- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
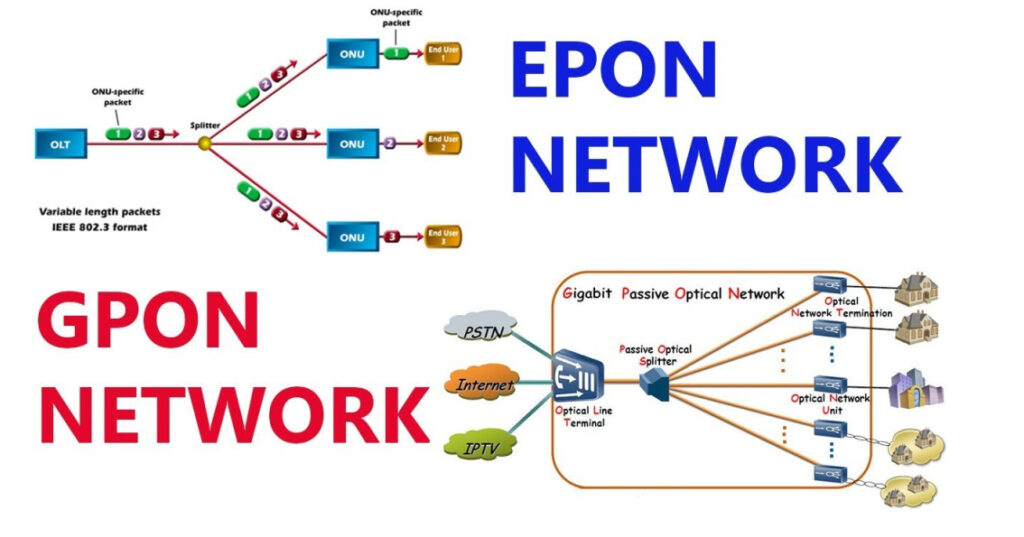
EPON is a type of Passive Optical Network (PON) that uses Ethernet as the communication protocol over optical fiber. It is based on the IEEE 802.3ah standard and is commonly used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) for delivering broadband services.
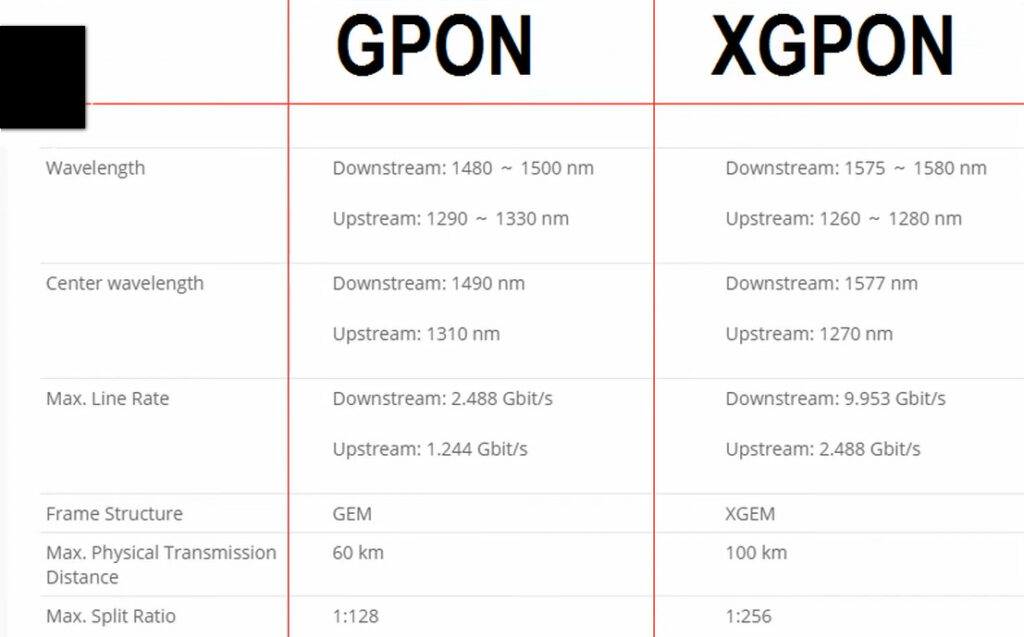
GPON is another type of Passive Optical Network that uses a higher-speed transmission standard than EPON. It is defined by the ITU-T G.984 standard and is widely used for FTTH and FTTP (fiber-to-the-premises) deployments.
XPON is a more general term that refers to any type of PON technology that can support multi-gigabit speeds, including both EPON and GPON, and sometimes even 10G-PON (10 Gigabit Passive Optical Network). In essence, XPON can refer to various versions of PON technologies that provide gigabit (or higher) data rates.
XPON is used in the context of 10G PON standards and solutions, which include both 10G-EPON and 10G-GPON technologies. XPON is essentially a marketing term used to denote systems that support the following:
In some cases, XPON may also be used as a generic term for systems that support both EPON and GPON, allowing network providers to offer flexibility in deployment. The key feature of XPON technologies is their scalability and ability to provide much higher speeds (10 Gbps and beyond) as demand for bandwidth grows.
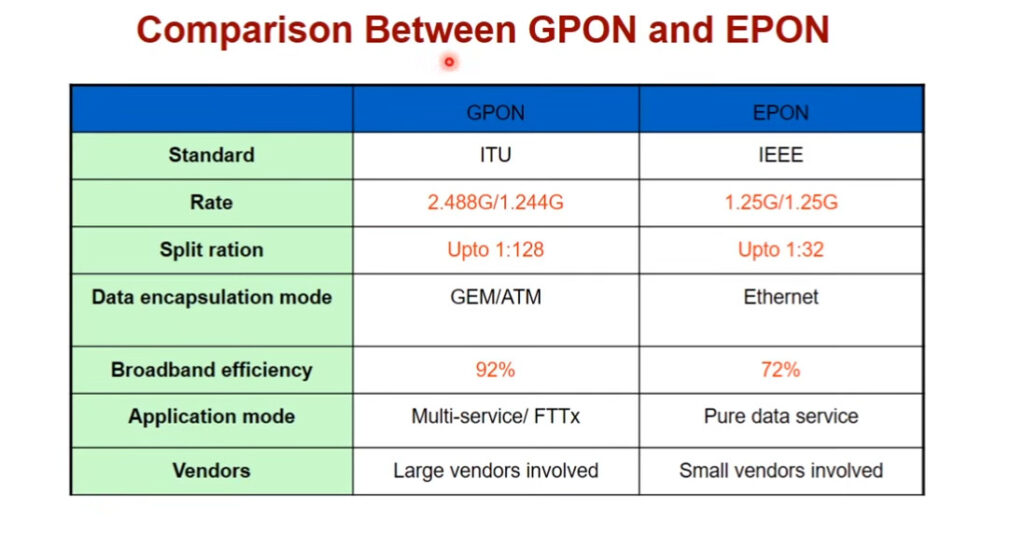
| Feature | EPON | GPON |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | IEEE 802.3ah (Ethernet) | ITU-T G.984 (Gigabit PON) |
| Downstream Speed | Up to 1 Gbps (or 10 Gbps for 10G-EPON) | Up to 2.488 Gbps |
| Upstream Speed | Up to 1 Gbps (or 10 Gbps for 10G-EPON) | Up to 1.244 Gbps |
| Bandwidth Efficiency | Efficient for Ethernet-based networks | More efficient for video, voice, and data |
| Reach | Up to 10 km | Up to 20 km |
| Applications | Internet, voice, and video over Ethernet | Internet, IPTV, VoIP, and data services |
| Cost | Typically lower equipment costs | Higher equipment costs due to more complex protocol |
| Compatibility | Easier integration with Ethernet networks | Requires more specialized equipment and management |
Each of these technologies has its own strengths, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs of the service provider and the end-user, such as the desired bandwidth, distance, and the complexity of the network deployment.
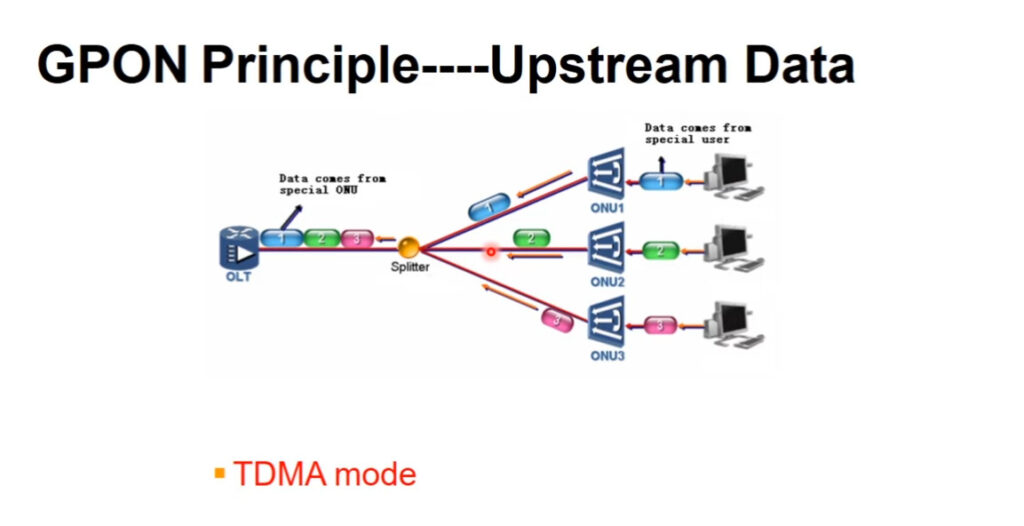
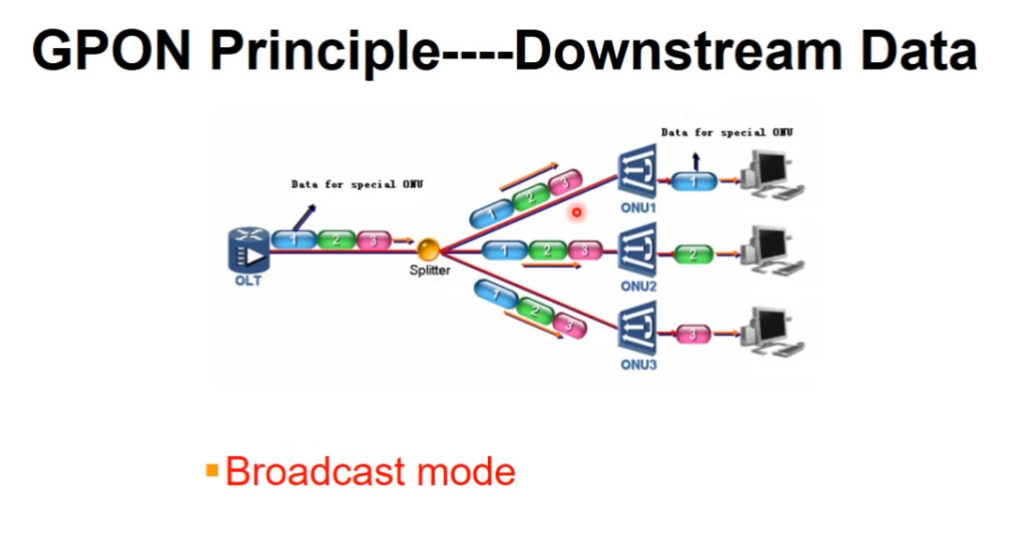
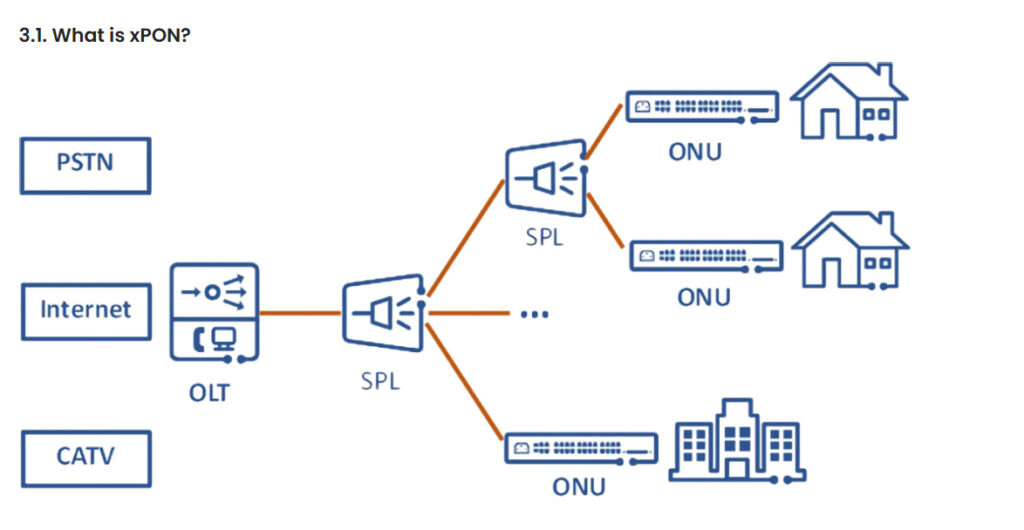
PON technology is vital for delivering high-speed broadband access. It has emerged as a crucial player in this realm. Data signals are transmitted from one point to multiple endpoints. Optical fibers are used for this operation. The PON ecosystem includes the Optical Line Terminal (OLT). The Optical Network Unit (ONU) is also a key component. Another key component is the Optical Distribution Network (ODN). In the opening chapter, we will explore the importance of PON technology. We will also introduce you to the main players in the PON arena: GPON and EPON.
The digital age is upon us, and the need for faster, more reliable internet is higher than ever. PONs have met the challenge. They offer a revolutionary solution for high-speed broadband services. PON technology uses optical fibers. Optical fibers can transmit lots of data with little signal loss.
PONs operate on the principle of sharing a single optical fiber among multiple users. This approach is ingenious. It reduces the need for extensive cabling. As a result, it saves costs and benefits the environment. PONs are attractive for homes and businesses because they are efficient and scalable.
In the following pages, we will explore the PON landscape. We will delve deeper into GPON, EPON, and the emerging xPON technology. By the end of this journey, you will understand how these technologies differ. You will also know which one is best for your needs.
To understand xPON, we need to first learn about GPON and EPON. These acronyms may sound technical. However, they represent two distinct approaches. These approaches aim to achieve high-speed Internet access over optical fiber networks.
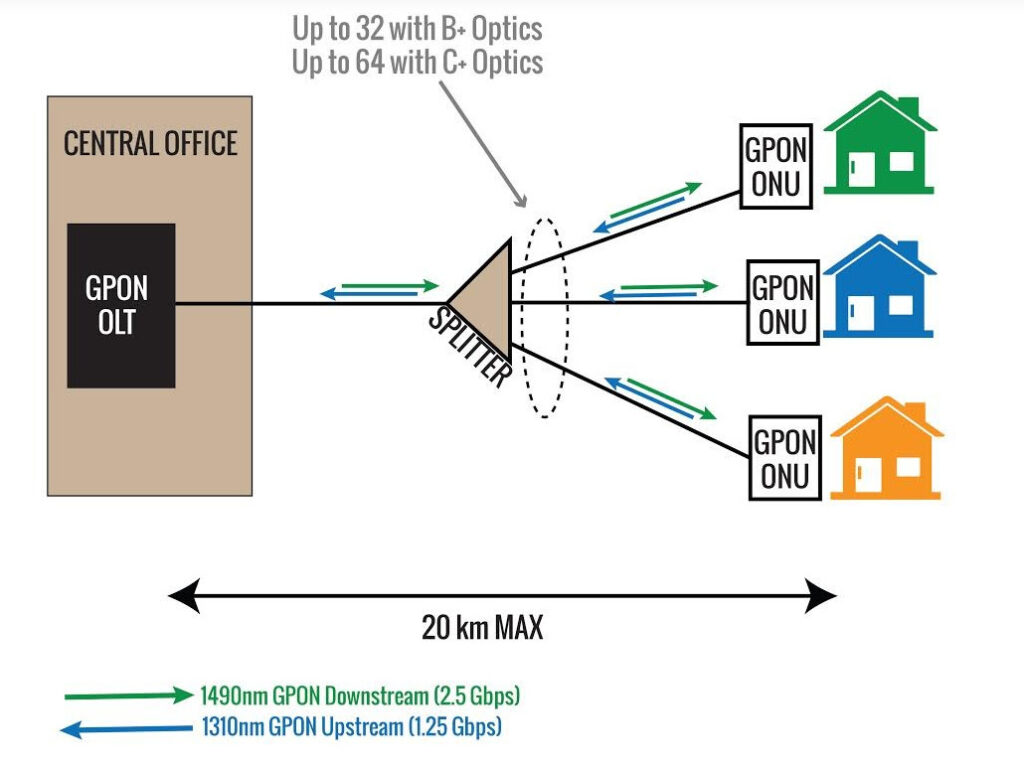
GPON is a network with impressive bandwidth and a wide coverage area. This technology is perfect for achieving full broadband network coverage. It offers maximum downstream and upstream rates of 2.5Gbps and 1.25Gbps. GPON is not only fast, but also supports multiple services. These services include TDM, ATM, Ethernet, and CATV. Its robust Quality of Service (QoS) guarantees a seamless user experience.
EPON follows the IEEE standard for Ethernet and is a cheaper option than GPON. EPON supports transmission rates of 1Gbps and 10Gbps. It provides high-speed connectivity without high costs. The cost-efficiency of this choice is compelling for many applications. It is especially suitable when the budget is not enough.
In the following chapters, we will discuss the world of xPON and how it builds upon the foundations laid by GPON and EPON. Together, we will explore the seamless integration, advantages, and applications of this emerging technology. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey into the realm of next-generation Passive Optical Networks.
Two strong companies have appeared in the telecommunications industry, and each of them has its advantages. Let’s explore GPON and EPON to understand their key features. They have greatly influenced the broadband industry.
GPON is a powerful force in optical networking. It stands tall. Here’s a closer look at its defining characteristics:
– GPON boasts impressive bandwidth capabilities, with downstream rates of up to 2.5Gbps and upstream rates of 1.25Gbps. The large bandwidth allows for fast data transmission. It is perfect for applications that require a lot of bandwidth.
GPON has a standout feature: it supports many services like TDM, ATM, Ethernet, and CATV. This versatility makes it a versatile choice for diverse communication needs.
GPON has extensive coverage capabilities, which makes it preferred by service providers. They aim to reach a large user base. Users in both urban and rural areas can access high-speed internet. This is possible because it covers vast geographical areas.
GPON includes strong Quality of Service features. These ensure a smooth and reliable user experience. It gives priority to important traffic. This ensures that applications such as video conferencing and online gaming function flawlessly. There are no interruptions or delays.
Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON)**, on the other hand, takes a cost-effective approach to optical networking. Let’s explore its defining characteristics:
EPON adheres to the IEEE Ethernet standard, making it a cost-effective solution for broadband access. The option has fast speeds. It also keeps costs low for providers. This makes it attractive to budget-conscious service providers.
EPON offers flexibility in terms of speed, supporting both 1Gbps and 10Gbps transmission rates. This adaptability allows service providers to tailor their network offerings to match user requirements, whether for residential or business use.
EPON’s compatibility with existing Ethernet infrastructure simplifies its integration into networks. Service providers can use their knowledge of Ethernet to easily transition to EPON.
EPON’s scalability makes it suitable for networks of various sizes. Whether you’re serving a small community or a bustling city, EPON can be scaled to meet the growing demands of your user base.
It is crucial to understand the role of Passive Optical Networks. These technologies have led to the development of xPON. We will explore the integration of GPON and EPON. This integration is part of xPON technology. It addresses the evolving needs of the broadband industry. We will discuss this in upcoming chapters.
In this chapter, we embark on a fascinating journey to unveil the innovative world of xPON. xPON, short for “eXtended Passive Optical Network,” is set to transform broadband access. It is ready to revolutionize the way we connect to the internet. It has distinct features and capabilities that will reshape the industry.
Integrating GPON and EPON:
xPON combines GPON and EPON, two robust technologies, into one integration. GPON and EPON are both passive optical networks. xPON accomplishes a remarkable synergy by combining the strengths of two systems. This synergy offers the best of both worlds.
Hardware Compatibility and Standards:
– The hardware compatibility of xPON is a pivotal aspect of its design. It leverages the standards and hardware indicators of GPON networks. This means that xPON hardware is fully capable of supporting multiple services, including TDM, ATM, Ethernet, and CATV, mirroring the capabilities of GPON systems.
Automatic Detection and Switching:
– One of the standout features of xPON is its ability to automatically detect and switch between GPON and EPON modes. When an ONU (Optical Network Unit) attempts to access the network, xPON OLT (Optical Line Terminal) detects the mode and adjusts accordingly. This automatic switching ensures seamless operation and registration, enhancing user experience.
Seamless Mode Switching:
– The ability of xPON to seamlessly switch between GPON and EPON modes is a game-changer. It eliminates the need for manual configuration or hardware replacements when transitioning between these two technologies. This not only simplifies network management but also reduces operational costs.
Unified Network Management:
– xPON offers a unified network management platform that caters to a wide range of business requirements. xPON’s unified approach streamlines network management. It supports ATM, Ethernet, and TDM services, making it efficient and cost-effective.
Supporting Various Business Requirements:
– In the ever-evolving world of telecommunications, diverse businesses have unique requirements. xPON rises to the challenge. It accommodates various business needs. It ensures that your network can adapt to changing demands easily.
When we discuss xPON, you’ll see that this technology connects GPON and EPON. It also offers exciting opportunities for expanding and optimizing networks. Stay tuned as we explore the applications powered by xPON. We will also discuss the products in the upcoming chapters.
In this chapter, we will discuss the practical applications of xPON. We will also explore the cutting-edge products that define the xPON landscape. You’ll learn about meeting market demands and exploring MINGHUO’s xPON ONUs. Gain valuable insights into the real-world impact of this technology.
Meeting Market Demands:
– xPON became popular in telecom because it meets market demands. Consumers and businesses want faster, reliable internet connections. xPON meets these expectations.
Dual-Mode Support:
– One of the standout features of xPON is its support for dual modes, encompassing both GPON and EPON. This dual-mode capability provides flexibility to network operators and end-users, allowing for a seamless transition between different technologies as needs change
| Feature | EPON | GPON | xPON (10G-EPON / 10G-GPON) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | IEEE 802.3ah (Ethernet) | ITU-T G.984 | IEEE 802.3av (10G-EPON), ITU-T G.987 (10G-GPON) |
| Downstream Speed | Up to 1 Gbps (10G-EPON up to 10 Gbps) | Up to 2.488 Gbps (10G-GPON up to 10 Gbps) | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Upstream Speed | Up to 1 Gbps (10G-EPON up to 10 Gbps) | Up to 1.244 Gbps (10G-GPON up to 2.5 Gbps) | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Reach | Up to 10 km | Up to 20 km | Up to 20 km |
| Protocol | Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) | ATM cells (for video, voice, data) | Ethernet (10G-EPON) or ATM cells (10G-GPON) |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher | Higher (due to 10G speeds) |
| Applications | Broadband internet, VoIP, IPTV | Broadband internet, IPTV, VoIP | High-bandwidth services, UHD video, cloud apps |
| Deployment | Typically FTTH, FTTP | Typically FTTH, FTTP | Next-generation FTTH, FTTP, and high-speed urban networks |
We address some of the most frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to xPON, GPON, and EPON technologies. These Frequently Asked Questions provide important information about passive optical networks. They explain the key differences and practical factors that can affect your decision. Use this knowledge to choose the right deployment for your needs.
To make informed decisions about your network, understand xPON, GPON, and EPON. Here, we break down the key distinctions:
– xPON: xPON, or eXtended Passive Optical Network, is an innovative solution that combines the strengths of both GPON and EPON. It offers seamless mode switching, unified network management, and support for various business requirements.
– GPON: GPON, or Gigabit Passive Optical Network, is renowned for its high bandwidth and extensive coverage capabilities. It excels in delivering multiple services and large-scale network access.
– EPON:EPON, or Ethernet Passive Optical Network, adheres to the IEEE standard for Ethernet. It offers cost-effective solutions with support for 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps transmission rates.
xPON introduces several enhancements to network management:
– Seamless Mode Switching: With xPON, there’s no need for manual configuration when transitioning between GPON and EPON. Automatic mode detection and switching simplify network management, reducing operational complexities.
– xPON offers unified network management. It meets various business needs, such as ATM, Ethernet, and TDM services. This unified approach streamlines network management and lowers costs.
– Support for Various Business Requirements: The versatility of xPON ensures that it can adapt to changing business needs. Whether you require strict Quality of Service (QoS) guarantees or wish to transmit downstream cable TV through WDM, xPON has you covered.
For residential users seeking xPON ONUs, several options are available:
– WiFi ONU HG8245C 1G3F: This xPON ONU is tailored for the home environment. It supports WiFi 5 and EasyMesh, providing speeds of up to 1200Mbps. With the ability to connect multiple devices simultaneously, it’s an excellent choice for households.
– CATV WiFi ONU HG8247H5:** For homes with diverse connectivity requirements, the CATV WiFi ONU HG8247H5 is an ideal solution. The device is highly reliable. It supports USB 3.0 for fast data transfer. It also includes CATV support for comprehensive connectivity.
Yes, xPON is designed to seamlessly integrate with both GPON and EPON technologies. Its automatic mode detection and switching feature ensures that xPON ONUs can adapt to the existing network infrastructure without the need for manual configuration or hardware replacements. xPON is a cost-effective choice for network operators. It is efficient, too. Operators can upgrade or expand their networks with xPON.
These FAQs offer insights into the capabilities of xPON networks. They help you navigate the intricacies and make informed decisions. In the upcoming chapters, we will discuss the future of xPON in fiber access. We will also examine the differences between xPON, GPON, and EPON.