- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
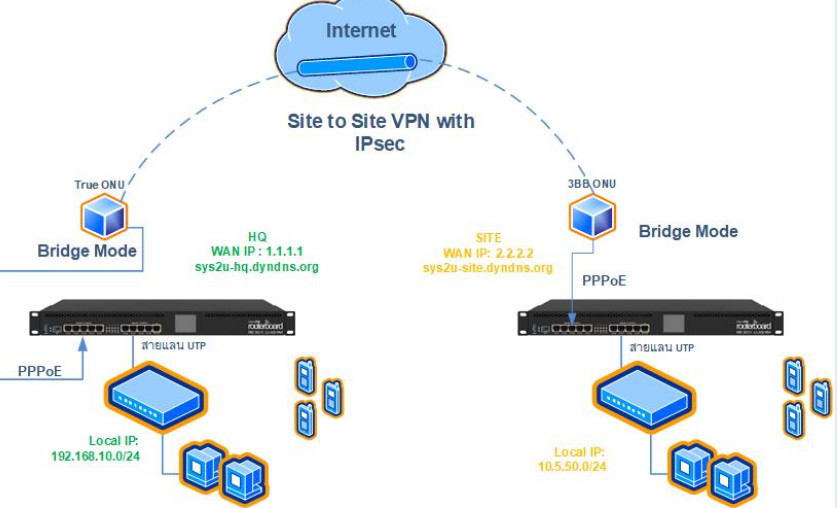
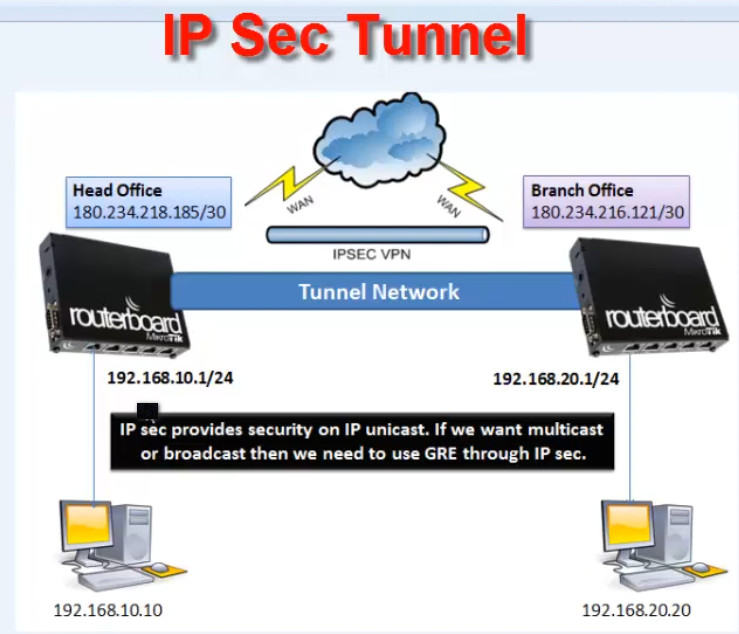
Setting up a Site-to-Site IPsec VPN on MikroTik routers allows two remote networks to securely communicate over the internet using encrypted tunnels. This setup involves creating an IPsec tunnel between two MikroTik routers at different locations, ensuring secure and private data transmission between them.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to configure a MikroTik Site-to-Site IPsec VPN:
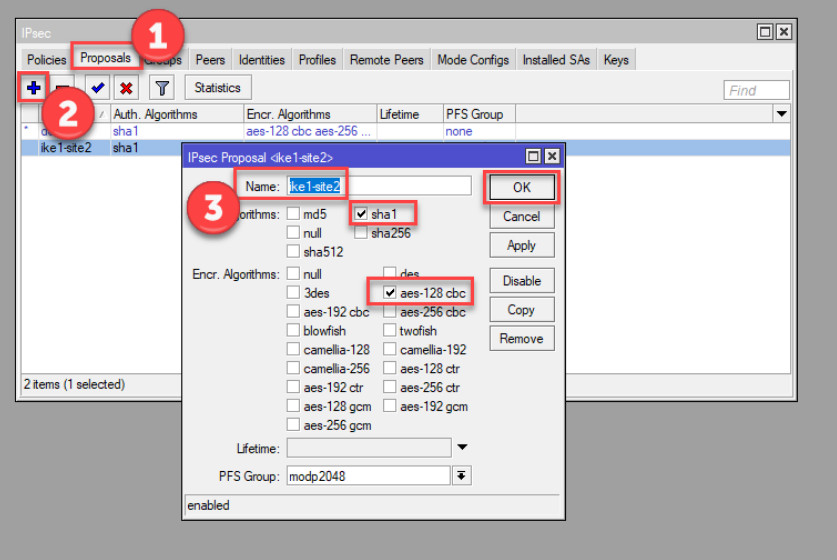
The proposal defines the encryption and hashing methods for the IPsec tunnel.
Go to IP > IPsec > Proposals.
Click on Add (plus sign) to create a new proposal.
Configure the following settings:
vpn-proposalsha256 (or use sha1 if needed).aes-256 (or aes-128 as an alternative).none or choose an appropriate PFS group.1d (you can adjust as per requirement).Click Apply and OK.
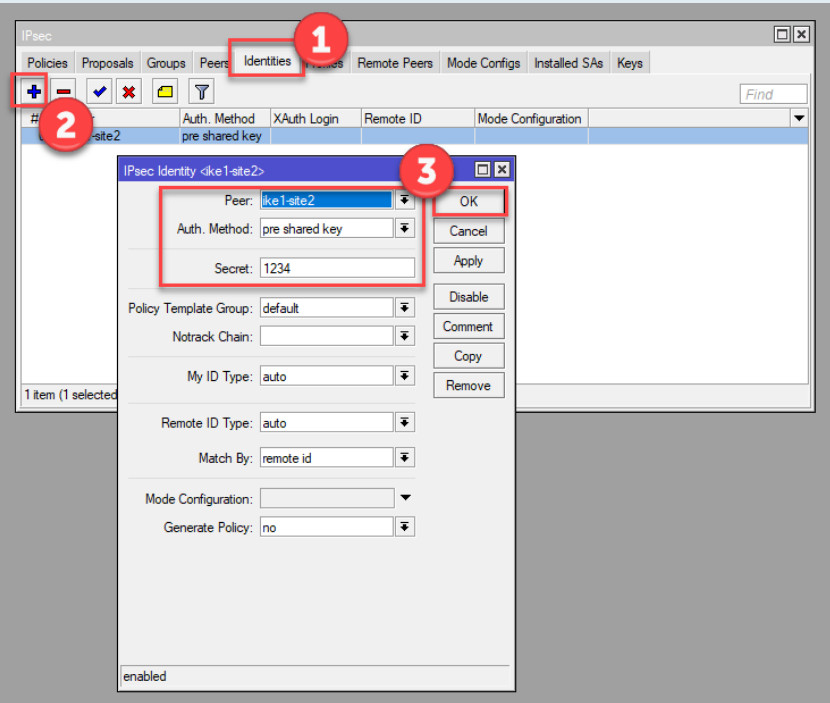
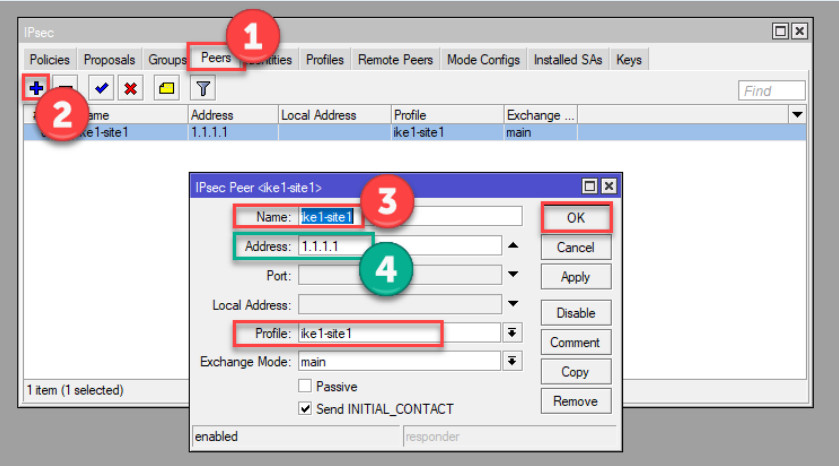
The peer defines the remote router’s IP address (the remote endpoint for the tunnel).
Go to IP > IPsec > Peers.
Click Add (plus sign).
Configure the following settings:
192.168.2.1).500 (default for IKE).pre-shared key.main.auto (or specify a static ID if necessary).strict.yes.Click Apply and OK.
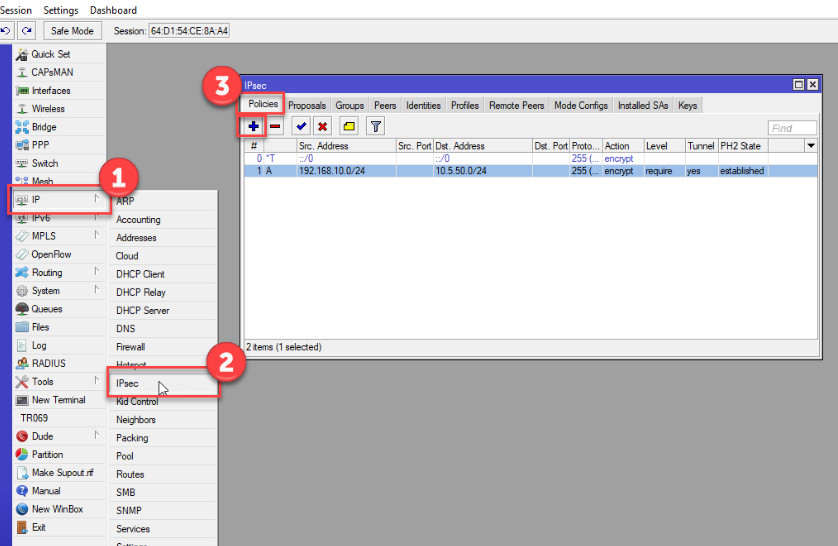
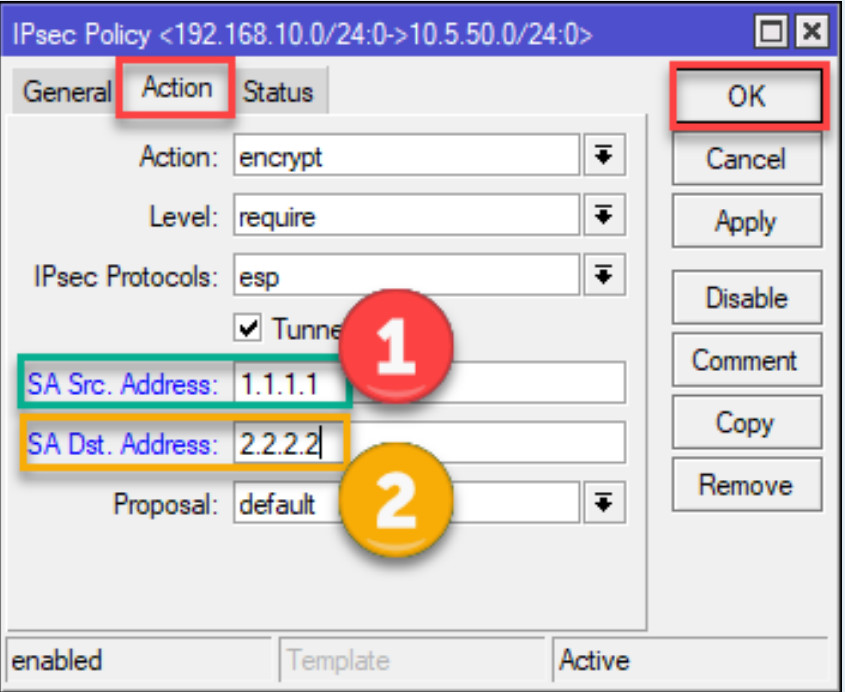
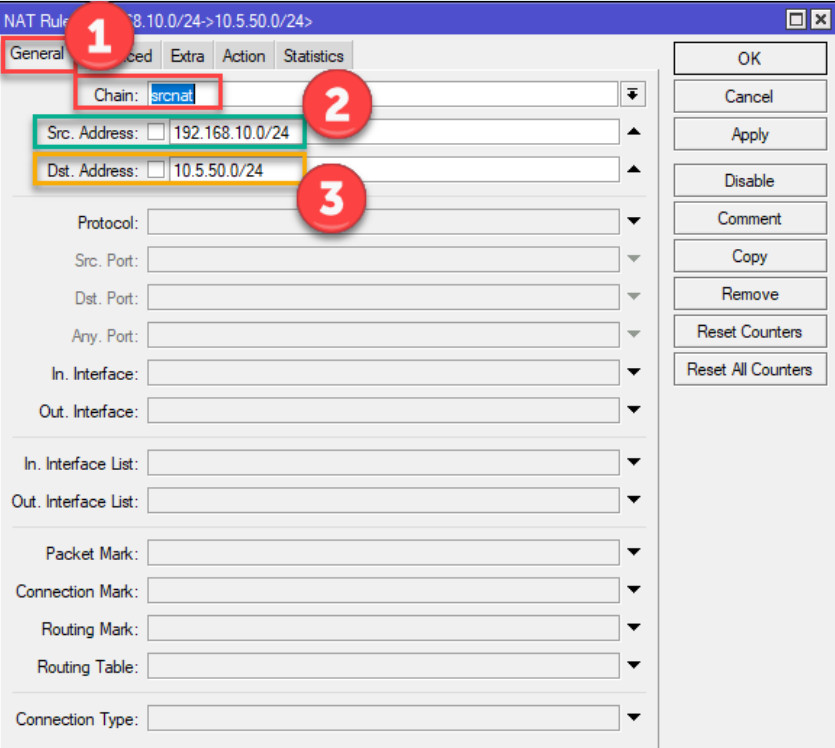
The policy defines the traffic that will be encrypted and routed through the VPN tunnel.
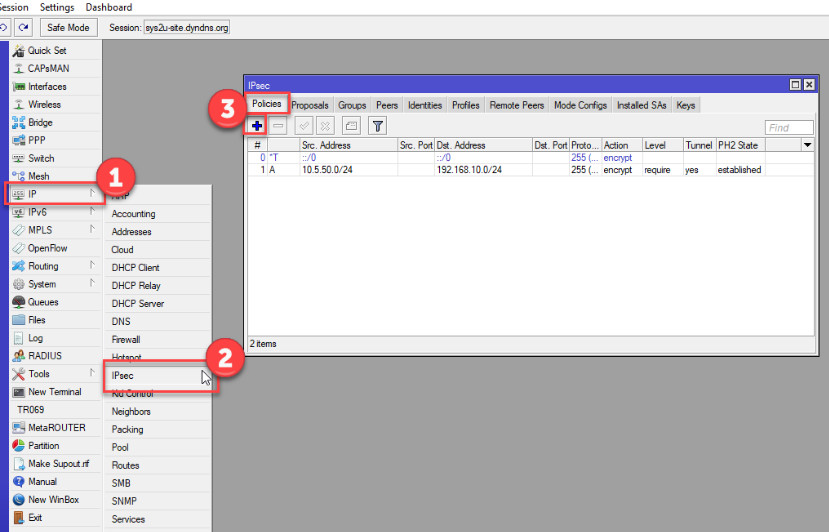
Go to IP > IPsec > Policies.
Click Add (plus sign).
Configure the following settings:
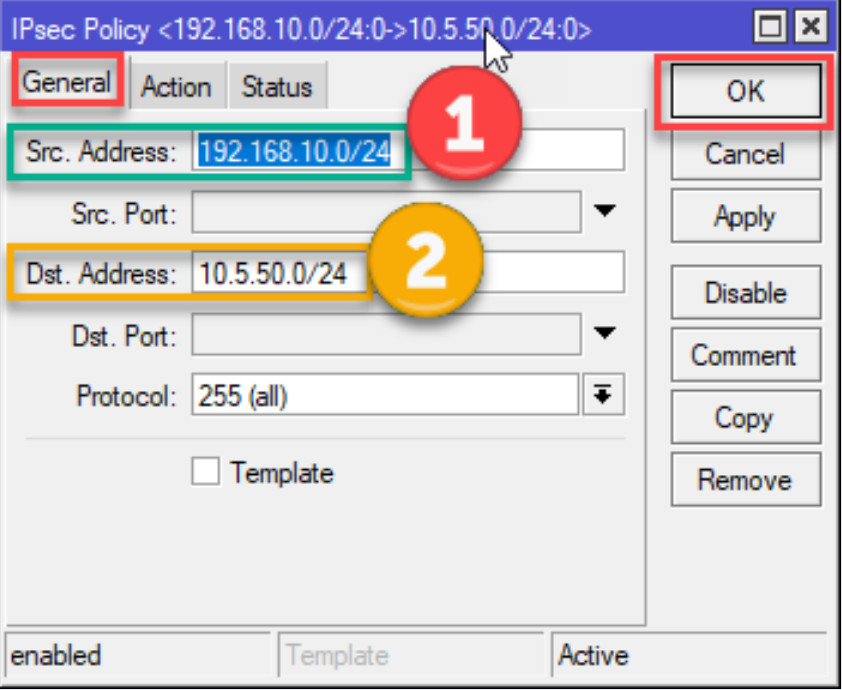
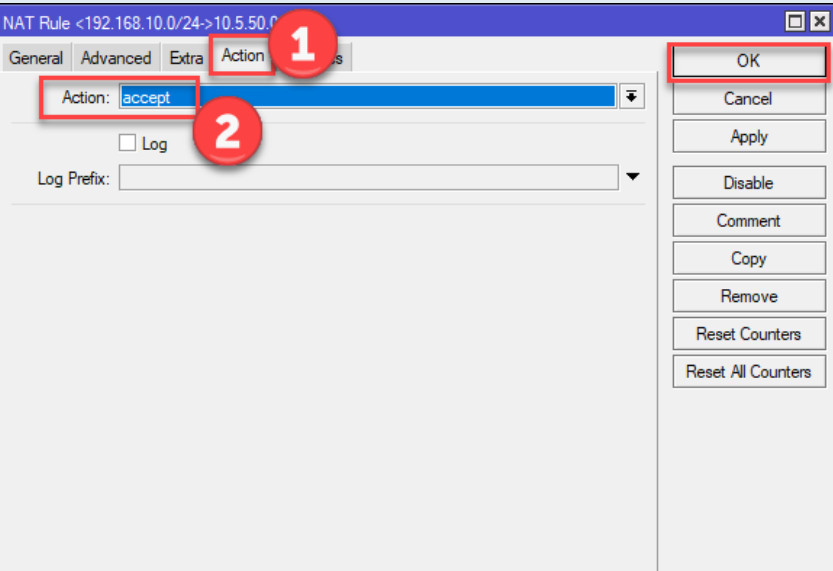
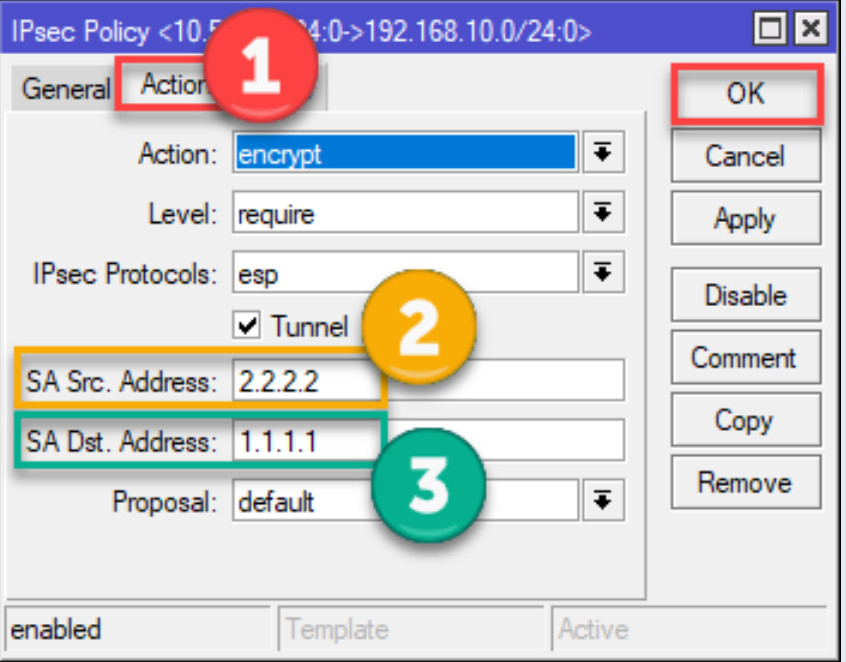
192.168.1.0/24).192.168.2.0/24).all (or specify tcp or udp if needed).encrypt.require.vpn-proposal you created earlier.Click Apply and OK.
Ensure the IPsec service is enabled on Router A.
Repeat the same steps as for Router A to create an IPsec proposal with matching settings:
vpn-proposalsha256 (or sha1)aes-2561d (or your choice)On Router B, set up the IPsec peer pointing to Router A:
Go to IP > IPsec > Peers.
Click Add (plus sign).
Configure the following settings:
192.168.1.1).500.pre-shared key.main.auto.strict.Click Apply and OK.
On Router B, configure the IPsec policy:
Go to IP > IPsec > Policies.
Click Add (plus sign).
Configure the following settings:
192.168.2.0/24).192.168.1.0/24).all.encrypt.require.vpn-proposal you created.Click Apply and OK.
Ensure the IPsec service is enabled on Router B as well.
Once the configuration is complete on both routers, you should verify that the tunnel is established.
Go to IP > IPsec > Active Peers.
Ping Test:
Check IPsec Logs:
Log > IPsec).NAT Traversal (NAT-T): If your routers are behind NAT devices (like a home router), you may need to enable NAT-T on both routers under IP > IPsec > Settings.
Routing: Ensure that static routes or dynamic routing protocols (like OSPF, if needed) are set up to route traffic between the local and remote networks.
Firewall Rules: Ensure that necessary firewall rules are in place to allow IPsec traffic (UDP port 500 for IKE, UDP port 4500 for NAT-T, and protocol ESP).
This setup should establish a secure Site-to-Site IPsec VPN between two MikroTik routers.