- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
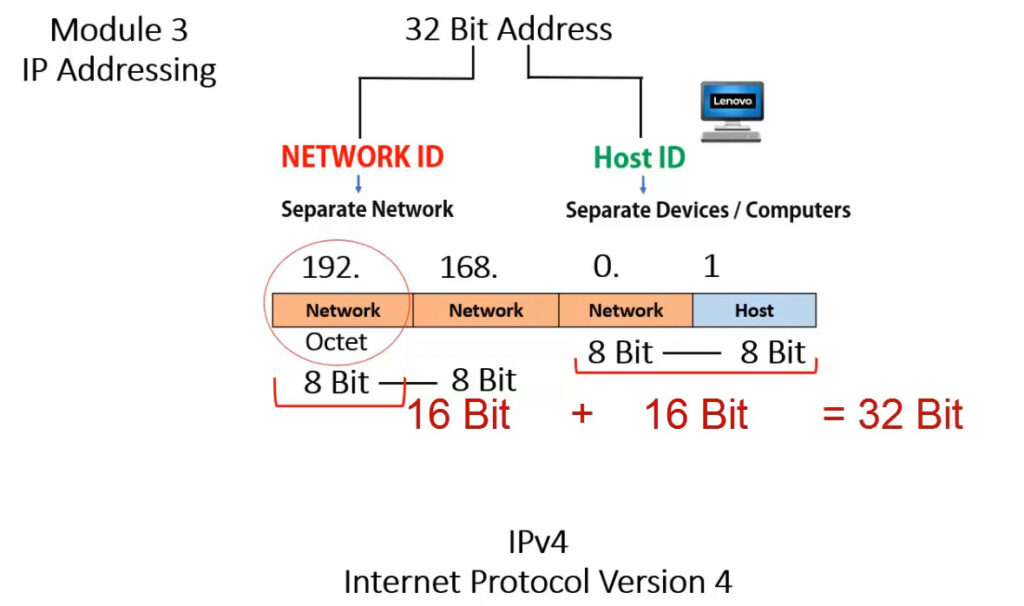
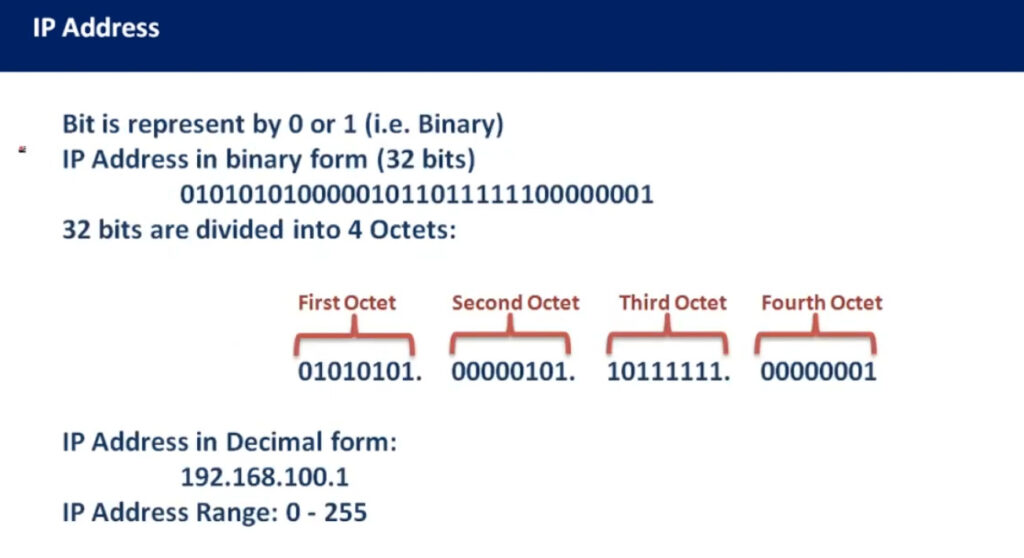
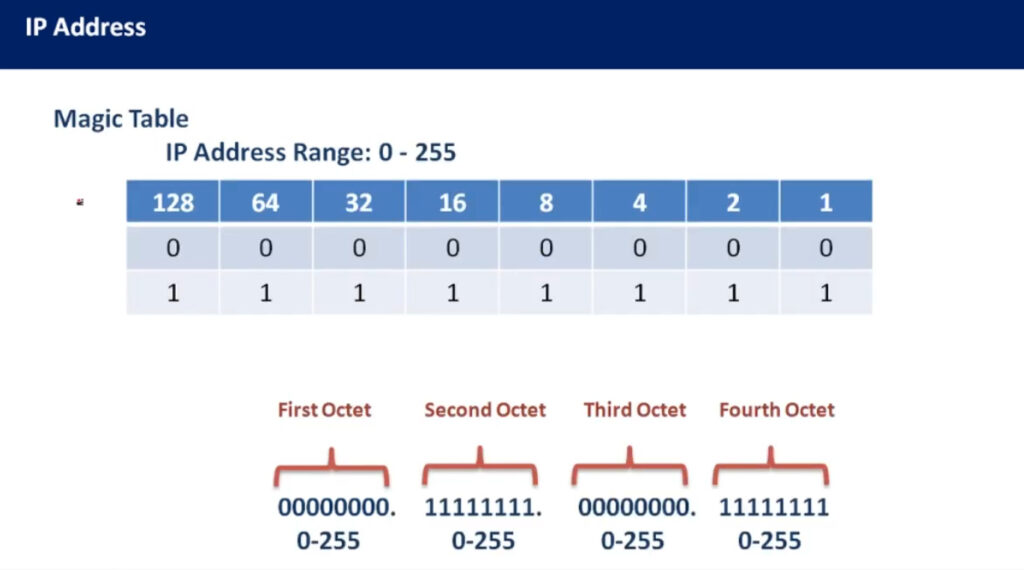
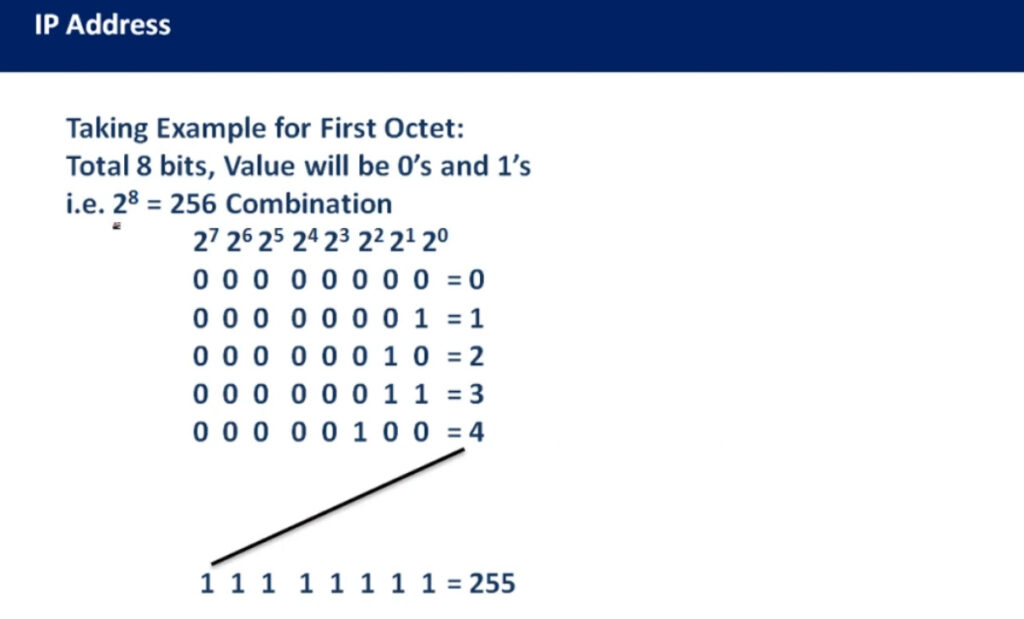
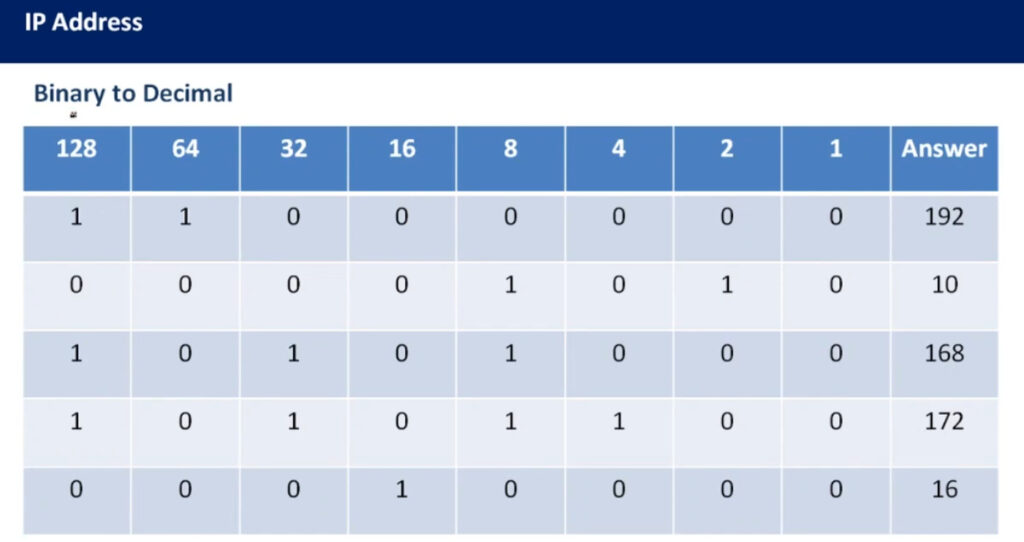
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network. It allows devices to communicate with each other over a network, such as the internet or a local network (LAN). An IP address functions similarly to a phone number or home address, enabling data to be sent to the correct destination.
There are two main types of IP addresses:
IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4):
192.168.1.1IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6):
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334While IPv4 is still the most commonly used version, IPv6 adoption is increasing as the number of devices on the internet grows and the pool of IPv4 addresses becomes exhausted.
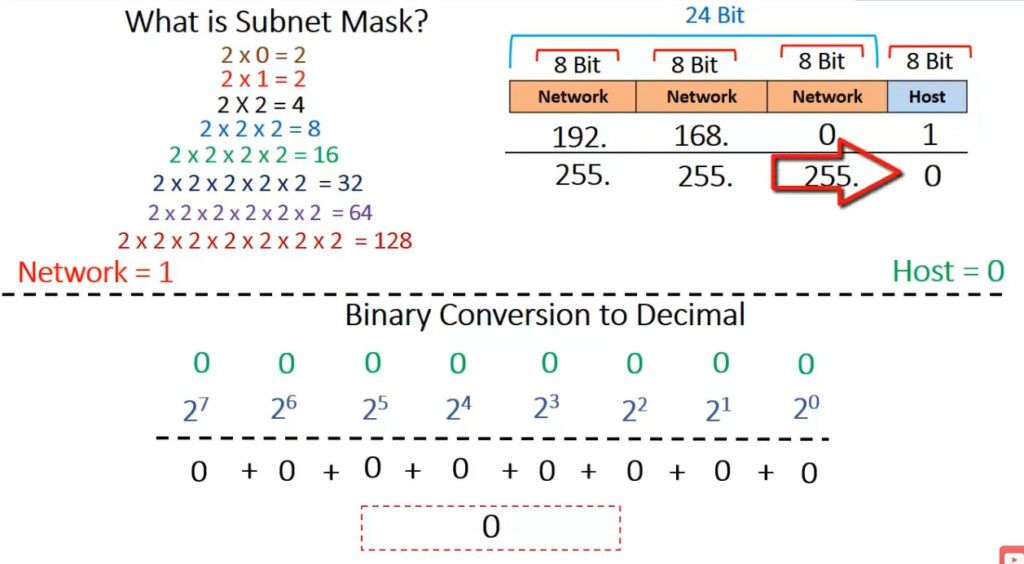
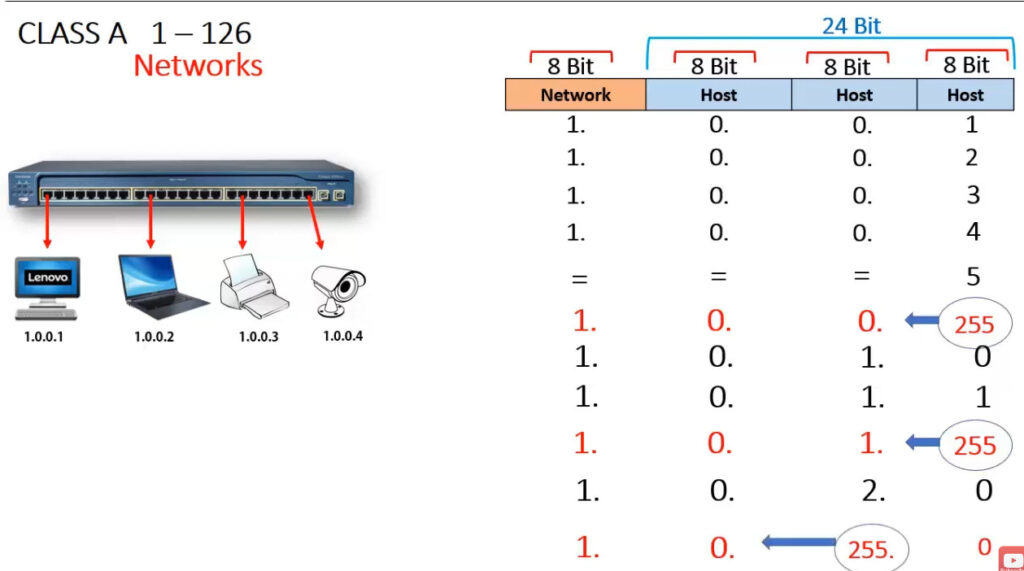
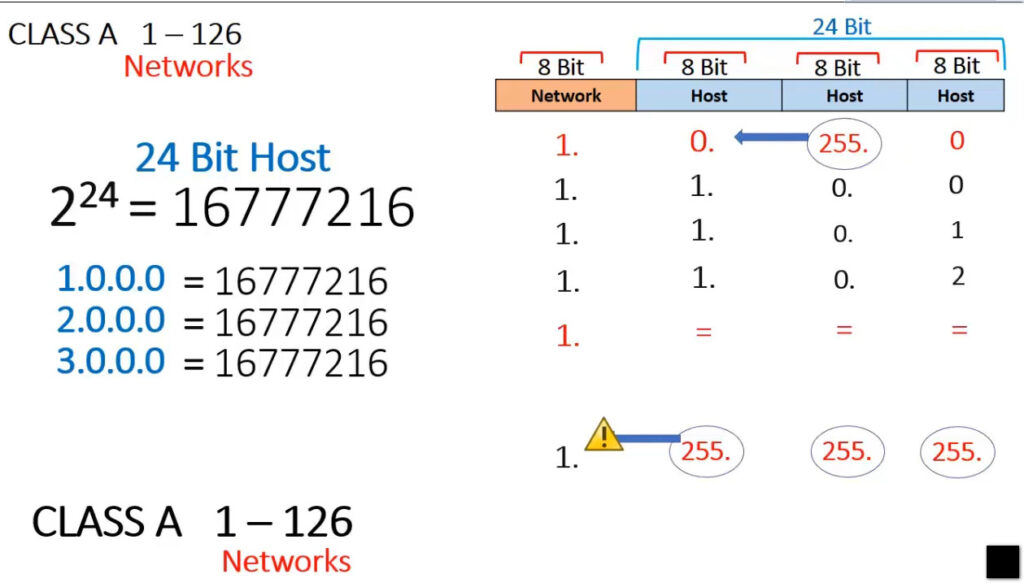
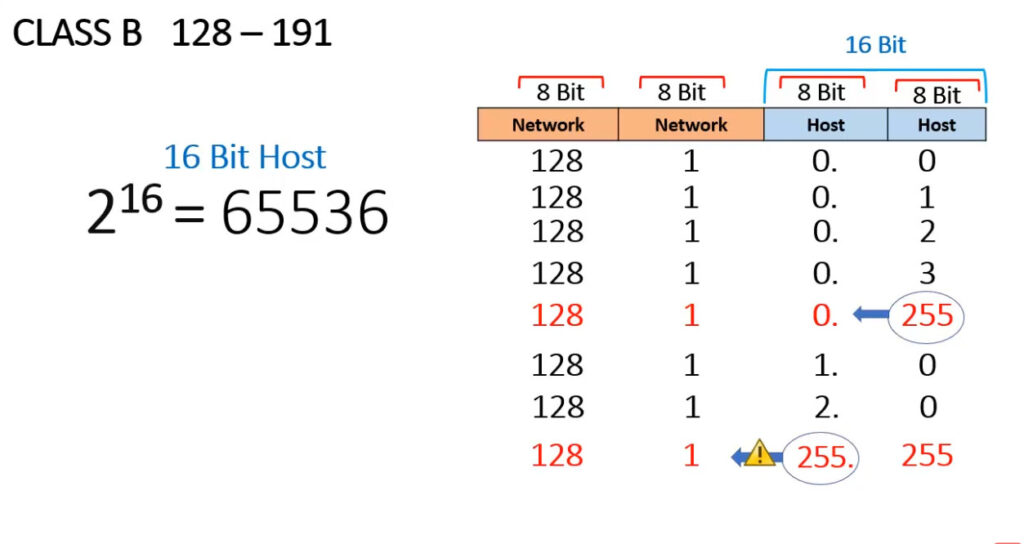
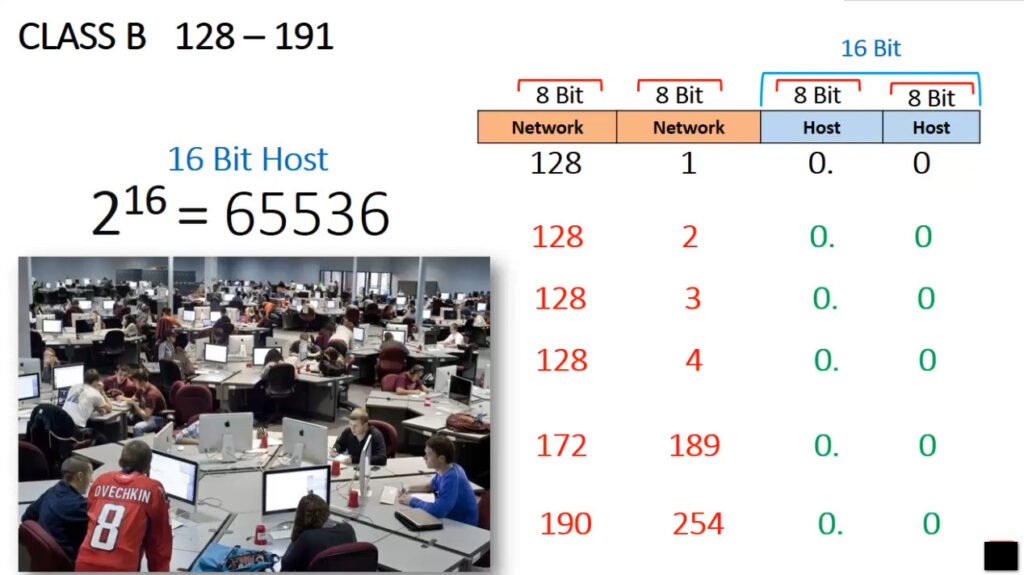
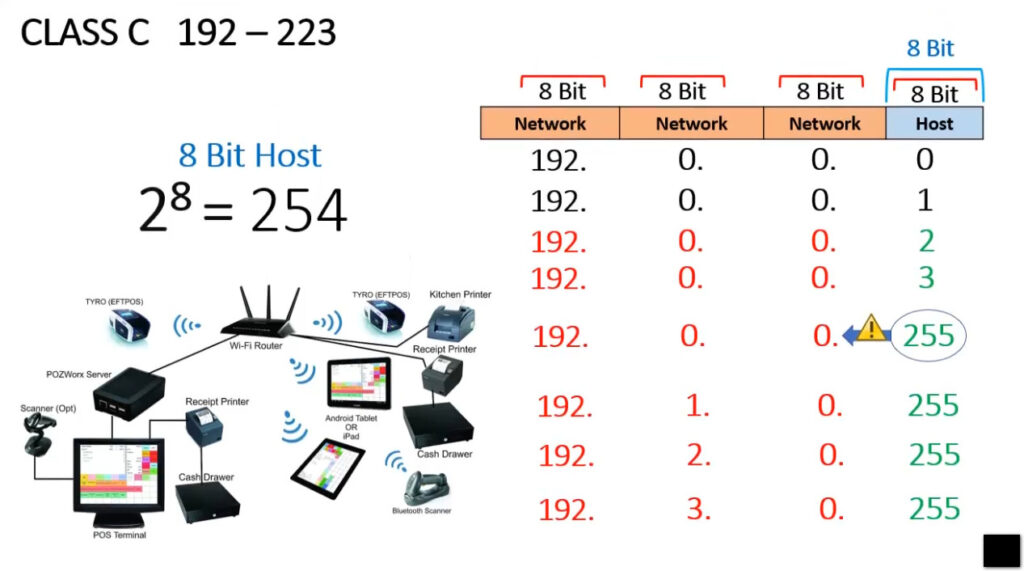
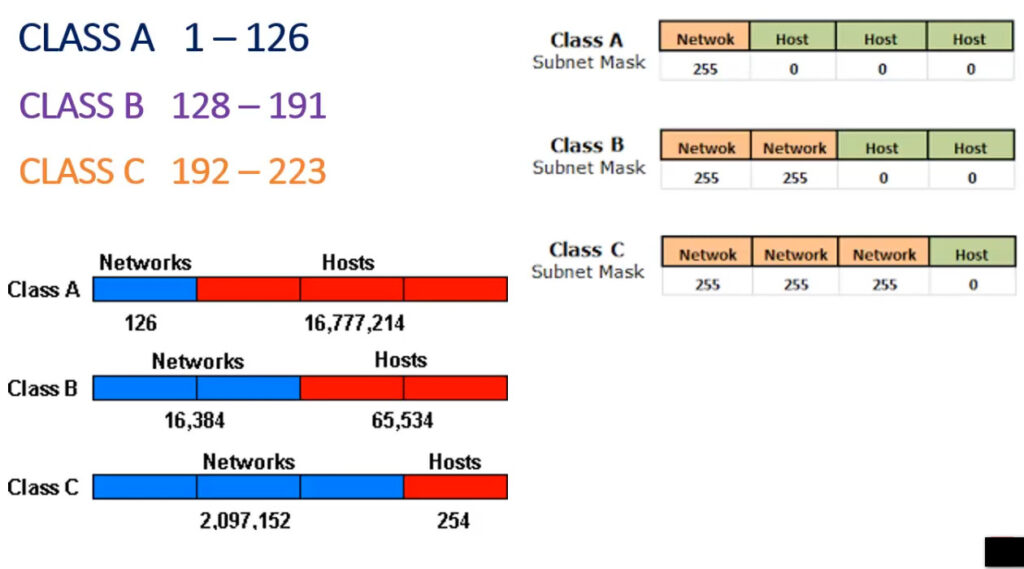
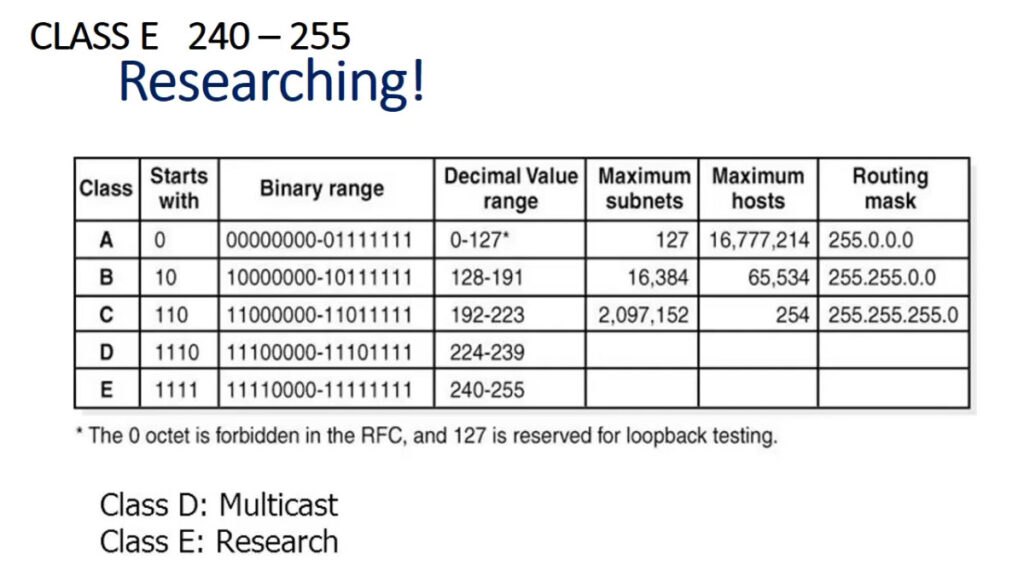
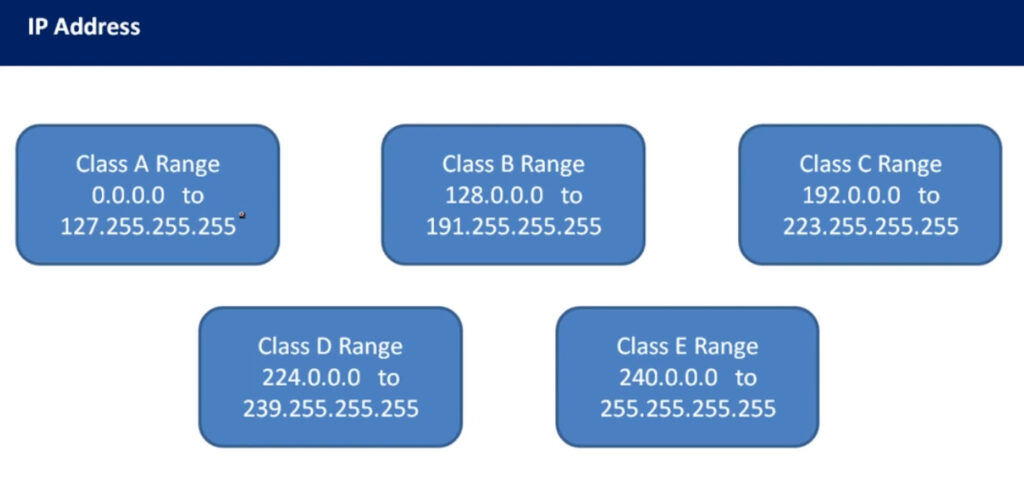
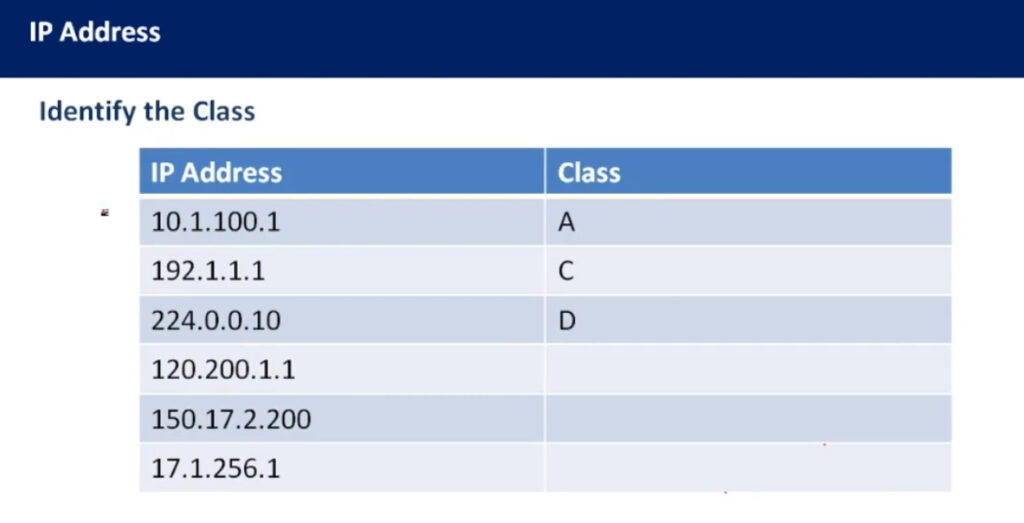
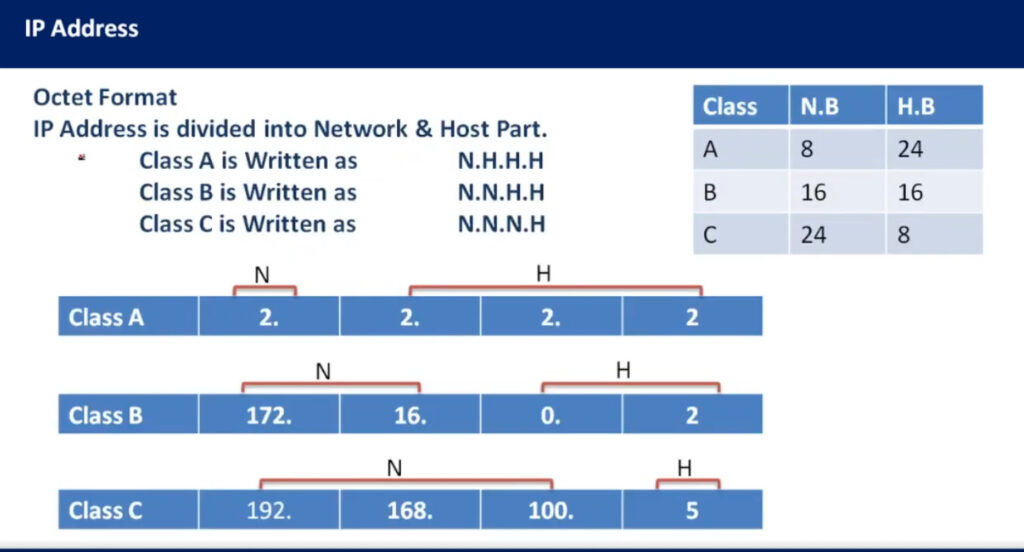
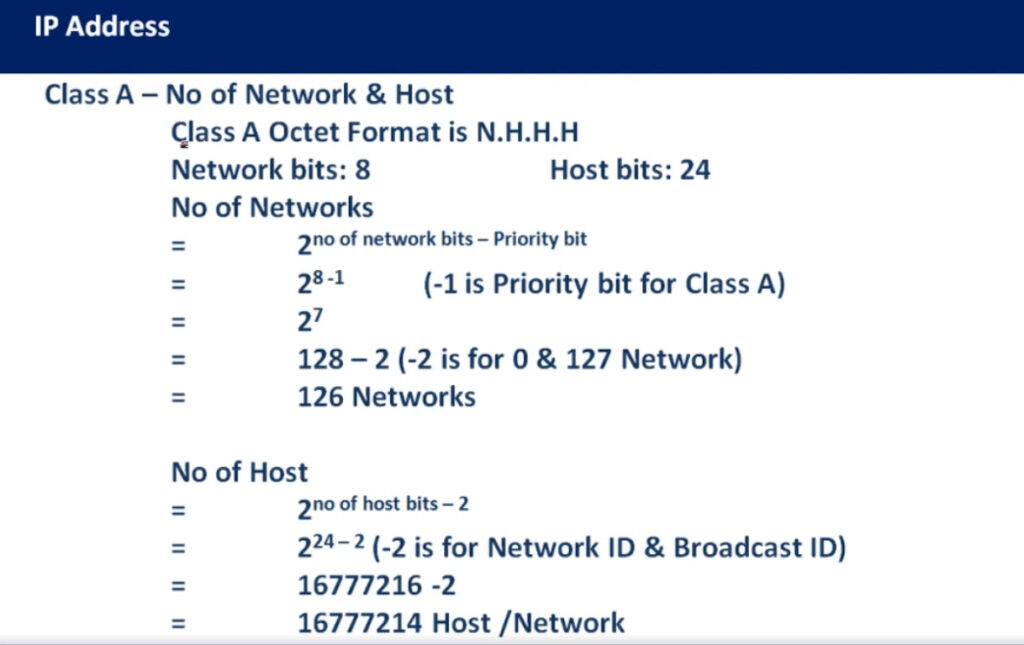
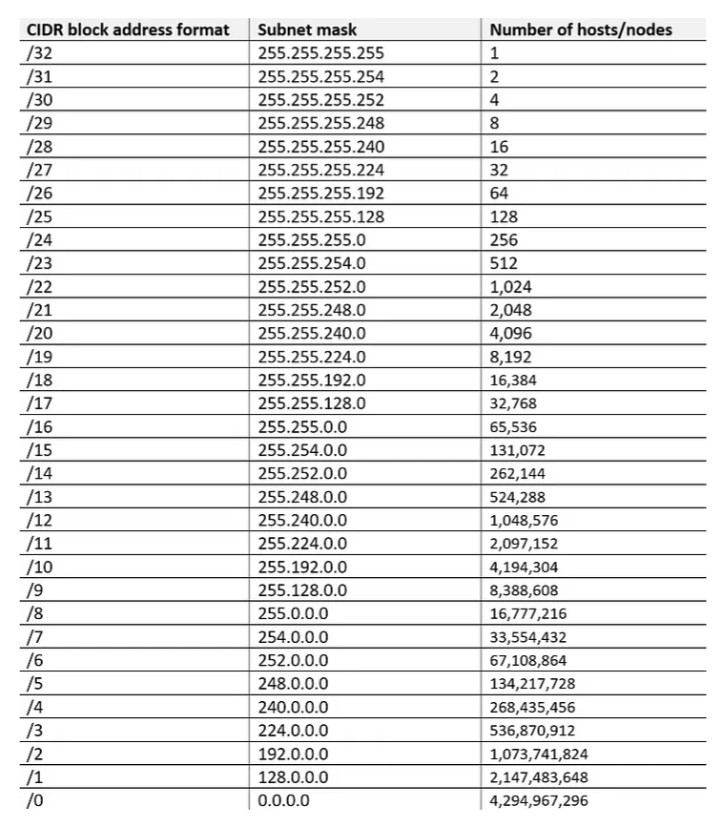
IPv4 addresses are categorized into different classes based on their range, and each class serves different purposes (e.g., public, private, reserved). There are 5 main classes of IPv4 addresses: A, B, C, D, E.
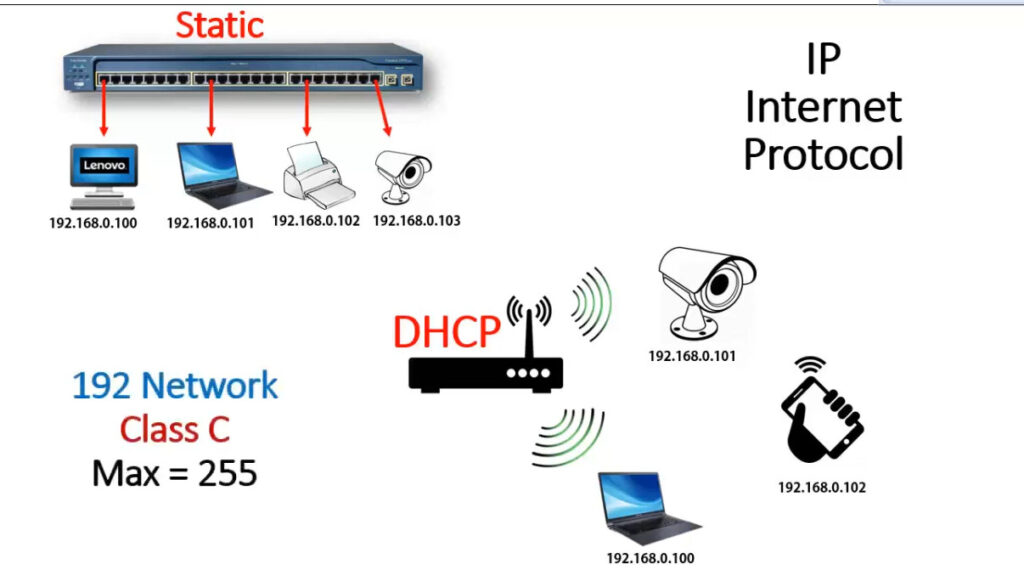
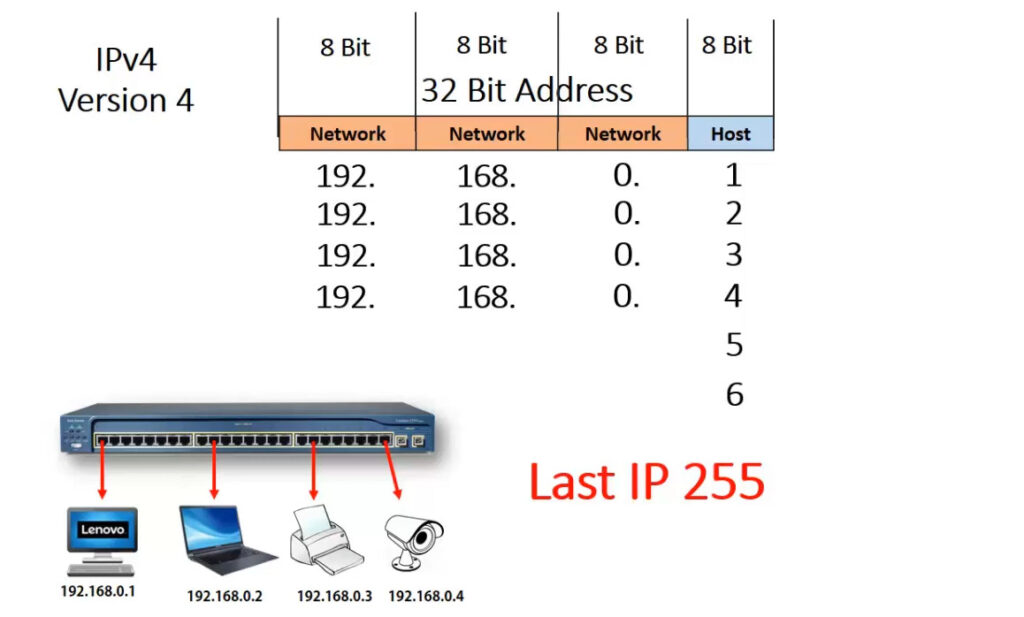
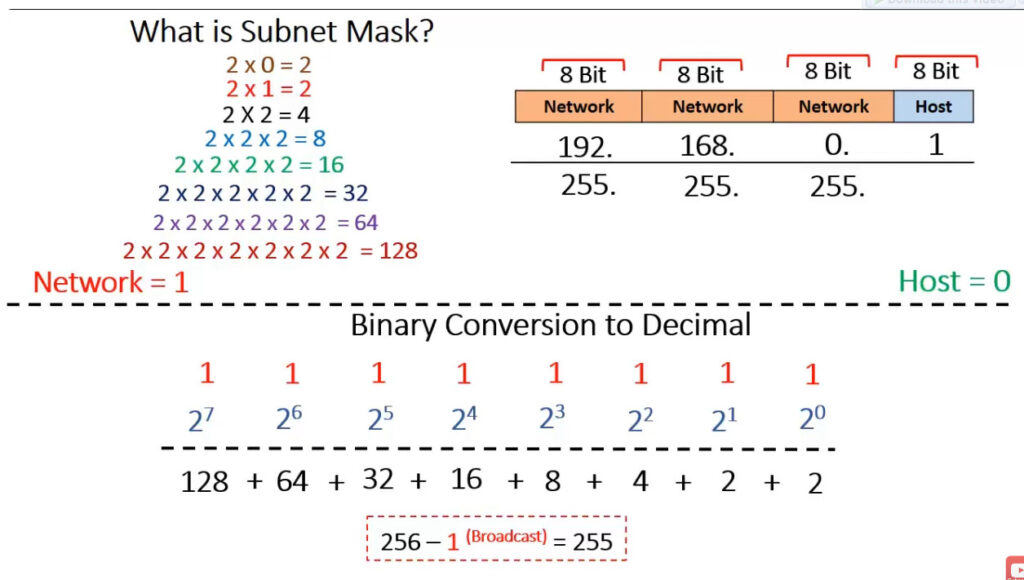
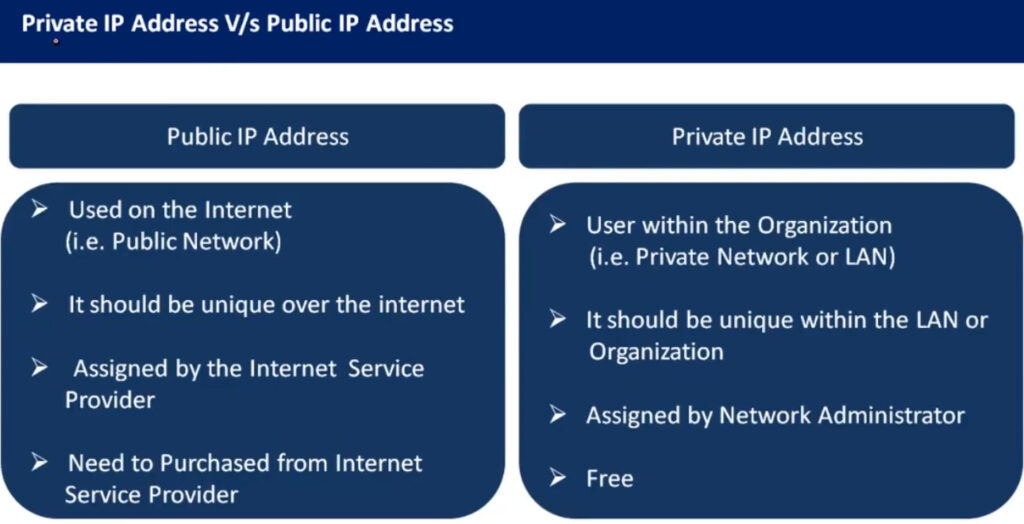
1.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255255.0.0.0 (or /8 prefix)0 to 12710.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255255.255.0.0 (or /16 prefix)128 to 191172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255255.255.255.0 (or /24 prefix)192 to 223192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255240.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255Private IP addresses are reserved for use within private networks (LANs) and cannot be routed on the internet. These are commonly used in home and business networks.
Here are the private IP address ranges:
10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255Devices using private IP addresses can access the internet through a Network Address Translation (NAT) service, typically provided by a router.
Loopback Address (for testing):
127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255127.0.0.1. It is used to test network interfaces locally.Link-Local Addresses (self-assigned for local communication):
169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255Broadcast Address (all devices on a network):
192.168.1.0/24, the broadcast address is 192.168.1.255.Here’s a summary of the range and purpose of each class:
| Class | Range | Subnet Mask | First Octet | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
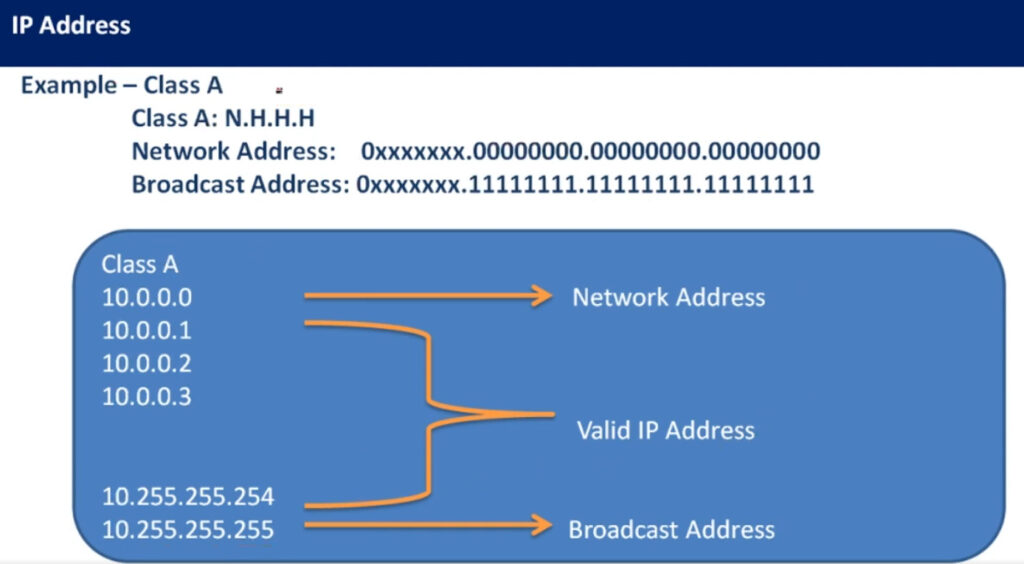
| Class A | 1.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 | 1-127 | Large networks (millions of hosts) |
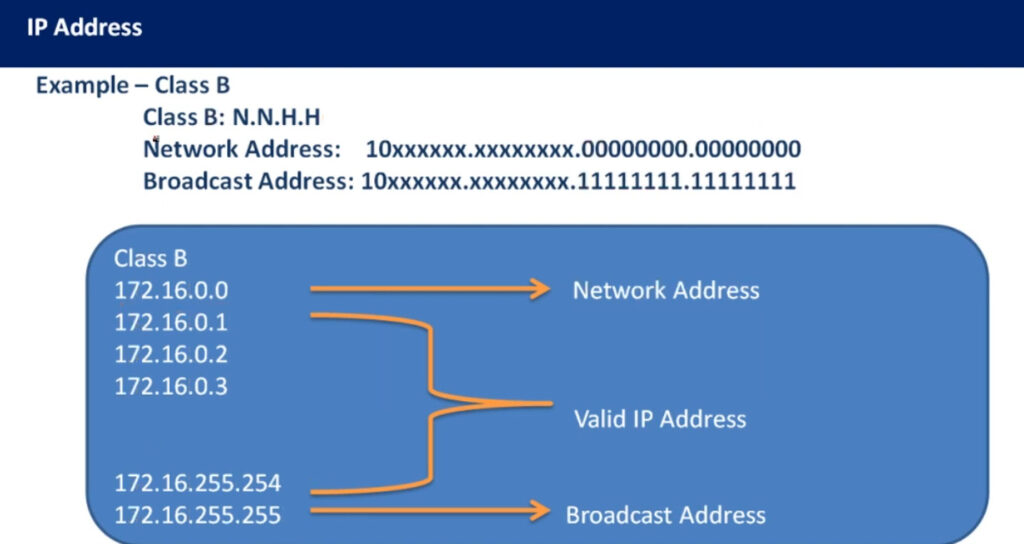
| Class B | 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 | 128-191 | Medium-sized networks |
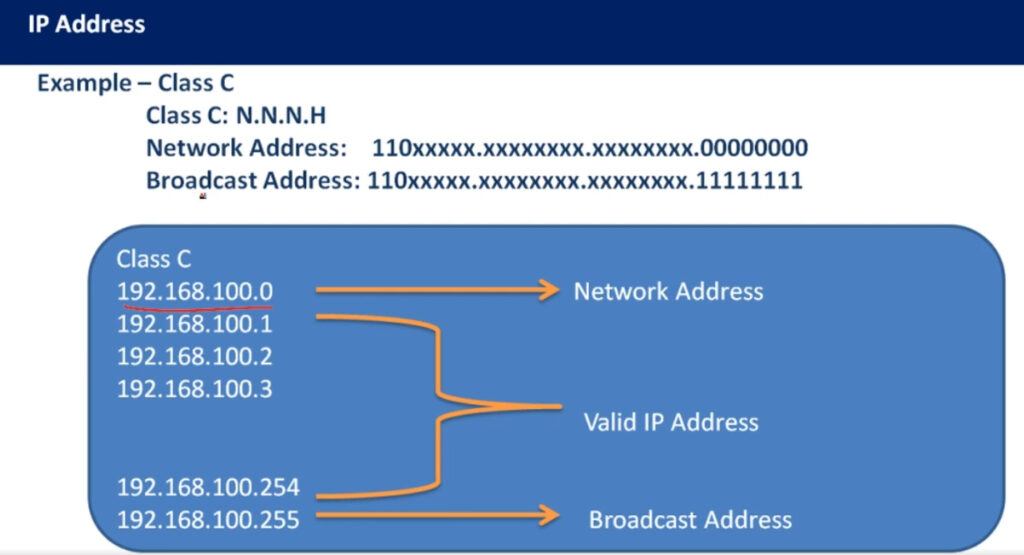
| Class C | 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 | 192-223 | Small networks |
| Class D | 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255 | N/A | 224-239 | Multicast addresses |
| Class E | 240.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255 | N/A | 240-255 | Reserved for experimental use |
IPv6 addresses are written in hexadecimal format and can be split into several parts (such as Global Unicast, Link-local, and Multicast). The ranges for the most common types are:
2000::/3FE80::/10FF00::/8192.168.1.1), while IPv6 uses 128 bits and is written in hexadecimal (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334).10.0.0.0/8 (Class A), 172.16.0.0/12 (Class B), and 192.168.0.0/16 (Class C).127.x.x.x), link-local (169.254.x.x), and broadcast addresses.Understanding IP address classes and ranges is fundamental when designing and configuring networks.