- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B


Security
Management
QoS
Advanced Features
Standards and functions of ports
+ IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T Ethernet (copper twisted-pair)
+ IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet (copper twisted-pair)
+ IEEE 802.3ab 1000BASE-T Gigabit Ethernet (copper twisted-pair)
+ Auto-ANSI / IEEE 802.3
+ IEEE 802.3x Flow Control
Number of Ports
24-port 10/100/1000 Mbit / s, 4 SFP ports
Network Cables
+ UTP category. 6, 5, 5e (max. 100 m)
+ EIA / TIA-568 100 ohm STP (max. 100 m)
Full / half duplex
+ Full / half duplex speed for 10 / 100Mbit / s
+ Full duplex for Gigabit speed
Interfaces transmission medium
Interfaces with support MDI / MDI-X
Performance
Bandwidth switch
58 Gbit / s
Transmission Method
Store-and-forward
MAC-address table
16,000 records
Study of MAC-addresses
+ Up to 256 static entries MAC-addresses
+ Enable / disable MAC-address avtoizucheniya
Maximum speed forwarding 64-byte
41.7 Mpps
Packet buffer memory
1 MB on the device
Software
Layer 2 functions
+ Table MAC-addresses: 16,000 records
+ Flow Control
– 802.3x Flow Control
– Prevent blocking HOL
+ Support for Jumbo-frames up to 10,000 bytes
+ IGMP Snooping
– IGMP v1 / v2 Snooping
– Supports up to 256 IGMP-groups
– Supports up to 64 static multicast groups
– IGMP on VLAN
– Supports IGMP Snooping Querier
+ Spanning Tree Protocol
– 802.1D STP
– 802.1w RSTP
+ Loopback Detection
+ 802.3ad Link Aggregation: max. the number of groups on the device 14/8 ports per group
+ Port Mirroring
– One-to-One
– Many-to-One
– Supports Mirroring for Tx / Rx / Both
+ Cable Diagnostics
+ Customizable interface MDI / MDIX
+ Multicast Filtering
– Redirect all unregistered groups
– Filtering of unregistered groups
+ LLDP, LLDP-MED
VLAN
+ 802.1Q
+ VLAN Group
– Max. 256 static VLAN groups
– Max. VID 4094
+ Management VLAN
+ Asymmetric VLAN
+ Auto Voice VLAN
– Max. 10 user defined OUI
– Max. 8 by default defined OUI
+ Auto Surveillance VLAN
QoS (Quality of Service)
+ 802.1p Quality of Service
+ 4 queues per port
+ Processing Queue
– Strict
– Weighted Round Robin (WRR)
+ CoS based
– 802.1p Priority Queues
– DSCP
– TOS1
– Non-TCP / UDP port 1
– Class 1 IPv6 traffic
+ Bandwidth Management
– Based on the port (incoming / outgoing, in increments of up to 64 Kb / s)
Access Control Lists (ACL)
+ 50 profiles (maximum)
+ Max. 240 Access Rules
+ ACL on the basis of
– MAC-addresses
– IPv4-address (ICMP / IGMP / TCP / UDP)
– VLAN ID
– 802.1p priority
– DSCP
– Class 1 IPv6 traffic
+ Actions ACL
– Allow
– Prohibit
Security
+ Port Security
– Supports up to 64 MAC-addresses per port
+ Protection against broadcast / multicast / unicast storm
+ Static MAC-address
+ D-Link Safeguard Engine
+ Function DHCP Server Screening
+ Preventing ARP Spoofing Attacks
– Max. 64 entries
+ SSL
– Support v1 / v2 / v3
– Support IPv4 / IPv6 1
+ Traffic Segmentation
+ Intelligent binding
– Detection of connected devices and their binding
– Inspection of ARP-packets: 512 entries
– Inspection of IP-packets: 128 entries
– Support for DHCP Snooping



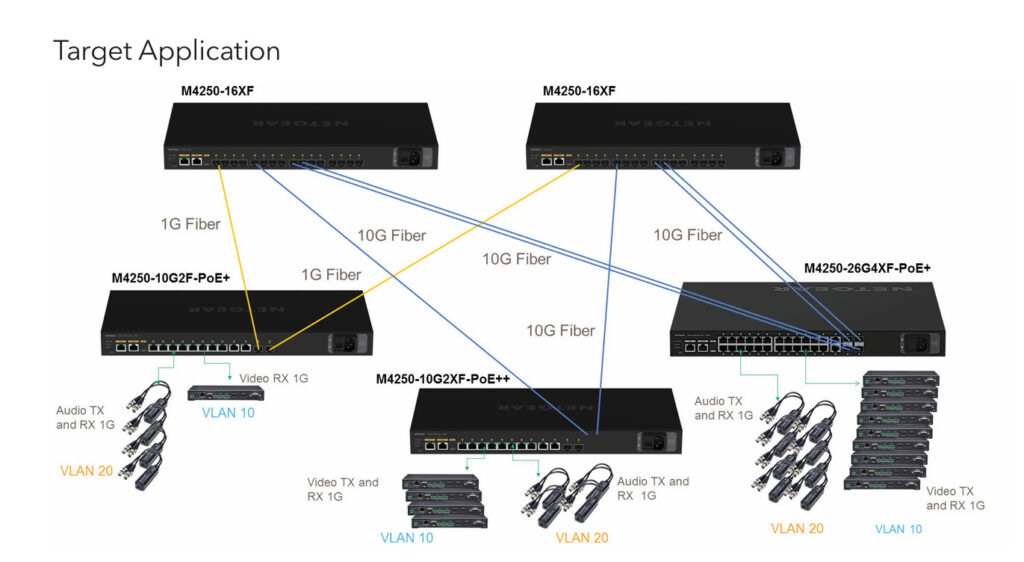
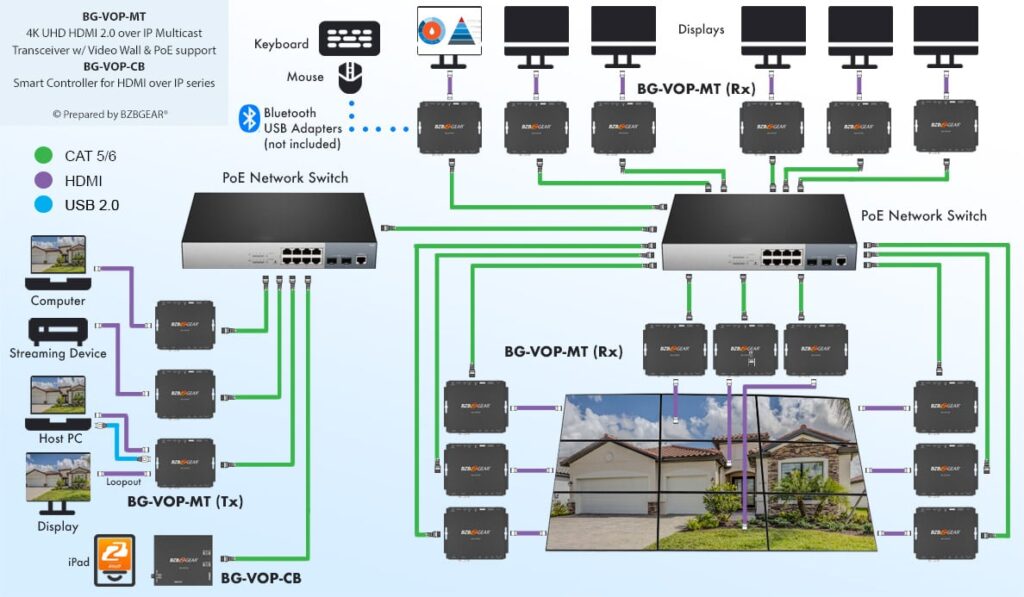
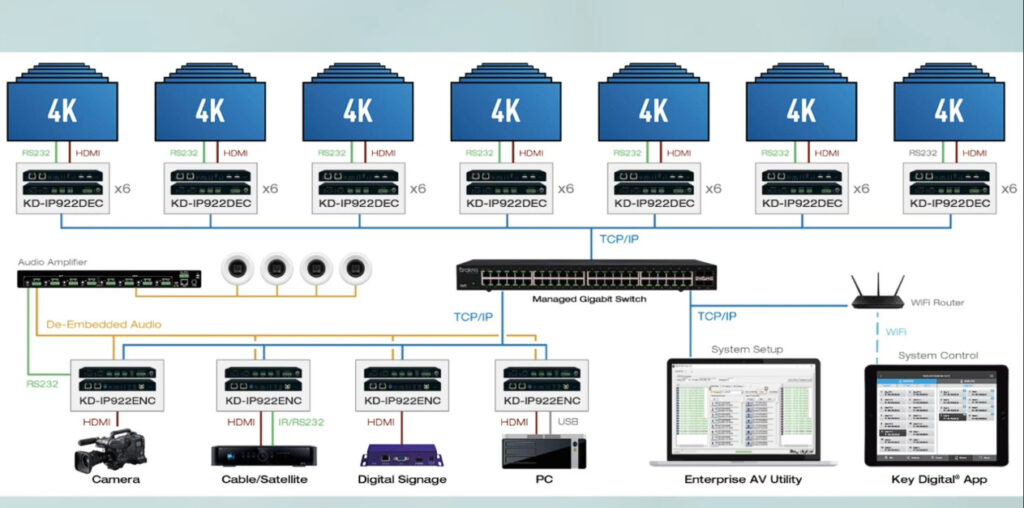


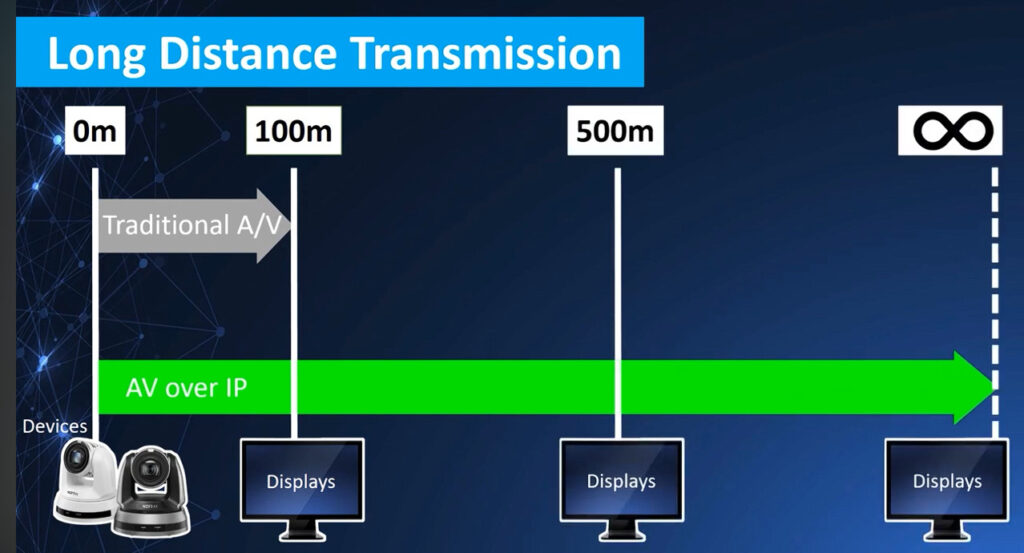
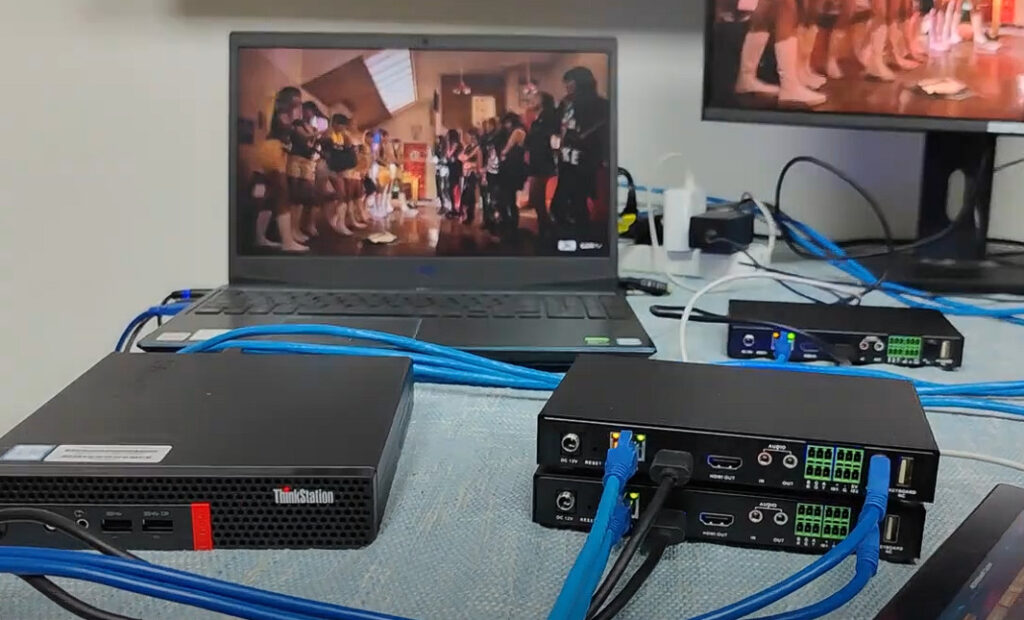
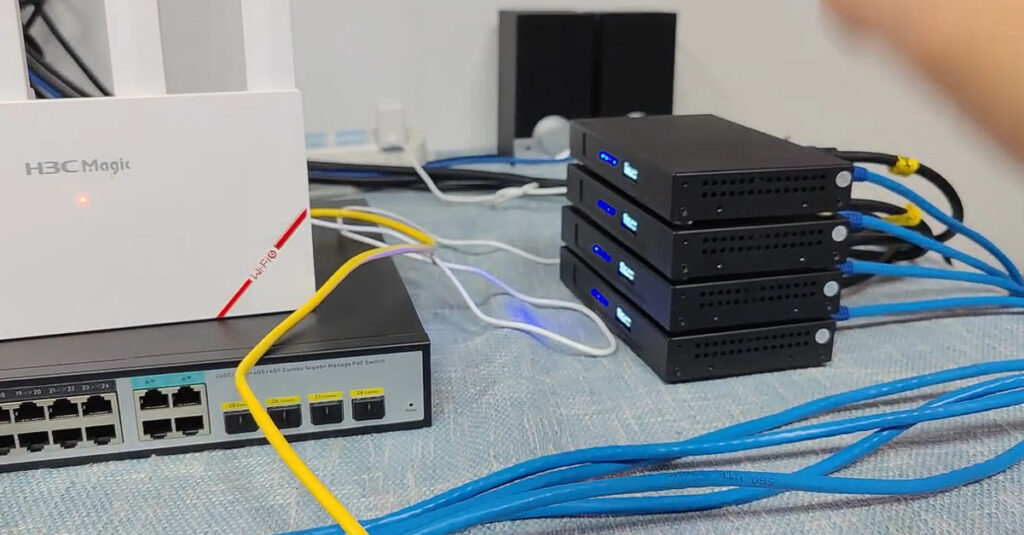
AV over IP stands for Audio-Visual over Internet Protocol. It’s a method of transmitting audio, video, and control signals over standard network infrastructure like Ethernet (instead of traditional AV cabling like HDMI or SDI).
Key Concepts:
AV: Audio and video signals, like what you’d use in a conference room, digital signage system, or broadcast setup.
IP: Internet Protocol, the same technology that powers computer networking and the internet.
How It Works:
Instead of sending AV signals through dedicated AV cables, the content is converted into data packets, sent over an IP network (LAN, WAN, or the internet), and then decoded back into audio/video at the receiving end.
Benefits:
Scalability: Easier to add or move displays and sources.
Flexibility: Can route signals to any device on the network.
Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for expensive proprietary switchers.
Longer Distances: Unlike HDMI or VGA, which degrade over long runs, IP can transmit over much longer distances with no signal loss.
Common Use Cases:
Digital signage in airports and malls
Corporate AV systems
Campus-wide broadcasting in schools
Live event production





