- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
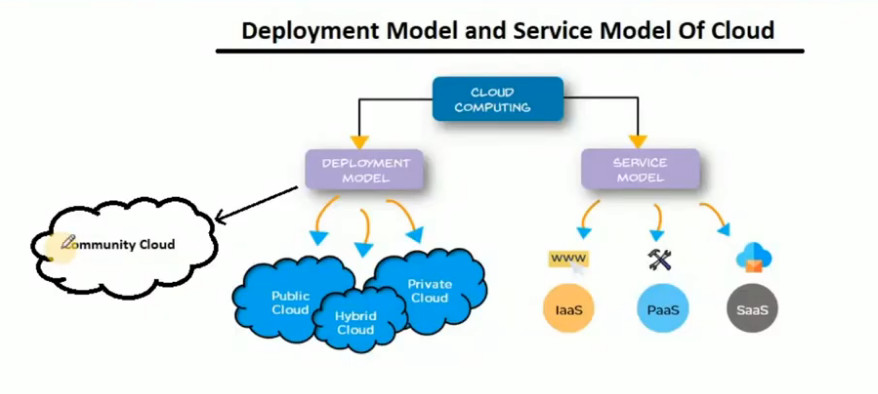
In cloud computing, deployment models define how cloud resources are made available to users and organizations. These models determine the level of control, security, and access that users have to the cloud environment. The four primary deployment models are:
Each model offers distinct advantages and is suitable for different use cases based on the organization’s needs, budget, and security requirements.
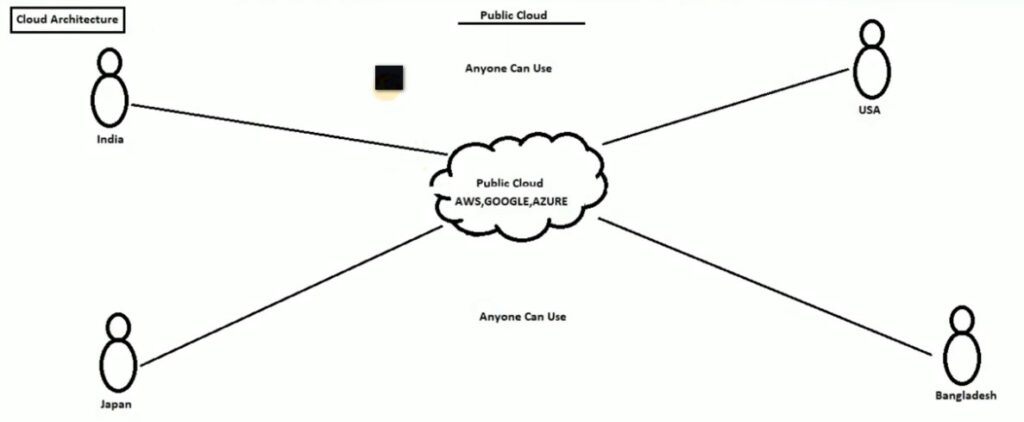
Definition: In the public cloud model, cloud services and infrastructure are owned and operated by a third-party cloud provider and made available to the general public or a large industry group. Resources (like servers, storage, and applications) are shared among multiple organizations (tenants).
Key Features:
Examples:
Use Cases:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
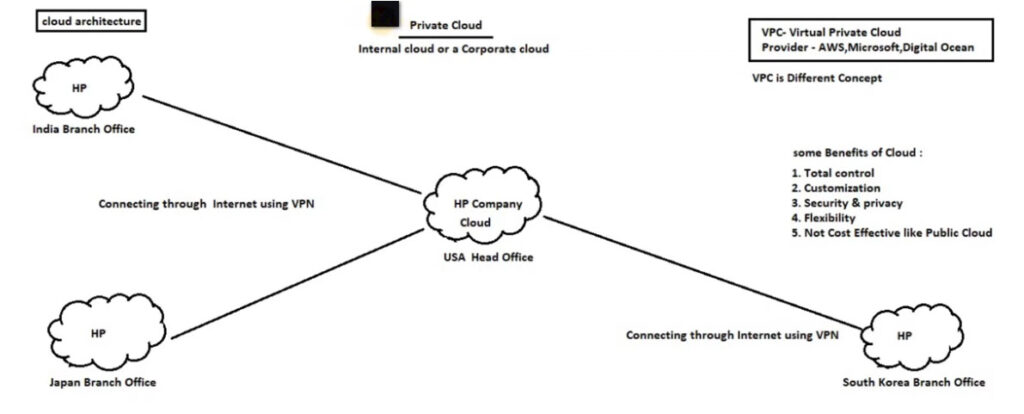
Definition: A private cloud is a cloud environment used exclusively by one organization. It can either be hosted on-premises (on the organization’s own hardware) or by a third-party provider. The key characteristic of the private cloud is that the infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization, providing more control over security, privacy, and performance.
Key Features:
Examples:
Use Cases:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
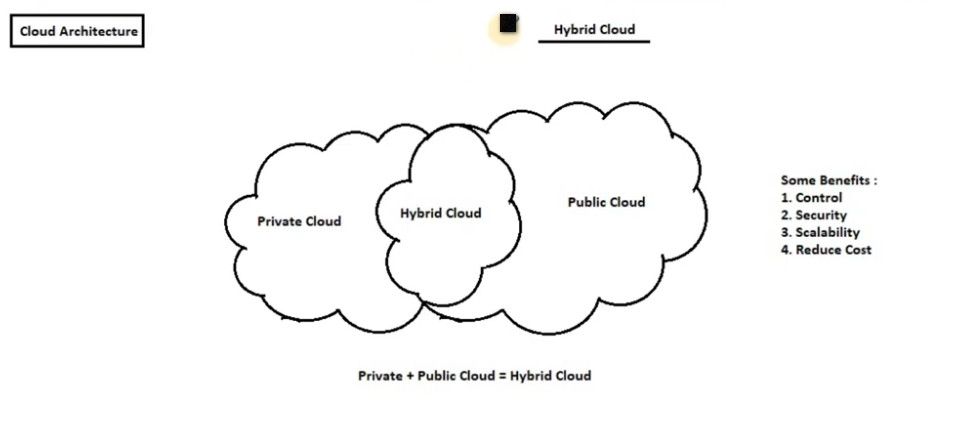
Definition: The hybrid cloud model combines both public and private cloud environments, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This model offers the flexibility to use the public cloud for less-sensitive workloads while maintaining private cloud resources for critical or sensitive data.
Key Features:
Examples:
Use Cases:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
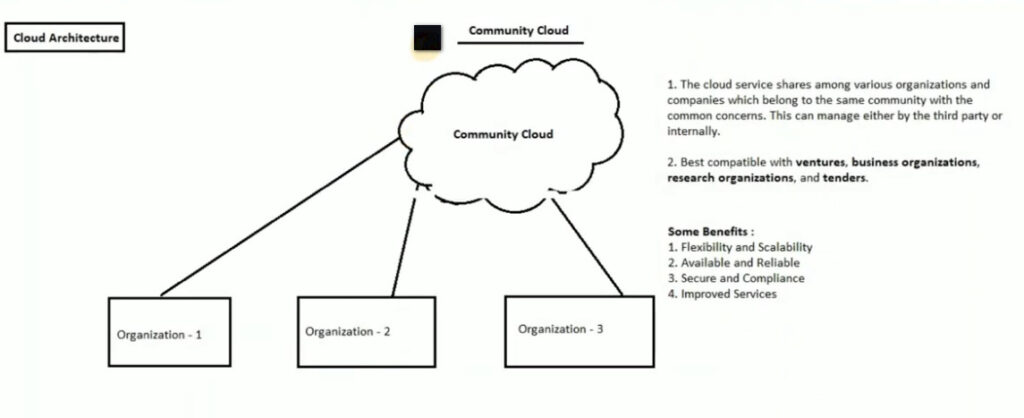
Definition: A community cloud is shared by several organizations with common concerns, such as security, compliance, or regulatory requirements. These organizations share the cloud infrastructure and resources while maintaining separate instances.
Key Features:
Examples:
Use Cases:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
| Deployment Model | Description | Best For | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Shared infrastructure by multiple organizations. | Small businesses, websites, mobile apps, scalable workloads. | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud. |
| Private Cloud | Exclusive infrastructure for one organization. | Large enterprises, sensitive data handling, compliance. | VMware, OpenStack, Microsoft Azure Stack. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combination of public and private clouds. | Businesses needing flexibility, scalability, and data security. | AWS Hybrid, Microsoft Azure Hybrid, Google Anthos. |
| Community Cloud | Shared infrastructure for organizations with common concerns. | Industry-specific groups (e.g., healthcare, government). | Government clouds, healthcare-specific clouds. |
The choice of cloud deployment model depends on an organization’s specific needs, including security, compliance, budget, scalability, and performance requirements. Public clouds are ideal for cost-effective, scalable solutions, while private clouds offer greater control and security. Hybrid clouds provide flexibility by allowing businesses to use both public and private cloud resources, and community clouds offer shared infrastructure for organizations with common concerns.