- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
What is EPABX
EPABX stands for Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange. It is a telephone exchange system used within an organization to manage internal communication and connect with external telephone lines. EPABX systems are commonly used in businesses, offices, and large institutions to handle multiple incoming and outgoing calls while also facilitating internal communication between extensions.
Key features of EPABX include:
EPABX has evolved from analog systems to digital and IP-based systems, providing greater flexibility and integration with other communication technologies.
Type Of EPABX
There are several types of EPABX (Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange) systems, each with distinct features and capabilities to suit various needs and scales of operations. The main types are:
| Type | Technology | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analog EPABX | Analog circuits | Simple, cost-effective, limited features | Small offices or low-traffic setups |
| Digital EPABX | Digital circuits | Enhanced features, better scalability, good quality | Mid-sized businesses or moderate traffic |
| IP EPABX | Internet Protocol | VoIP support, scalable, advanced features, remote access | Large businesses, remote work, global offices |
| Hybrid EPABX | Mixed (Analog + Digital/IP) | Combines old and new tech, flexible, cost-effective | Businesses transitioning between systems |
| VoIP EPABX | VoIP (Internet) | Lower costs, integrates with IT, advanced features | Businesses with remote teams or multiple locations |
| Cloud-based EPABX | Hosted on Cloud | Managed service, scalable, flexible, no physical hardware | Organizations preferring off-site management |
| Wireless EPABX | Wireless signals | Mobility, no physical wires, can integrate with mobile | Large offices, warehouses, or factories |
Each type of EPABX system is designed to meet specific needs, so the best choice depends on factors like the size of the business, budget, communication requirements, and the need for scalability.
What is difference EPABX and PBX
EPABX and PBX are both systems used to manage internal and external communication within an organization, but there are key differences between the two in terms of technology and features.
| Aspect | PBX | EPABX |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Private Branch Exchange | Electronic Private Automatic Branch Exchange |
| Technology | Analog or digital circuits | Analog, digital, or IP-based technology |
| Automation | Manual switching or basic automation | Fully automated with advanced electronic management |
| Advanced Features | Basic features like call forwarding, voicemail | Advanced features like IVR, call queuing, ACD, call recording |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, relies on physical hardware | Highly scalable, especially with digital/IP systems |
| Flexibility | Basic call routing, suited for small businesses | Flexible call management, better suited for large businesses and call centers |
| Integration | Less integration with modern technologies | Can integrate with VoIP, CRM, and other modern IT systems |
| Cost | Typically lower cost for basic systems | Higher initial setup cost due to more advanced features and technology |
In essence, EPABX can be considered a modern, electronic upgrade of the traditional PBX system.













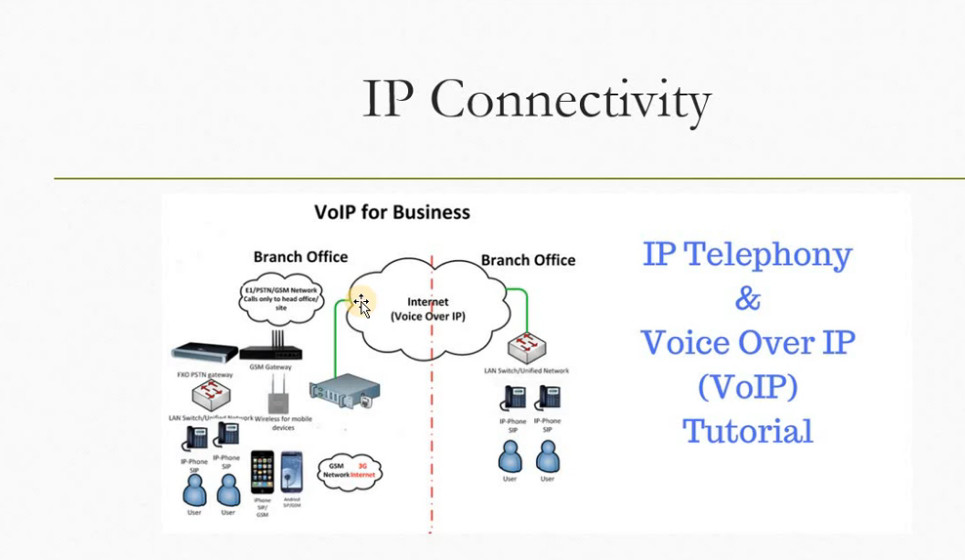

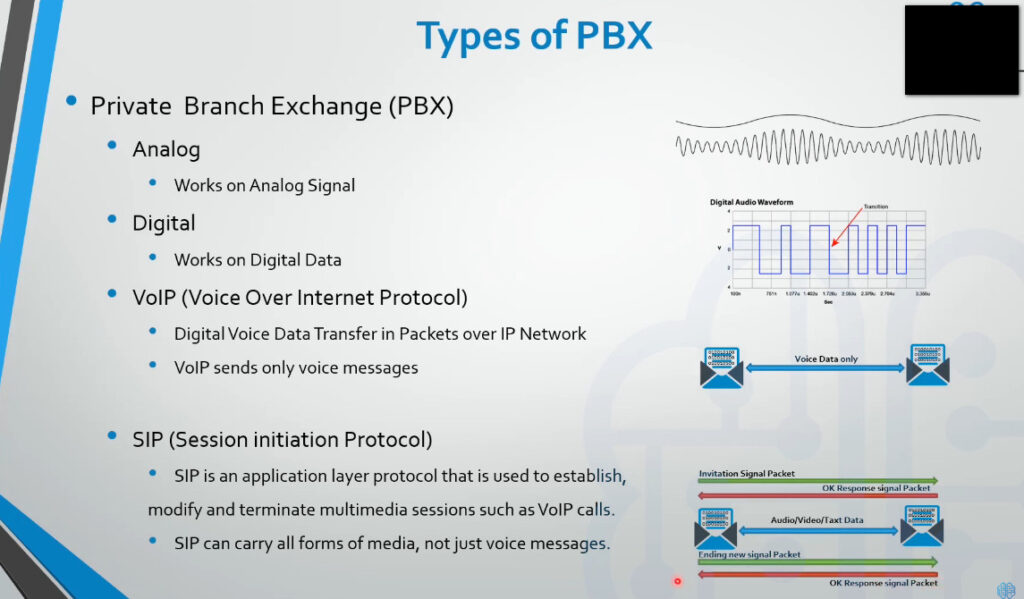


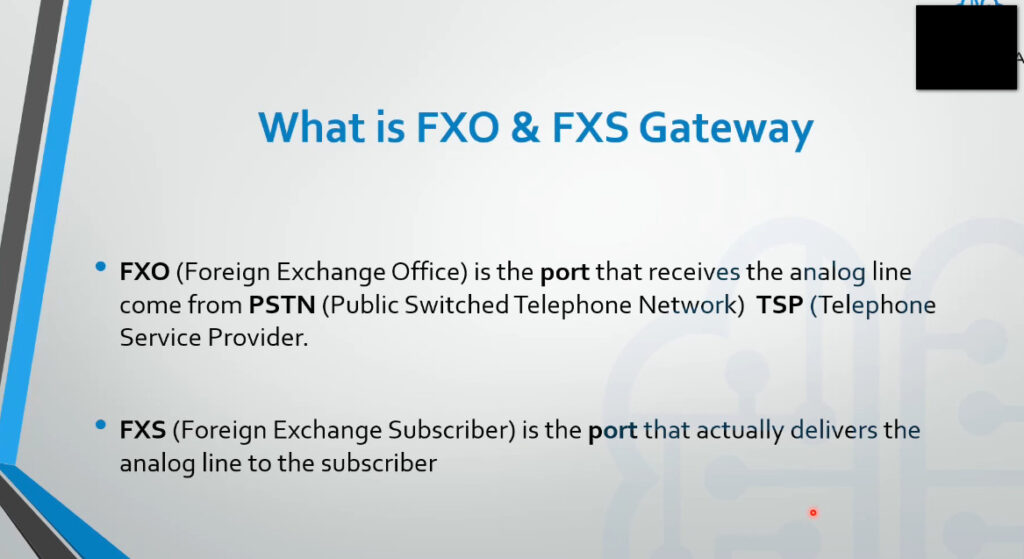
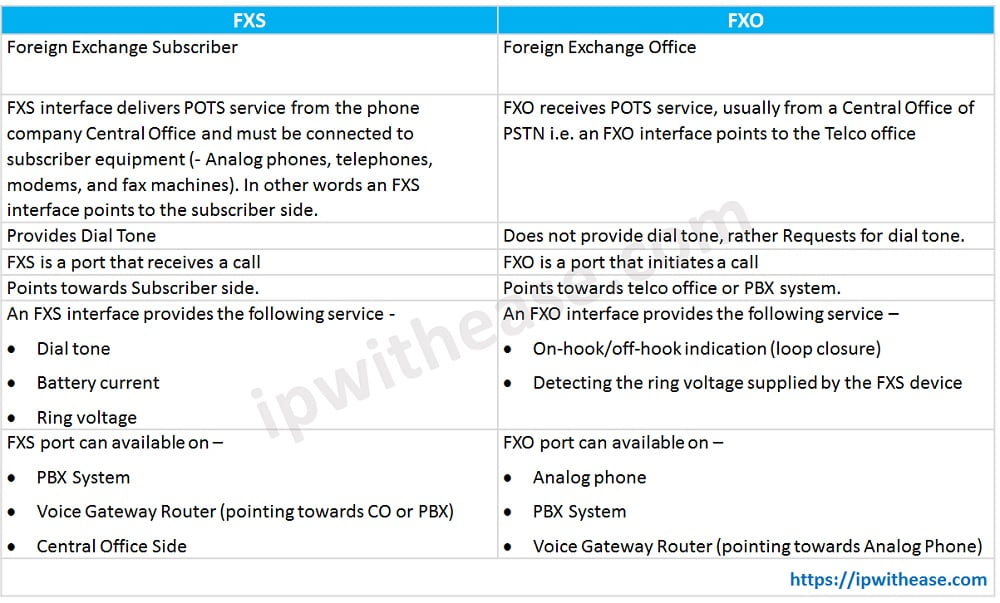
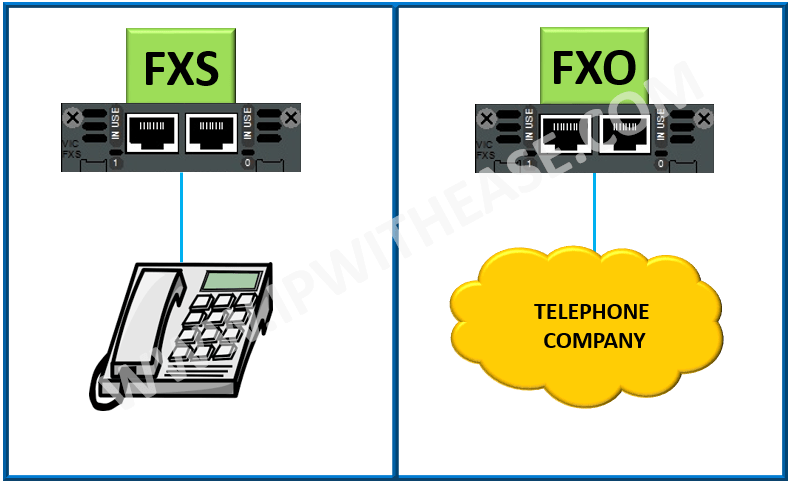

What do FXS and FXO Mean?
When FXS and FXO refer to the two types of ports used by the POTS (“Plain Old Telephone System”). POTS is an analog system using twisted copper wires; it was the only type of telephone system offered until around 1988, when ISDN, cellular, and VoIP services began to be offered. Although analog phone systems are no longer as prevalent as they once were, they are still widely used in situations when other technologies are either unavailable or not costeffective.
FXS/FXO connections are mainly used in phone line extensions, which is the context in which we will be discussing them.
FXS (Foreign Exchange Subscriber) is the port that delivers POTS service from a phone company’s Central Office within the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) to devices such as analog phones and fax machines. In other words, it is a wall jack that points away from the Central Office to the subscriber, or end device. The FXS interface delivers dial tone, ringing voltage, and battery power to FXO end devices.
FXO (Foreign Exchange Office) is the port on the subscriber device that receives the analog line. The FXO interface points away from the device towards the Central Office and receives the POTS service from the Central Office. That is to say, it connects office devices like fax machines, modems, and analog phones to an outside telephone line via an FXO port on the device. For this reason, these end devices are often referred to as “FXO devices.” The FXO interface delivers an on-hook/off-hook loop closure.
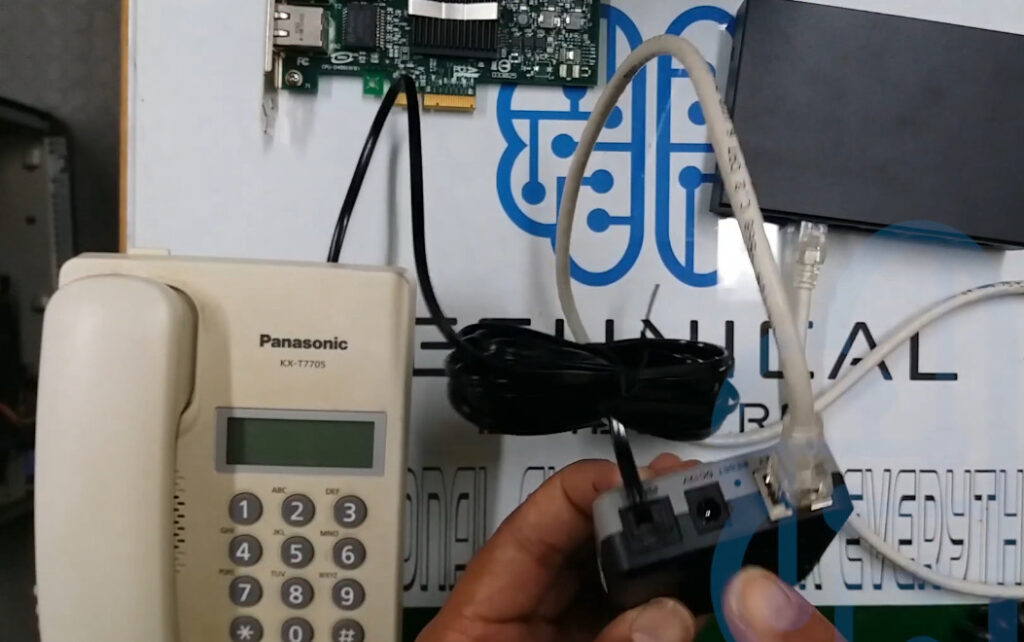
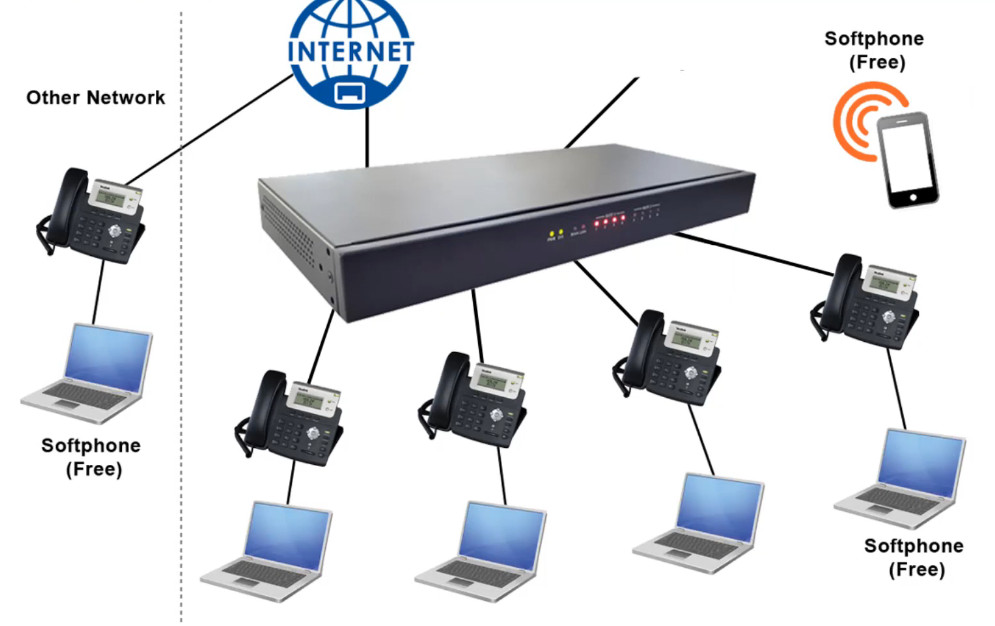

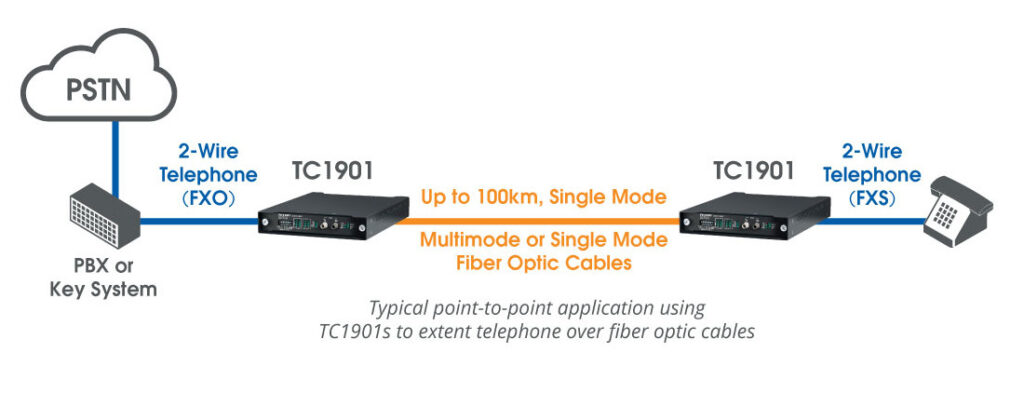
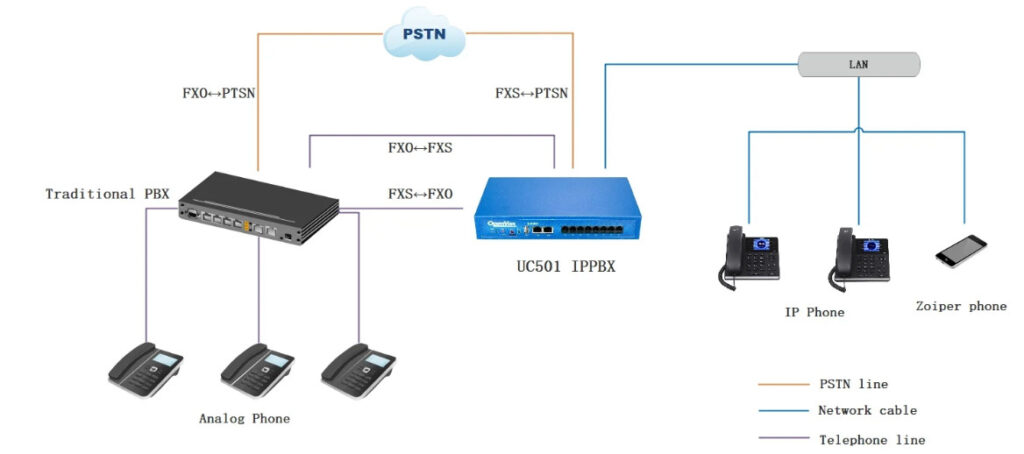
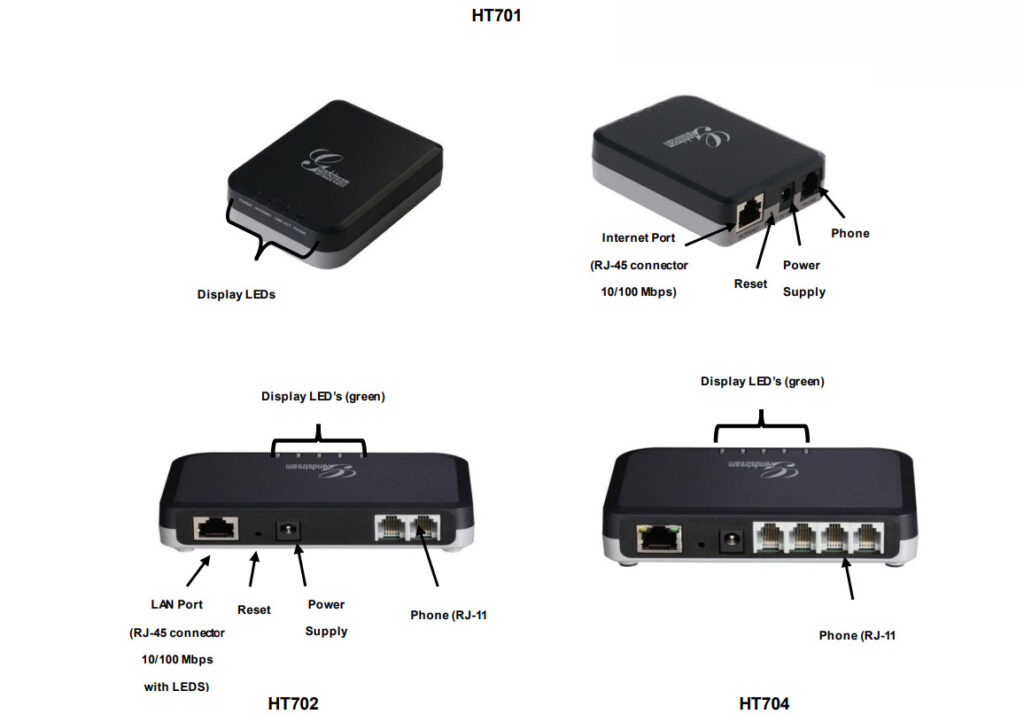

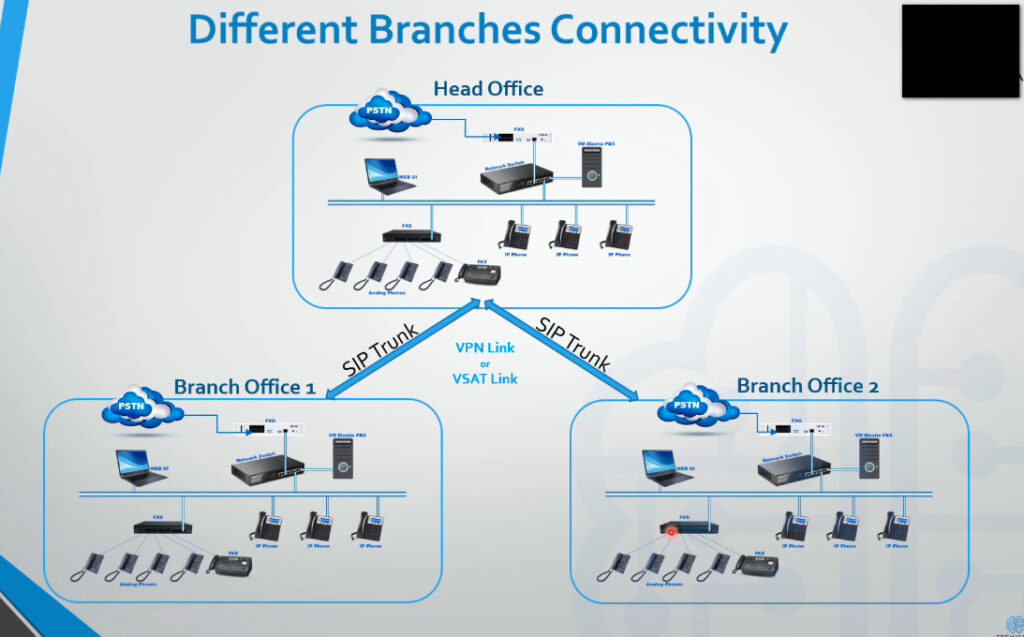





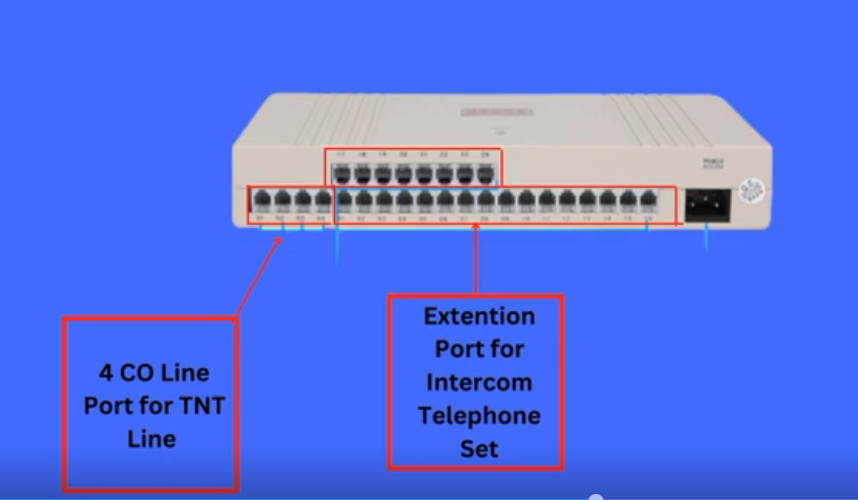
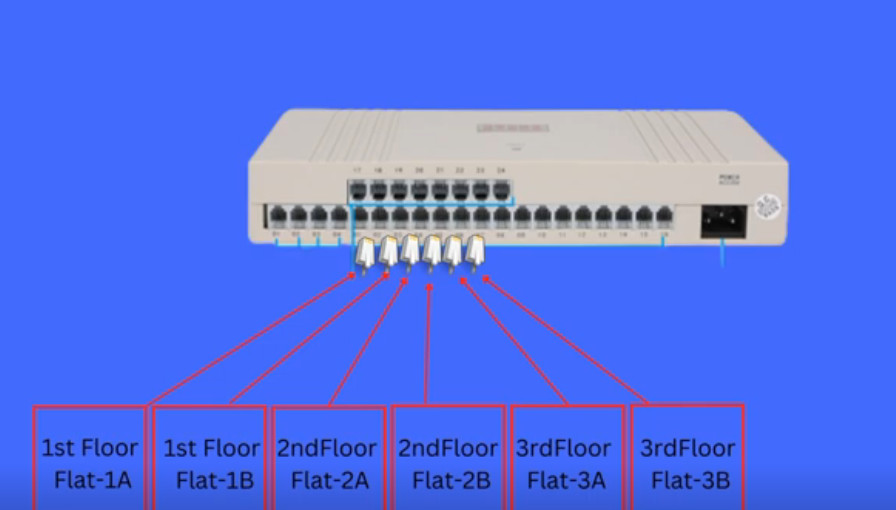
Intercom System Top Vendor