- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
A Security Policy in Palo Alto Networks firewalls is a set of rules that determine how network traffic is handled, allowing or blocking traffic based on specified criteria. Here’s how it works:
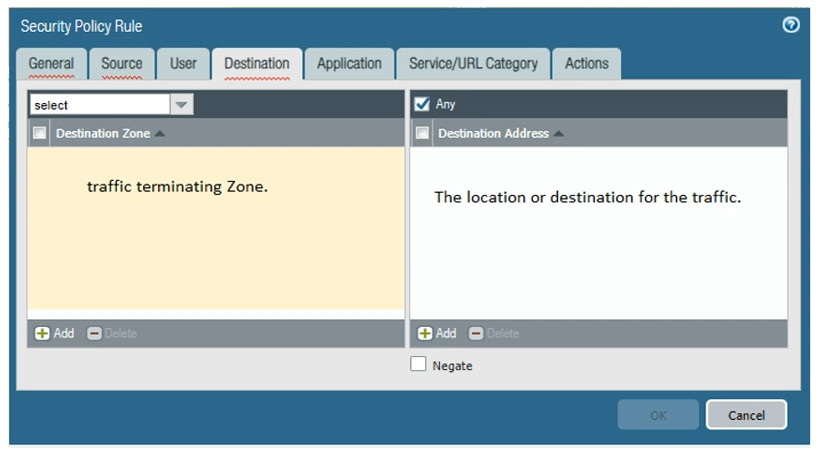
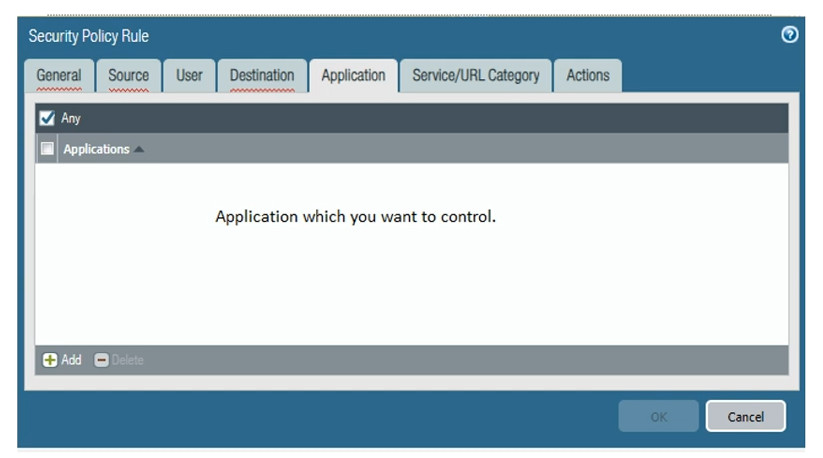
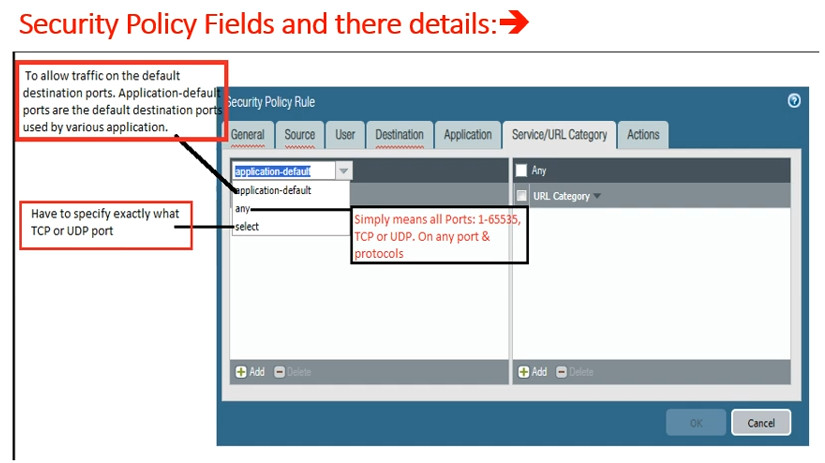
Rules: Each rule in a security policy specifies:
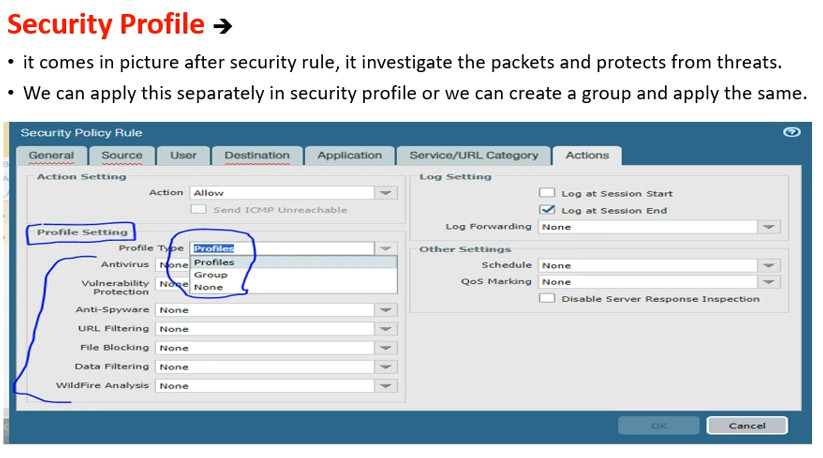
Profiles: Security profiles can be attached to rules to provide additional protection, such as:
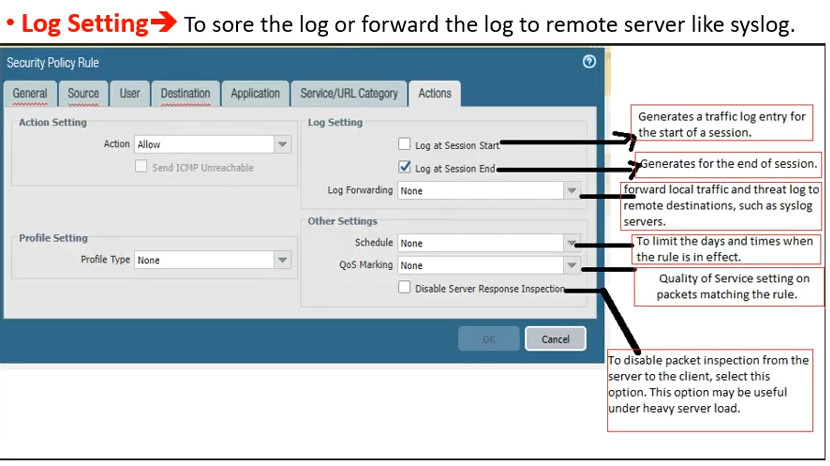
Logging and Monitoring: Security policies can be configured to log traffic, which helps in monitoring and auditing.
Traffic Identification: When traffic passes through the firewall, the device inspects it based on the defined security policies.
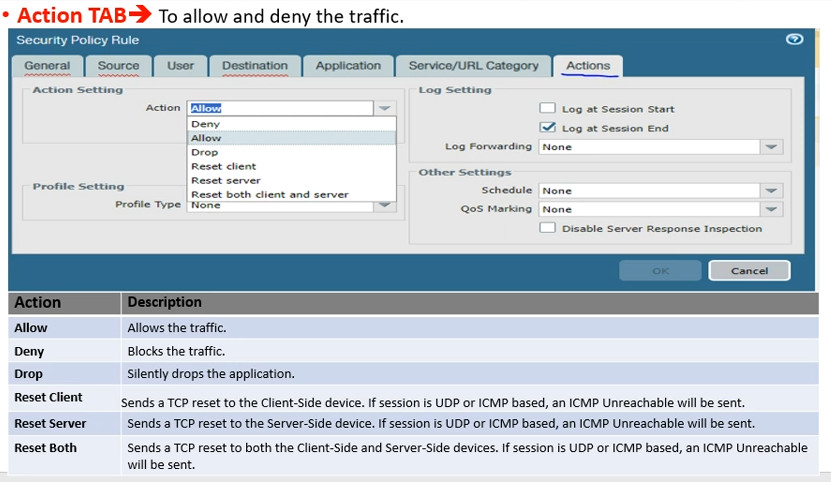
Rule Matching: The firewall checks the incoming traffic against the security policy rules in a top-down manner. The first rule that matches the traffic is applied.
Action Enforcement: Depending on the matched rule, the traffic is either allowed or denied. If allowed, associated profiles are applied.
Logging: If logging is enabled, the firewall records the event for monitoring and analysis.
Define Security Zones: Group interfaces into zones (e.g., trust, untrust, DMZ) to manage traffic between different segments.
Create Security Rules: Define the necessary rules based on your organization’s security requirements.
Apply Security Profiles: Attach profiles to rules to enhance security.
Test and Monitor: After implementing the policies, monitor traffic and logs to ensure proper operation and adjust rules as needed.