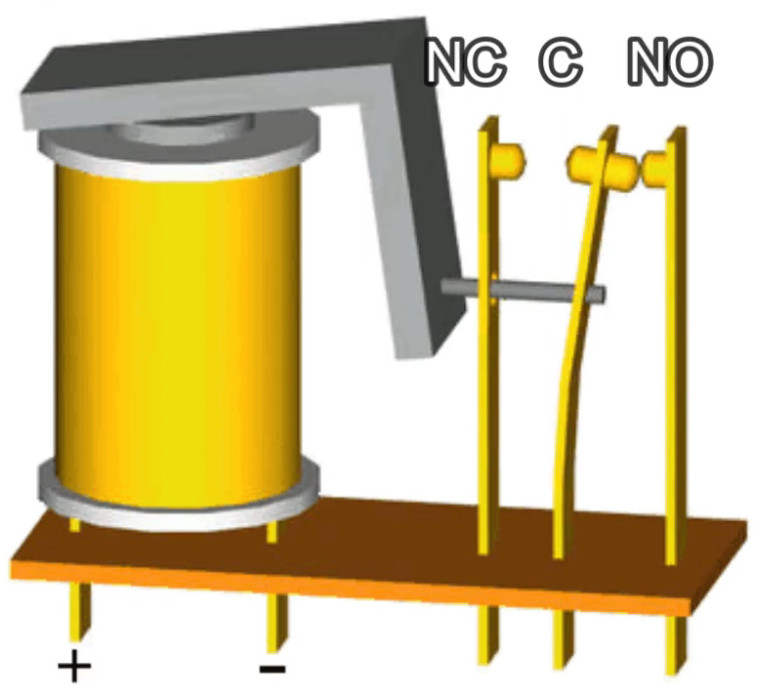
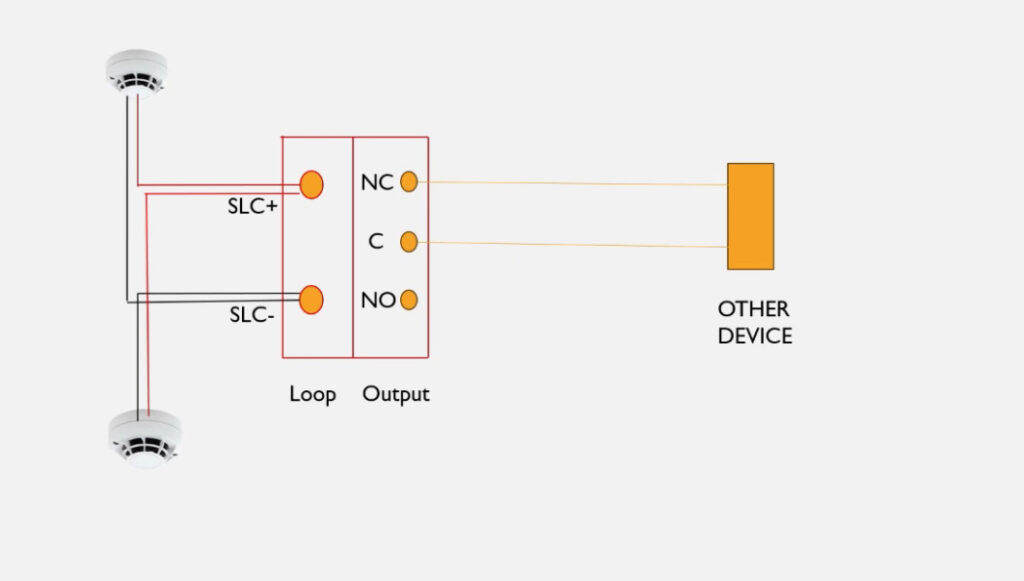
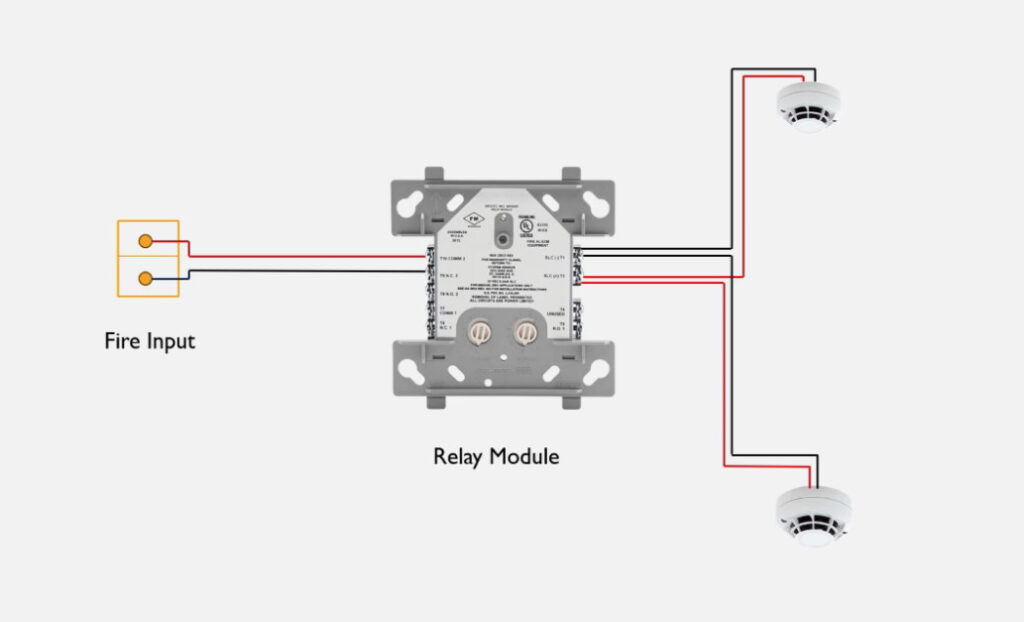
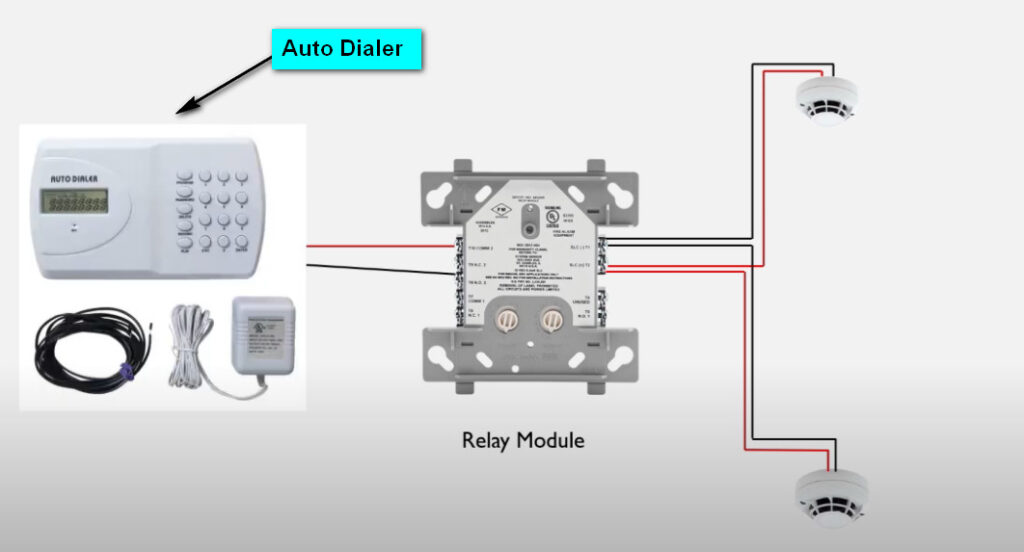
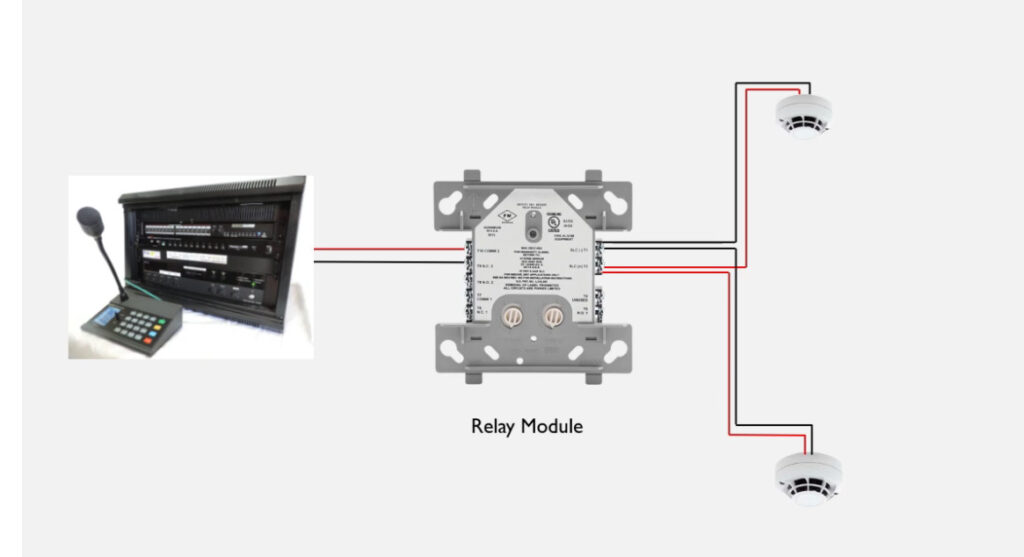
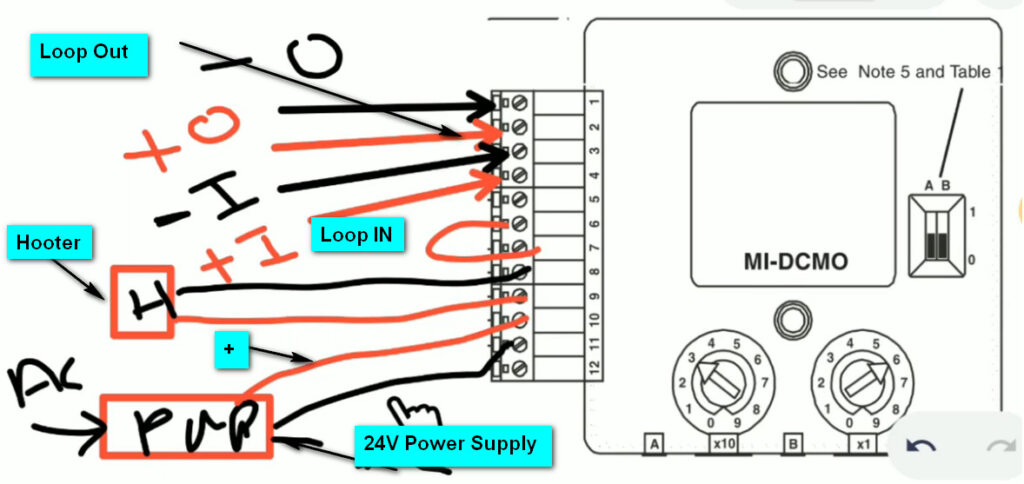
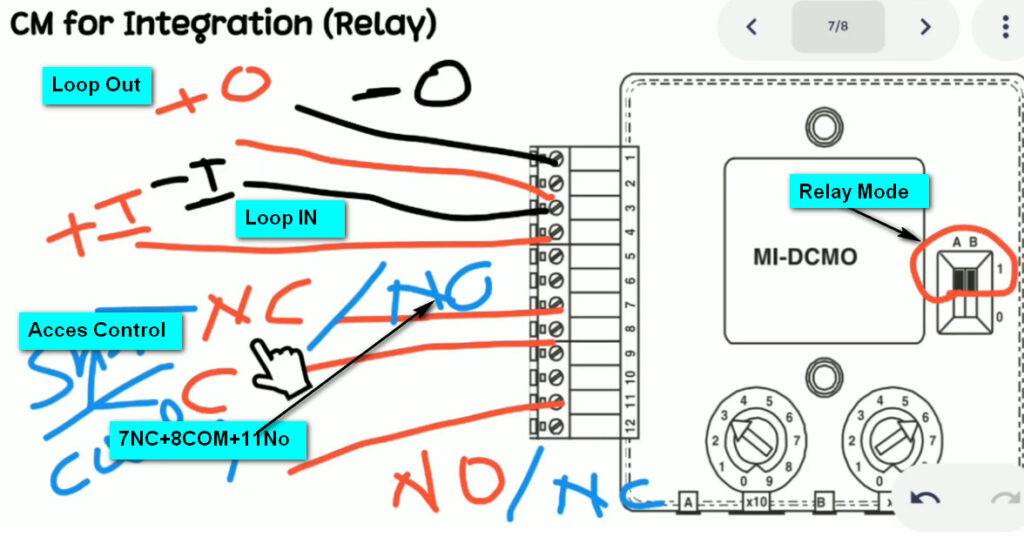
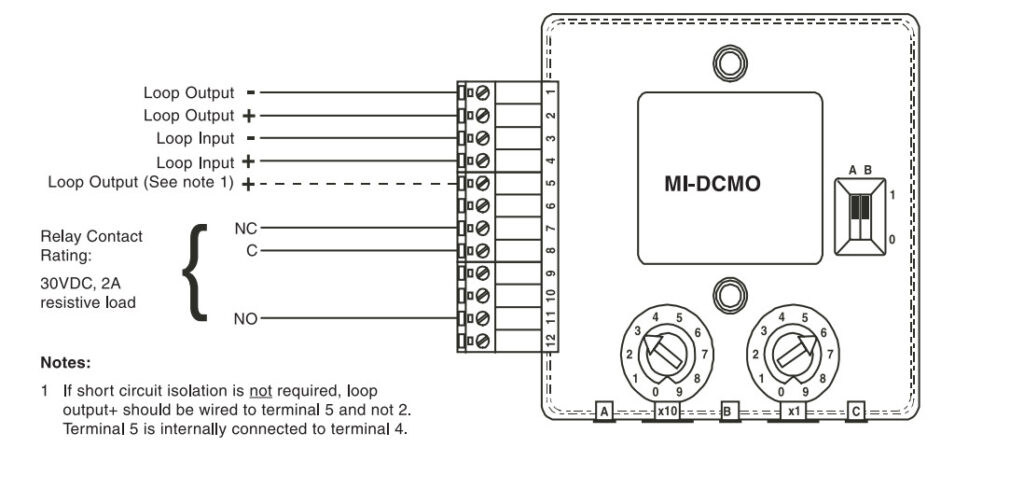
7. Relay Modules
- Function: Interface between the fire alarm system and external systems (e.g., door releases, smoke vents, HVAC systems).
- Operation: Relay modules can activate or deactivate external devices (e.g., releasing fire doors, activating fire dampers, turning off fans).
- Types:
- Normally Open (NO): Closes the circuit when triggered.
- Normally Closed (NC): Opens the circuit when triggered.
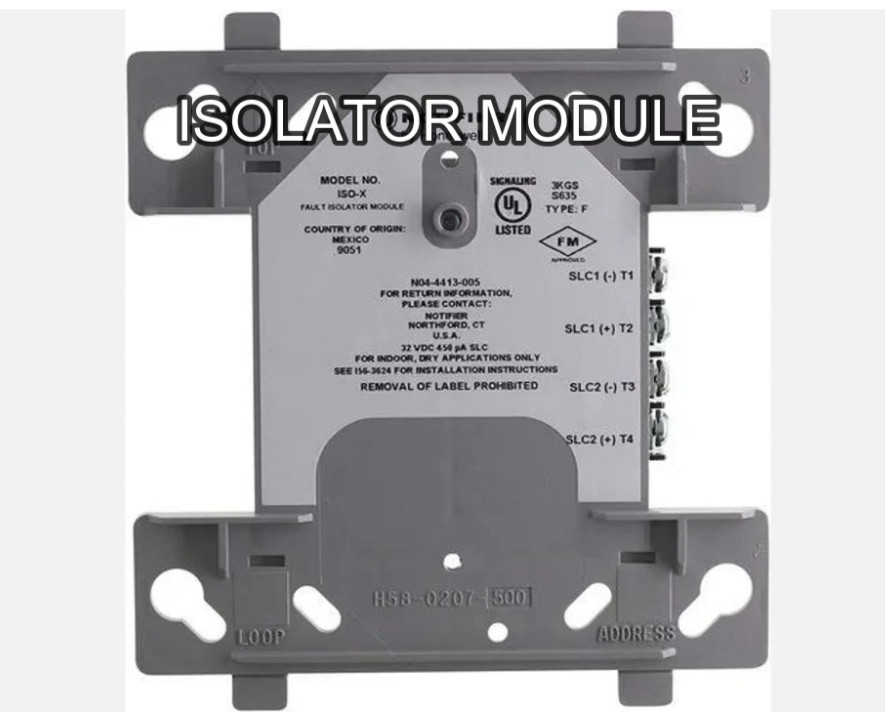
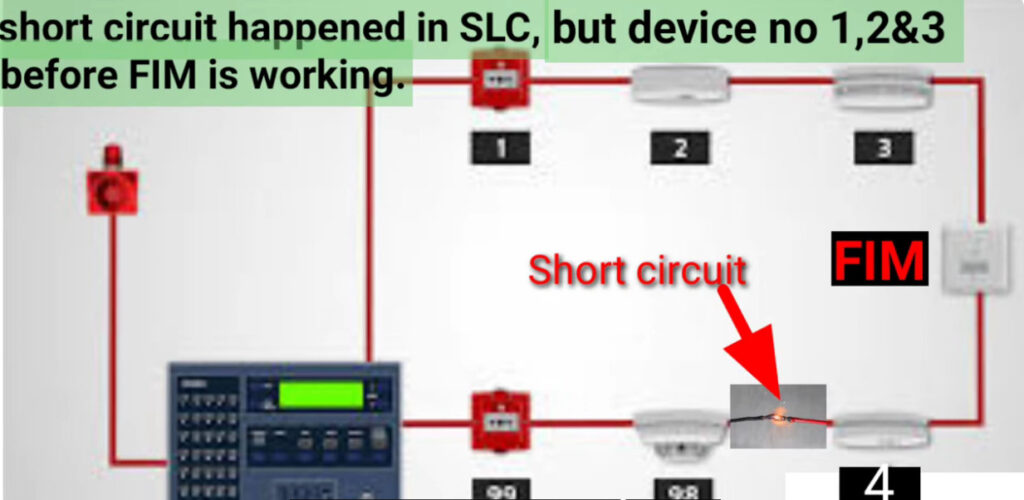
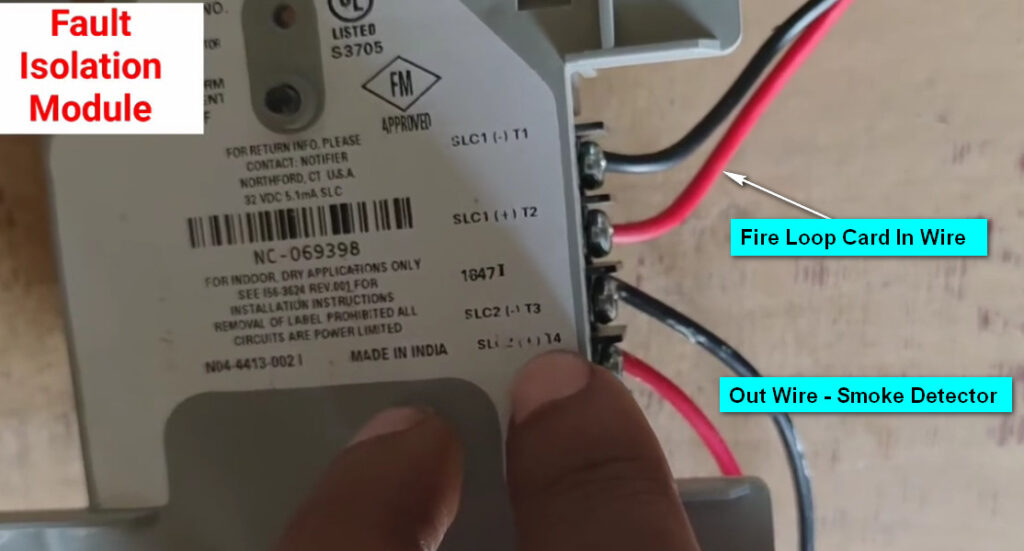
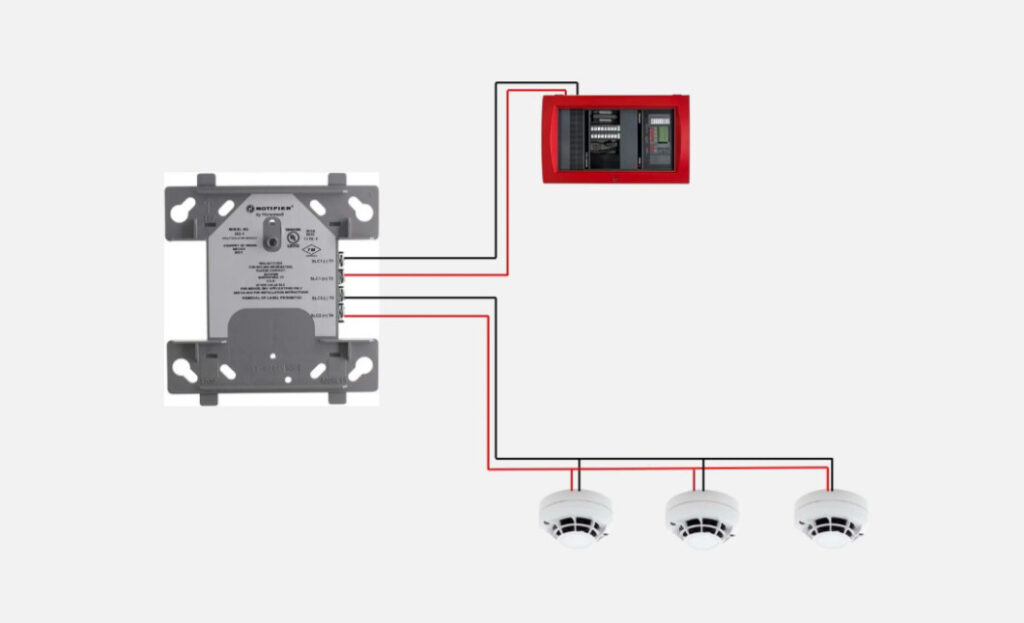
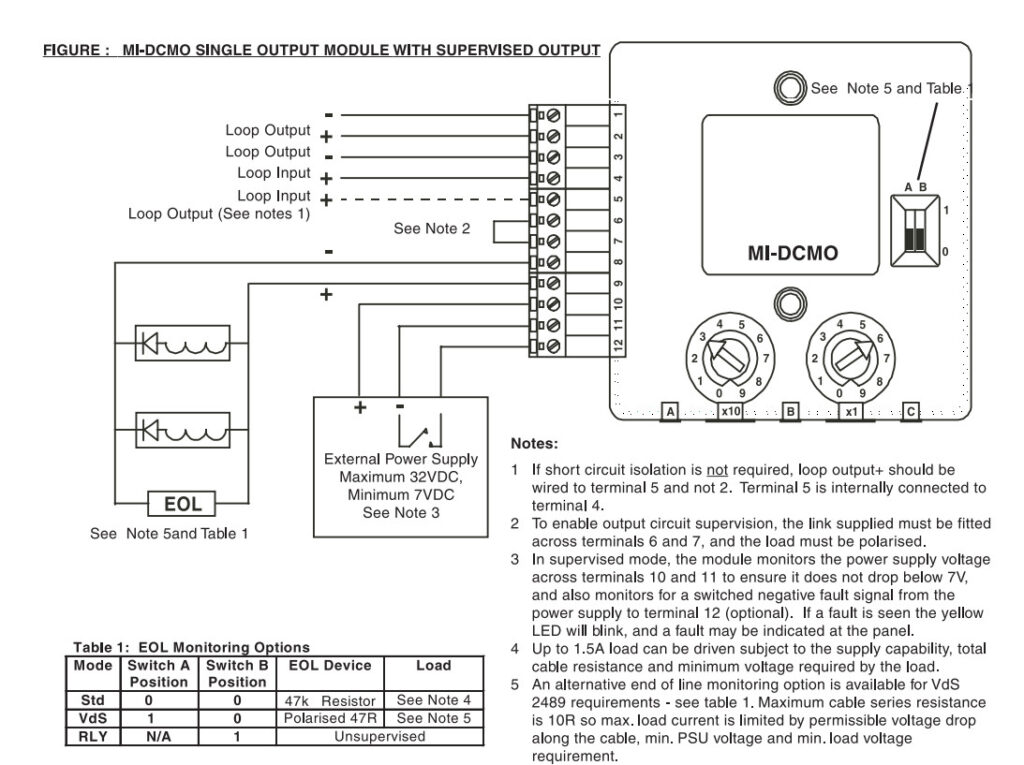
8. Isolator Modules
- Function: Prevent faults from affecting the entire fire alarm system.
- Use: These modules detect faults such as short circuits or open circuits on the loop and isolate the affected section to maintain system integrity.
- Application: Particularly useful in large installations, where isolating faulty areas prevents the rest of the system from going offline.
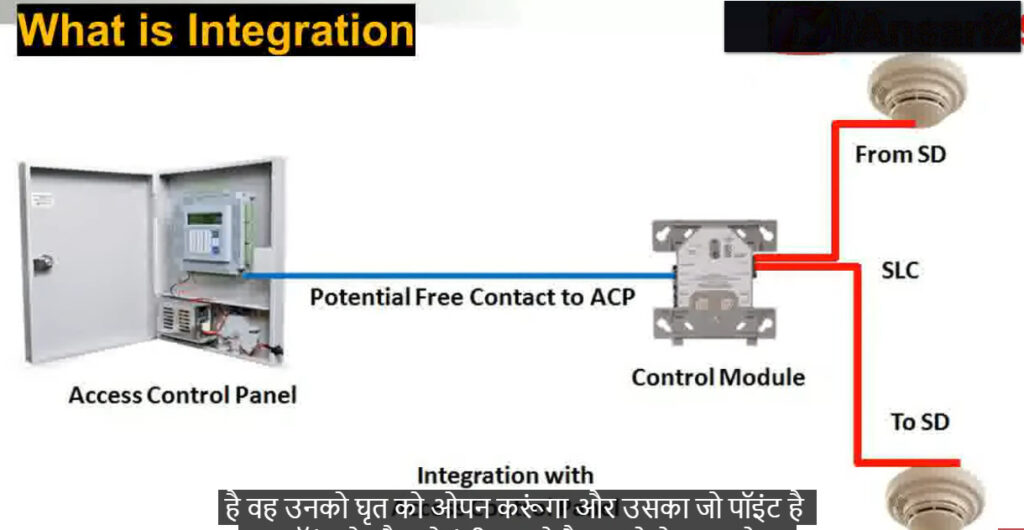
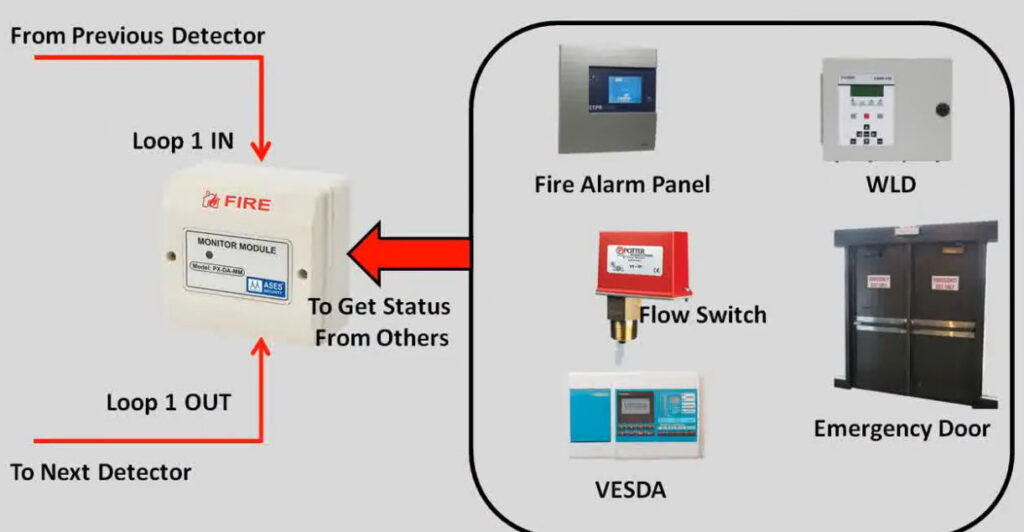
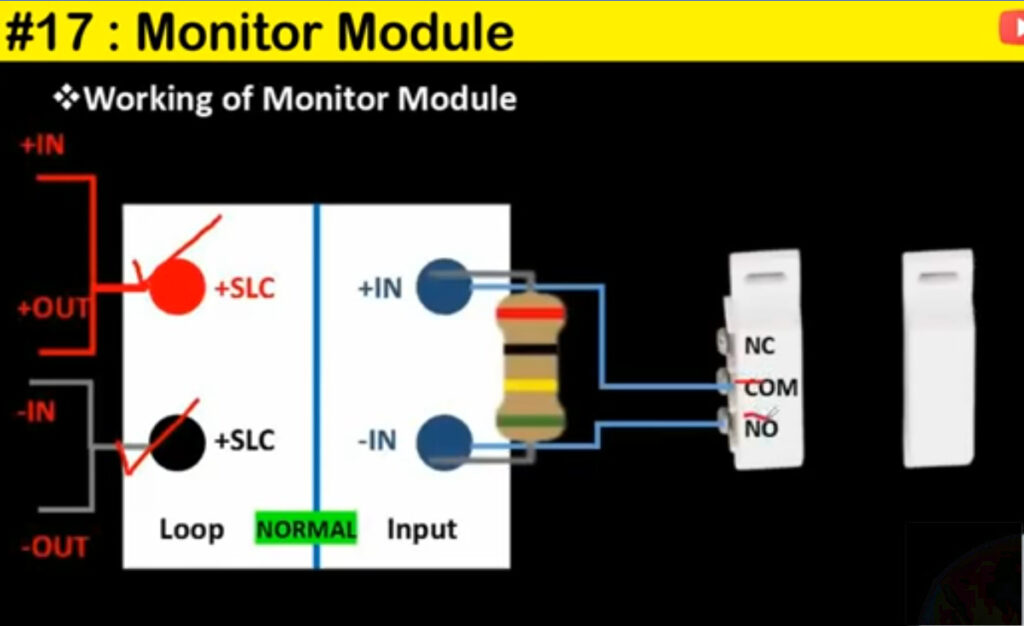
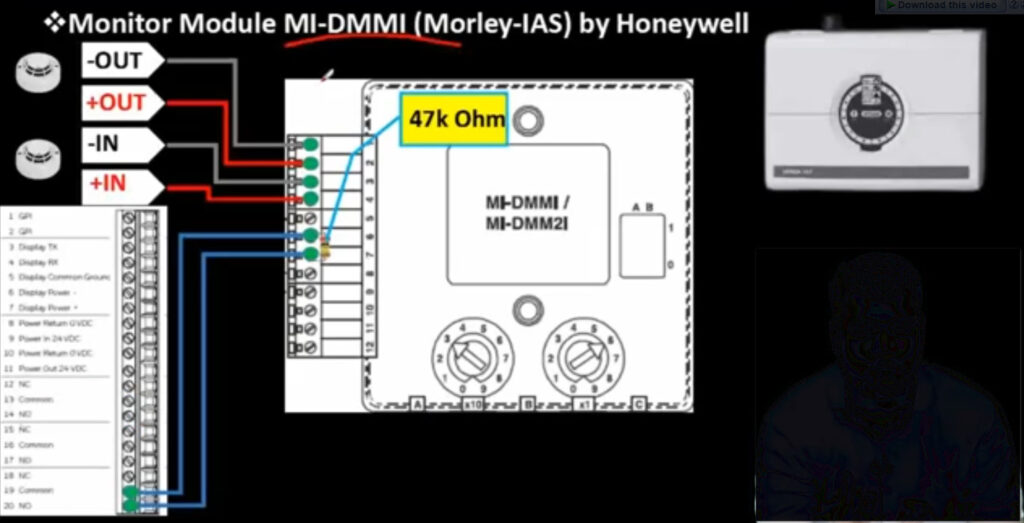
9. Input/Output (I/O) Modules
- Function: Allow the fire alarm system to communicate with other systems and devices.
- Types:
- Input Modules: Receive signals from other systems (e.g., security systems, HVAC).
- Output Modules: Send signals to activate external devices (e.g., activating sprinklers, emergency lighting).
- Application: Used to interface with non-fire-related systems, improving overall safety and response capabilities.
10. Sounder Controller Modules
- Function: Manage the operation of sounders within a system.
- Use: Adjusts volume, tone, and timing for the sounders in various zones to ensure effective communication of the alarm.
11. Door Release Modules
- Function: Controls the operation of electromagnetic door locks, ensuring fire doors close during an emergency to prevent the spread of smoke and flames.
- Operation: In the event of a fire alarm, the door release module de-energizes the magnetic locks, allowing doors to close automatically.
12. Gas Detection Modules
- Function: Detect the presence of specific gases (e.g., CO, methane, LPG) that may indicate a potential fire or explosion hazard.
- Application: These modules are used in environments like kitchens, industrial settings, or areas where gas-related fires are a concern.
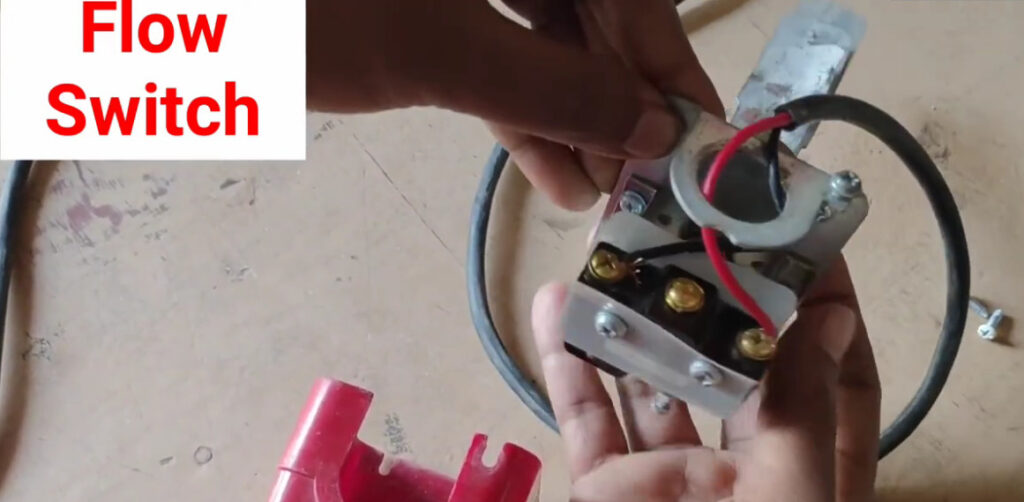
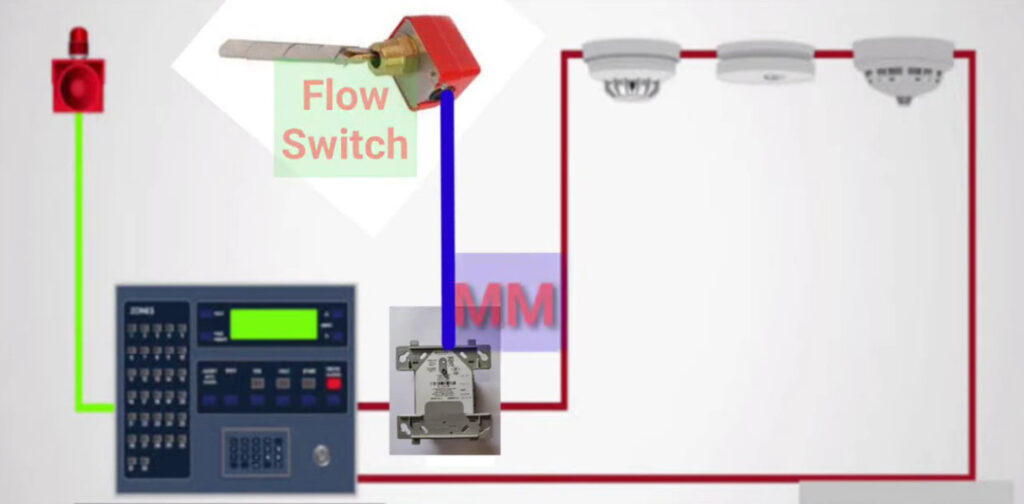
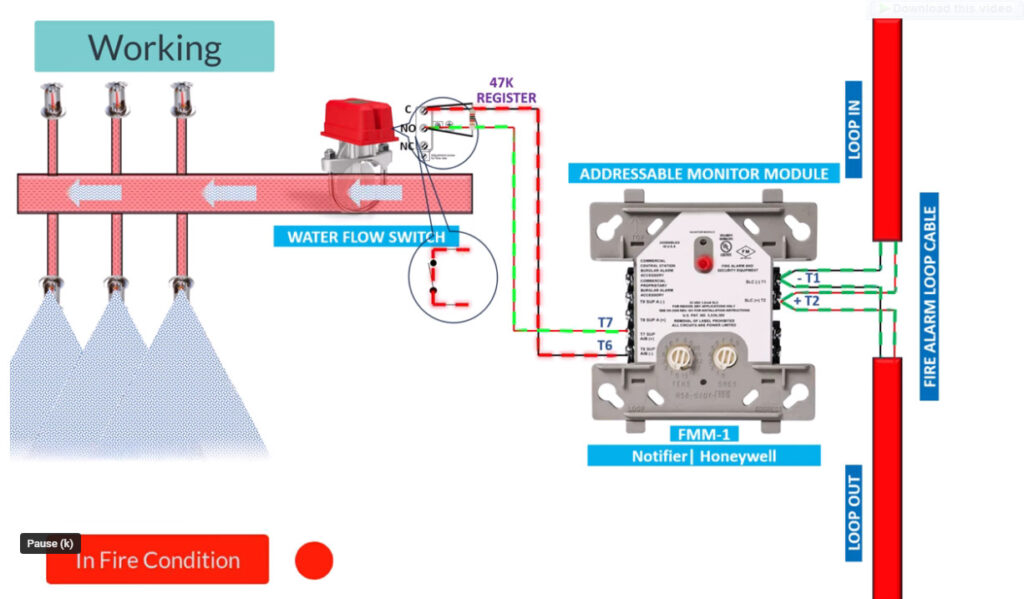
13. Water Flow Monitoring Modules
- Function: Monitors the flow of water in fire suppression systems (such as sprinklers).
- Application: Detects when a sprinkler system has been activated due to fire and provides confirmation to the fire alarm panel.
- Use: Typically paired with fire sprinklers or other automatic suppression systems.
14. Fire Door Monitoring Modules
- Function: Ensures that fire doors are properly closed and remain operational during a fire emergency.
- Application: Used to control fire doors, ensuring they close automatically in case of fire or alarm activation.
15. Air Sampling Smoke Detectors (ASD)
- Function: These detectors actively sample the air in their environment for smoke particles and can detect fire at an earlier stage than conventional smoke detectors.
- Application: Ideal for environments where early detection is critical, such as data centers, server rooms, and clean rooms.
16. Aspirating Smoke Detection (ASD) System
- Function: Similar to air sampling detectors, but uses a network of pipes to draw air into a detector. The system continuously analyzes the air for signs of smoke or particulate matter.
- Application: Used in high-value asset protection areas like server rooms, museums, or industrial settings.
Summary of Fire Alarm Modules:
| Module Type | Function | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Control Panel | Central hub that monitors all fire detection devices | All fire alarm systems |
| Smoke Detectors | Detects the presence of smoke | Offices, residential buildings, industrial facilities |
| Heat Detectors | Detects temperature rise or fixed threshold temperatures | Kitchens, industrial areas, warehouses |
| Manual Call Points (MCP) | Allows manual activation of the alarm system | Hallways, exits, public spaces |
| Sounders | Emits an audible alarm for alerting occupants | Throughout buildings to signal alarm |
| Visual Indicators | Flashing lights to signal alarm | Areas for people with hearing impairments, noisy areas |
| Relay Modules | Controls external systems like doors and HVAC | Smoke control, fan control, emergency doors |
| Isolator Modules | Isolates faulty system areas to maintain operation | Large installations with multiple zones |
| I/O Modules | Interfaces with other systems and devices | Integration with security, HVAC, or building management |
| Sounder Controller Modules | Controls sounders’ operation | Systems with multiple sounder devices |
| Door Release Modules | Manages fire door closures during alarm activation | Fire-rated doors in commercial or residential buildings |
| Gas Detection Modules | Detects gases like CO or methane | Kitchens, industrial spaces, laboratories |
| Water Flow Monitoring | Monitors sprinkler system activation | Sprinkler systems in large commercial buildings |
| Fire Door Monitoring | Monitors fire door status | Emergency exits, fire-rated areas |
| Air Sampling Smoke Detectors (ASD) | Actively samples air for early smoke detection | Data centers, museums, clean rooms |
| Aspirating Smoke Detection | Continuously samples air for smoke particles | Critical infrastructure, high-risk areas |
These modules work together to provide a complete fire detection and alarm system that offers enhanced safety, communication, and response capabilities