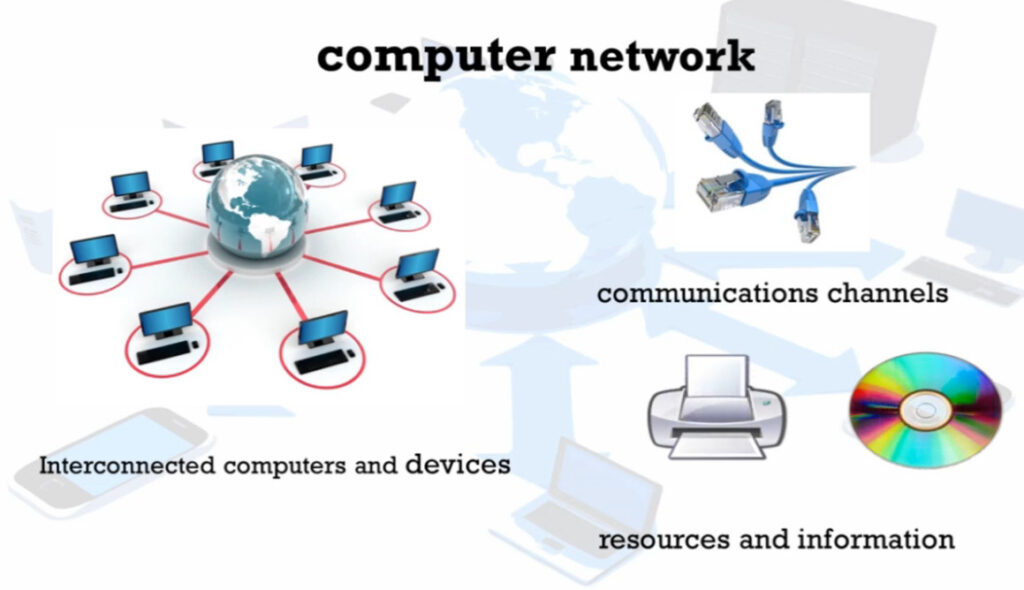
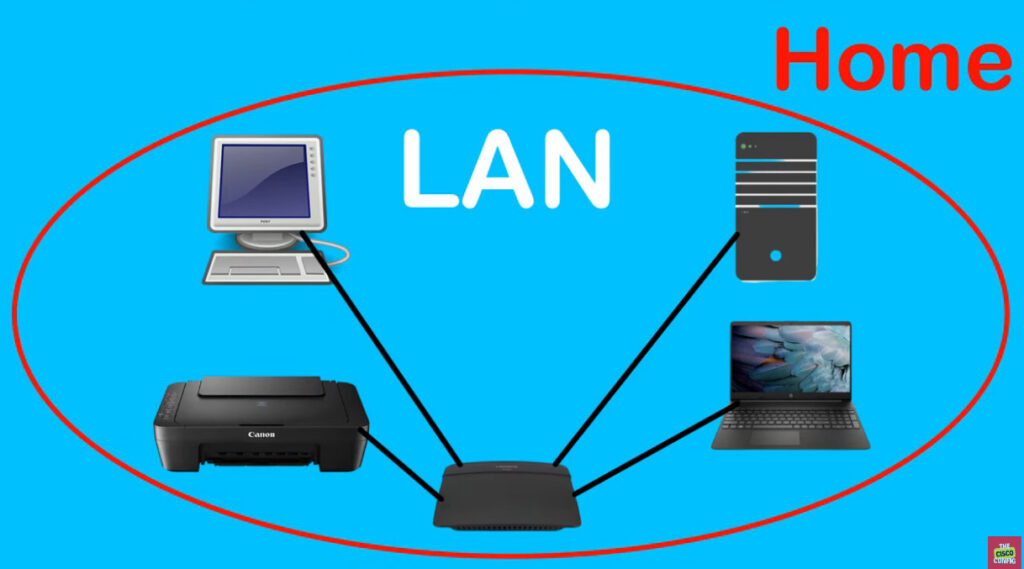
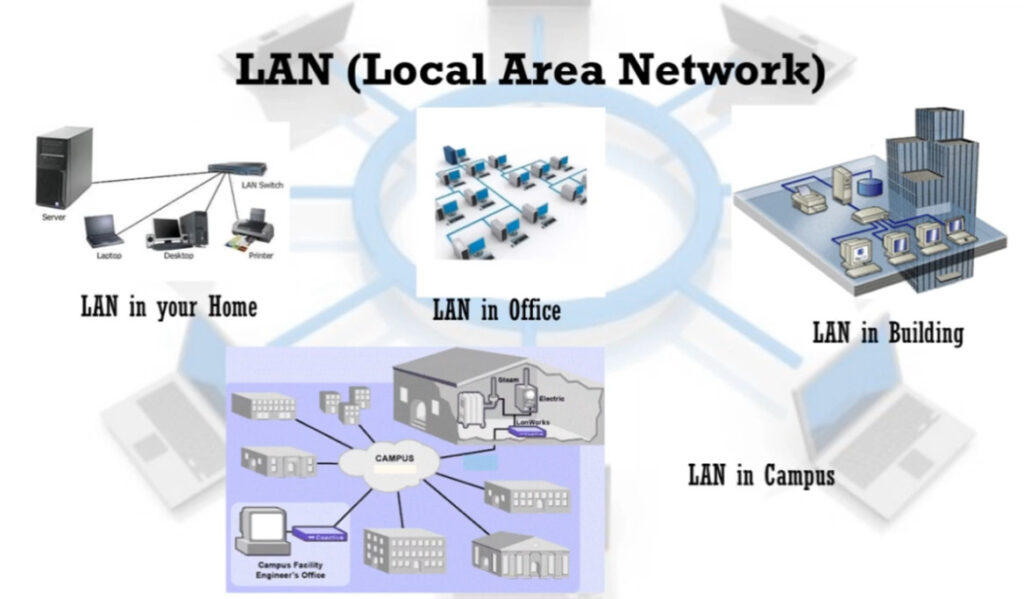
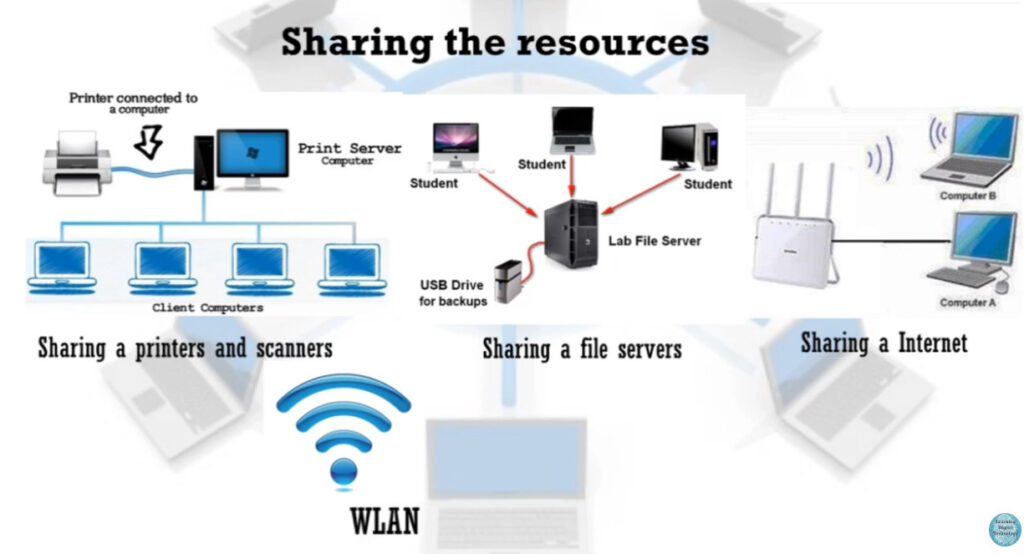
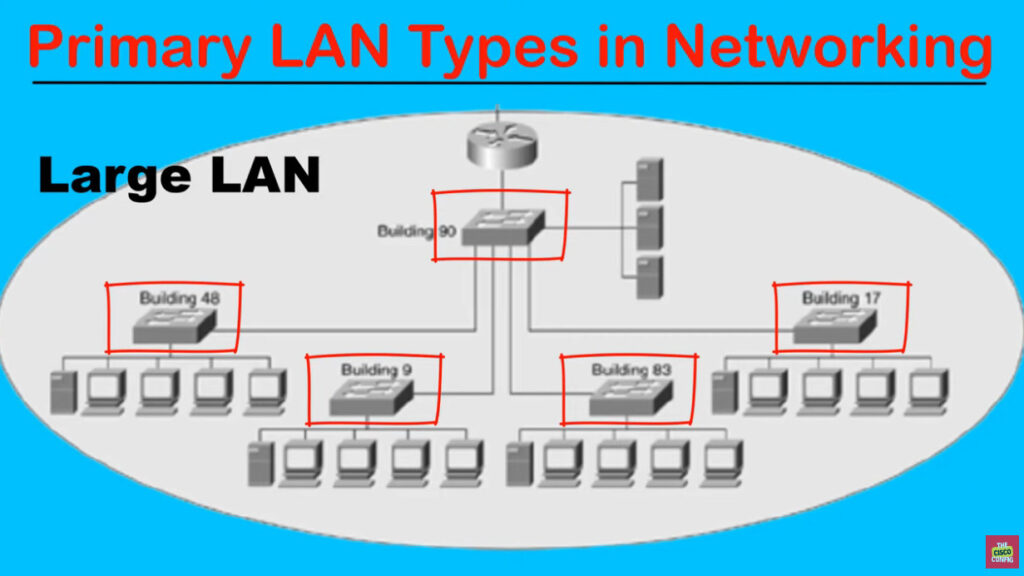
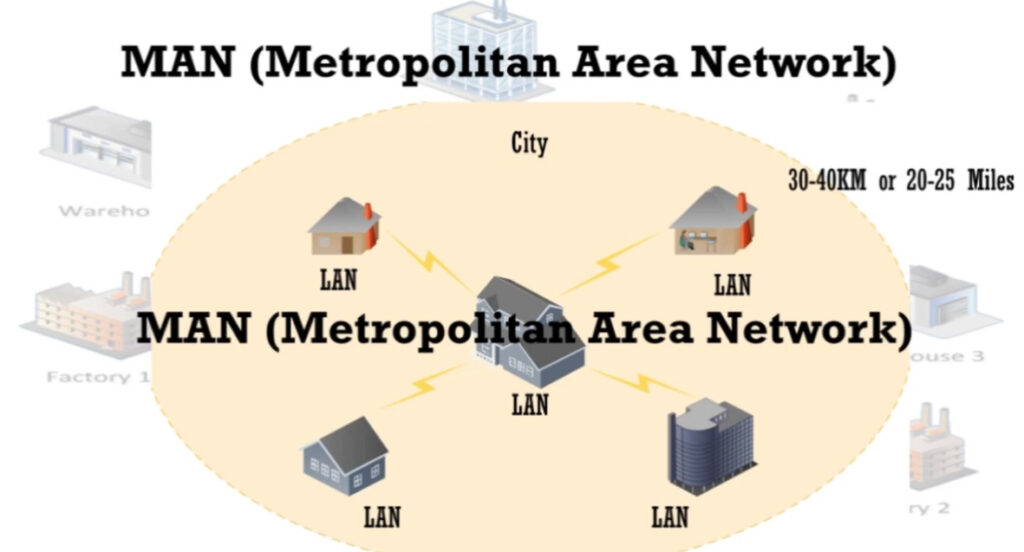
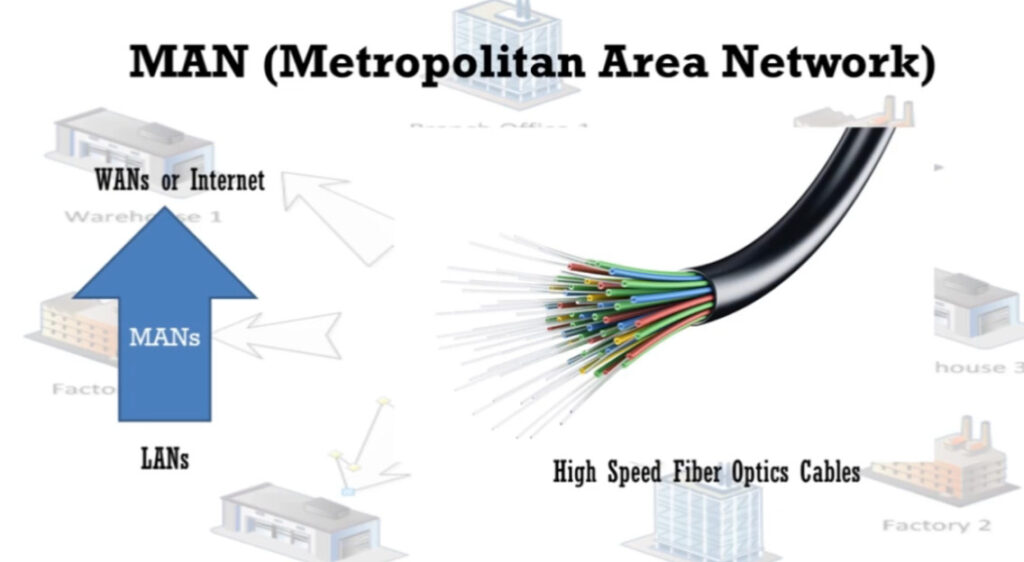
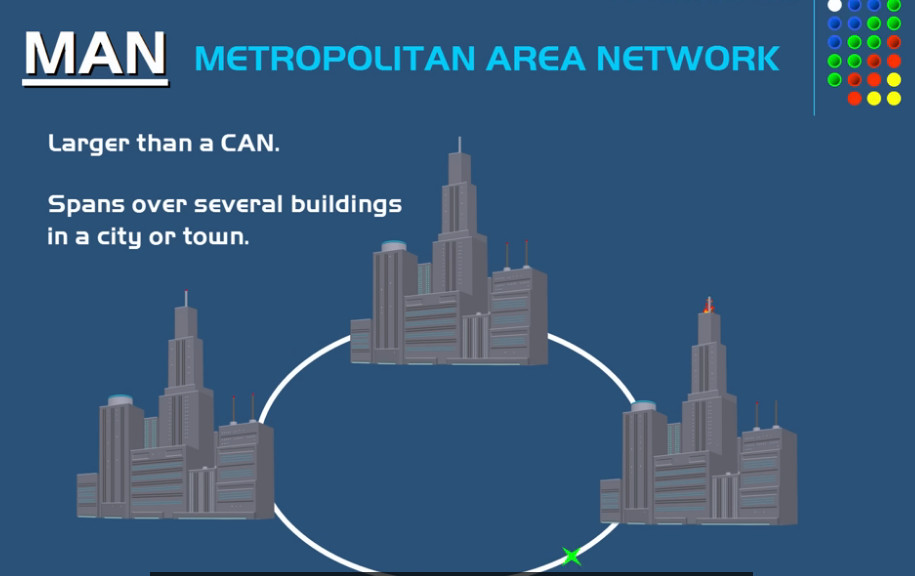
MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. It is a type of computer network that covers a larger geographical area than a Local Area Network (LAN) but is smaller than a Wide Area Network (WAN). Typically, a MAN spans a city or a large campus and is used to connect multiple LANs within that area.
Key Characteristics of MAN:
Coverage Area:
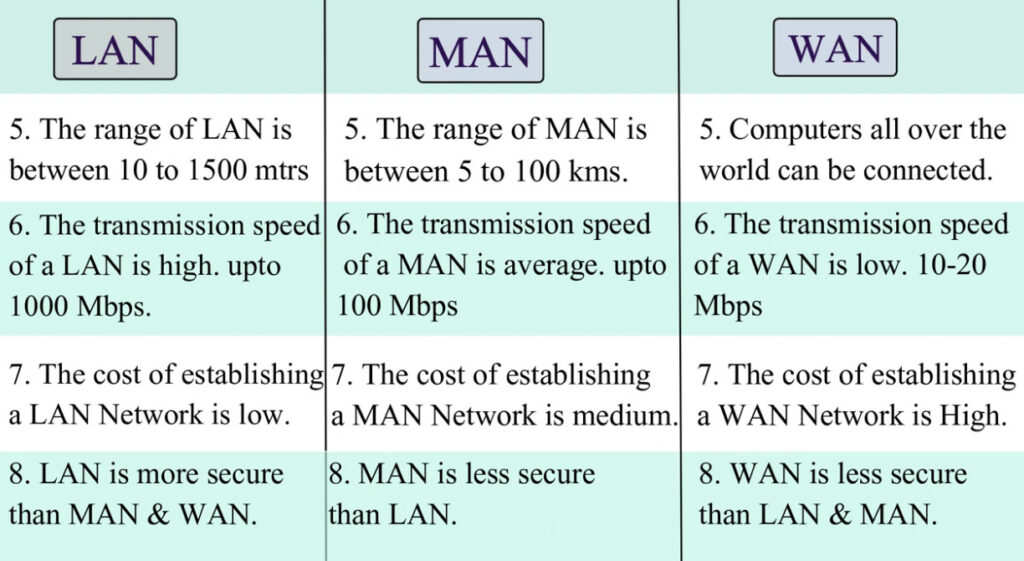
- A MAN typically covers a city or a metropolitan area (ranging from several kilometers to a few hundred kilometers).
- It connects different buildings, offices, or campuses within a city.
Speed:
- MANs typically offer moderate speeds, which are faster than WANs but slower than LANs.
- Technologies such as fiber-optic cables or high-speed broadband connections are commonly used for faster data transmission.
Ownership:
- A MAN can be owned and operated by a single organization, or it can be managed by a telecommunication company or ISP (Internet Service Provider) that provides connectivity to businesses or consumers in a metropolitan area.
Purpose:
- The primary purpose of a MAN is to connect multiple LANs within a city or region, allowing for the sharing of data and resources like internet access, printers, or file servers.
- It is also used by businesses to interconnect multiple offices, data centers, or campuses spread across a metropolitan area.
Technology:
- Fiber optics, Wi-Fi, leased lines, and other high-speed technologies are often used to build a MAN.
- The network typically relies on high-bandwidth communication links for large data transfer.
Examples:
- A MAN could connect several university campuses within a city.
- It could also be used by a company with multiple branches within a metropolitan area.
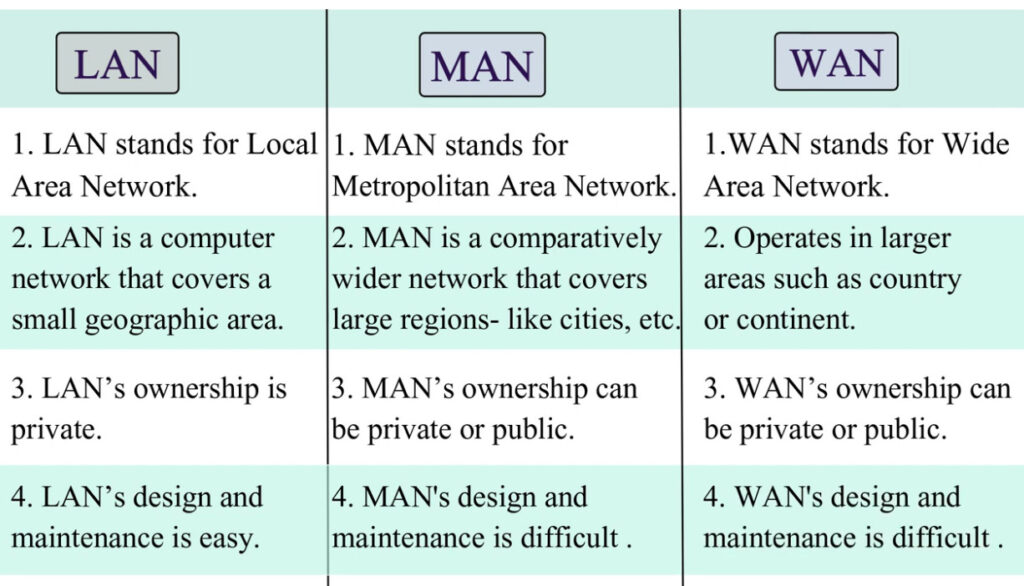
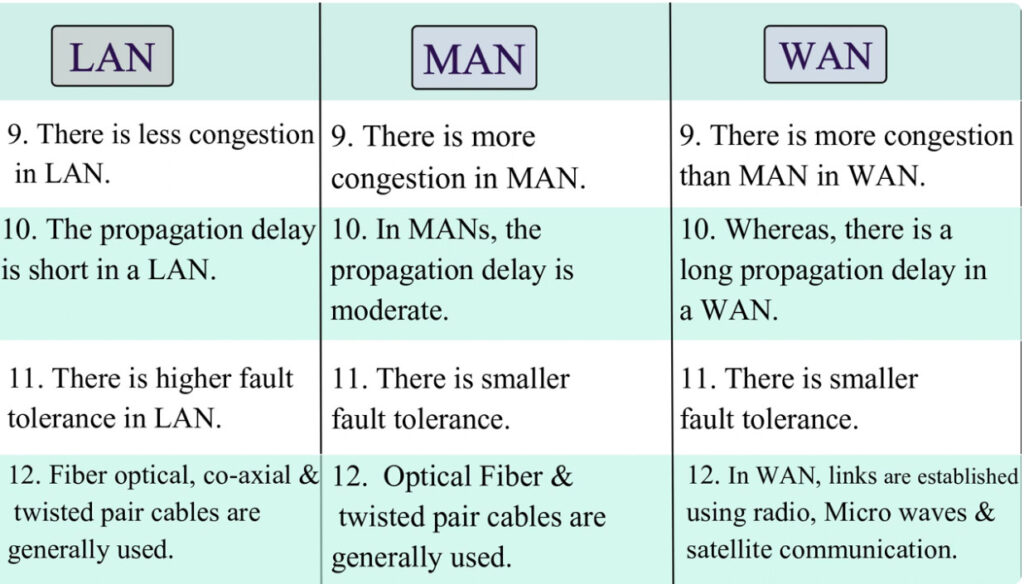
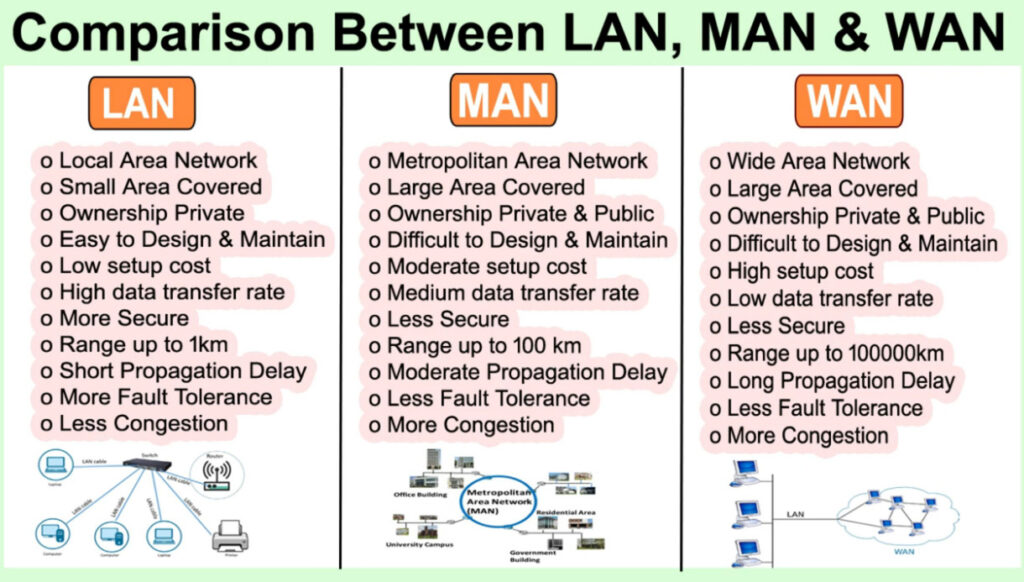
Comparison with Other Networks:
- LAN (Local Area Network): A LAN covers a small area (like a home or office), while a MAN covers a city or metropolitan area.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): A WAN spans much larger distances, such as across countries or continents, while a MAN is localized within a city or region.
Summary:
A MAN is a medium-sized network that connects LANs within a metropolitan area, offering moderate speed and higher capacity than a LAN but typically covering less area than a WAN. It is ideal for businesses or organizations that need to interconnect multiple locations in a city, providing efficient communication and resource sharing.