- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
Difference Between Trunk Port and Access Port
When it comes to networking, two terms that are “access port” and “trunk port” arises in our mind. They both sound familiar but both of these types have different functions. While commonly associated with Cisco, access ports and trunk ports are standard networking concepts utilized across various network equipment vendors. Access Port is a port that is assigned to a single VLAN whereas Trunk Port is a port that is assigned to multiple VLANs. Let’s see in what aspects they differ.
What is a Trunk Port?
A trunk port is a type of port used to connect switches or routers, transmitting data from multiple VLANs simultaneously. It uses tagging to ensure data reaches the correct destination, offering higher bandwidth and lower latency. Operating at layer 2 of the OSI model, it utilizes IEEE 802.1Q encapsulation for traffic delivery.
Advantages
It offers higher bandwidth and lower latency.
It sends all signals across a single trunk link which is for each switch or router.
It can carry traffic for several VLANs simultaneously.
Disadvantage
It is quite complex to set up when compared with the Access port.
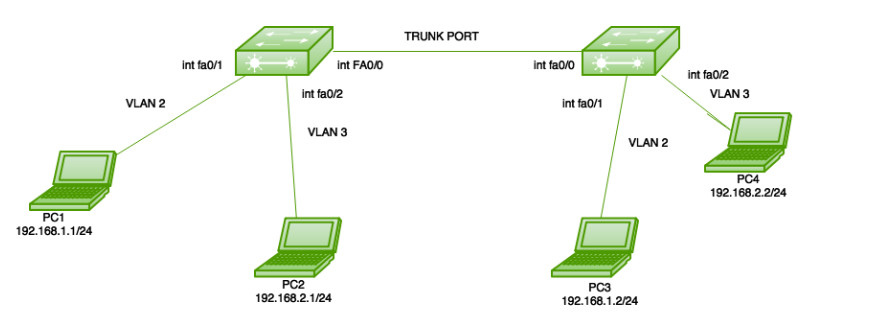
What is an Access Port?
An access port connects virtual machines to a switch or VLAN, transmitting data within a single VLAN. While it avoids signal issues, it may not be efficient for complex networks, though it can be optimized as a host port.
Advantages
It sends and receives frames that aren’t tagged.
There are no signal issues in the access port as the frame remains in a single VLAN.
To decrease the time it takes the designated port to begin to forward packets, use the host port.
Disadvantages
It can carry traffic for only one VLAN.
Only an end station can be set as a host port.
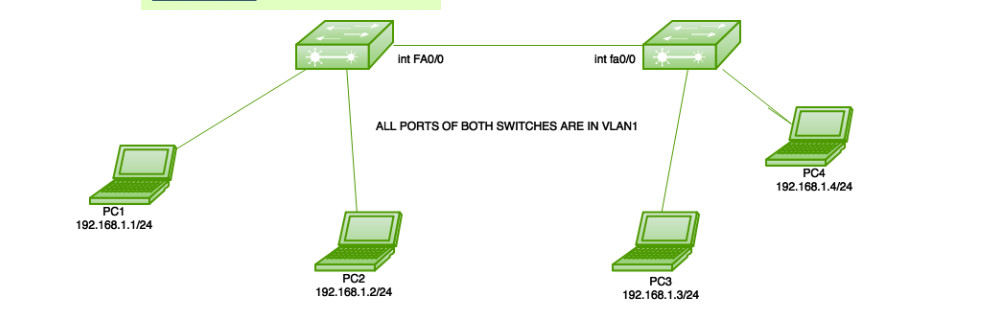
Mobaile View Image


| Parameters | Trunk Port | Access Port |
|---|---|---|
| VLAN assignment | It supports multiple VLANs. | It supports a single VLAN. |
| Tags | Multiple VLANs are allowed to traverse and add tags. | Single VLAN is allowed to traverse and removes tags. |
| Purpose | It connects switches or routers together. | It connects end devices to the network. |
| Protocols | It uses encapsulation protocol which are
| It uses only one encapsulation protocol-
|
| VLAN tagging | It supports VLAN tagging. | It does not support VLAN tagging. |
| Bandwidth | In Trunk Port, bandwidth is high. | In Access Port, bandwidth is low as compared to Trunk Port. |
| Broadcast domain | It allows segmentation into separate broadcast domains. | Traffic is part of the same broadcast domain. |
| Voice VLAN | Voice VLAN is a feature that is not supported in Trunk Port. | Voice VLAN is the feature that is supported in Access Port. |
| Frames | It supports tagged frames | It supports untagged frames. |
| Ideal for | It is ideal for larger networks with multiple VLANs that are basically used to connect between the switches. | It is ideal for connecting end-user devices to the network and is used to connect laptops, printers, computers, etc. |
The main and basic use of these both the trunk port and access port is to move traffic between VLANs. The user can carry more than one VLAN traffic from one switch to another switch with Trunk Port whereas data is transmitted simultaneously with Access Port. Both ports have their own pros and cons and it all depends on the user to select which port according to their own requirement.
Frequently Asked Questions on Trunk Port and Access Port – FAQ’s
Can a Trunk Port carry traffic for a single VLAN?
Yes, however its main purpose is to transport traffic between various VLANs.
Why is the Access Port easier to configure?
Because it only handles one VLAN, the Access Port requires less setup complexity.
What is the primary use of a Trunk Port?
Trunk ports are mostly used to transmit traffic from several VLANs and link switches or routers.
Is VLAN tagging necessary for Access Ports?
Since access ports handle untagged frames, they do not support VLAN tagging.