- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
MBR vs. GPT, What Makes GPT Surpass MBR
When it comes to comparing MBR with GPT, the GPT disk surpasses the MBR disk in many aspects, for example:
To learn more about the difference between MBR and GPT, visit MBR vs.GPT
Hence, converting MBR to GPT is necessary for most new Windows system fans to fulfill different demands.
When dealing with disk partitioning and boot management, GPT (GUID Partition Table) and MBR (Master Boot Record) are two different partitioning schemes used to define how data is organized on storage devices (such as hard drives or SSDs). Here’s an overview of each:
MBR is an older partitioning scheme that has been used since the 1980s. It is supported by almost all operating systems but has limitations in terms of disk size and number of partitions.
GPT is a more modern partitioning scheme and part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) standard, which has gradually replaced the older BIOS systems in newer computers. It overcomes many of MBR’s limitations.
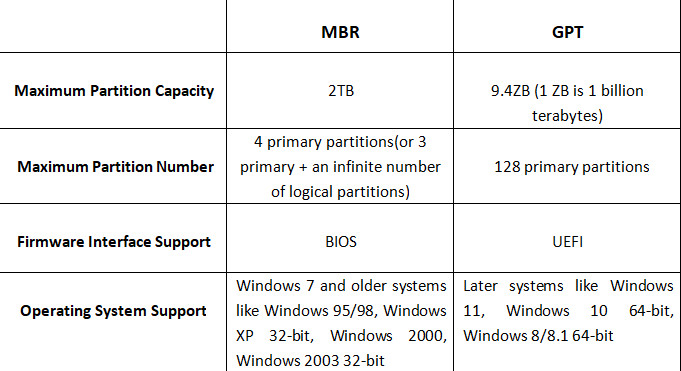
| Feature | MBR (Master Boot Record) | GPT (GUID Partition Table) |
|---|---|---|
| Max Disk Size | 2 TB | 9.4 ZB (theoretically) |
| Max Partitions | 4 primary partitions (or 3 + 1 extended) | 128 partitions (on Windows) |
| Partition Structure | 32-bit, 4 primary or 3 primary + extended | 64-bit, GUID for each partition |
| Boot Mode | BIOS-based booting | UEFI-based booting |
| Partition Table Location | One copy at the beginning of the disk | Multiple copies (beginning and end of disk) |
| Backup Partition Table | No backup | Yes, redundancy for better protection |
| Support for Large Disks | No (limited to 2 TB) | Yes (supports disks >2 TB) |
| UEFI Support | No (only works with BIOS) | Yes (required for Secure Boot and modern systems) |
| OS Compatibility | Widely compatible with older systems | Supported by newer systems, some older OS may not support GPT |
In general, for modern systems and larger disks, GPT is the preferred choice, while MBR is mostly used for compatibility with older hardware and software.

No matter whether you know MBR and GPT, you must have encountered such a situation. Your disk has 4TB of space, but you can only use 2TB of space. Why does a 4TB hard drive only show 2TB? This is because MBR only supports up to 2TB volume size and 4GB file size. Unlike MBR disk, GPT disk doesn’t have such limitations. You can see their difference in this table.
Converting from MBR (Master Boot Record) to GPT (GUID Partition Table) can offer several significant advantages, particularly for modern computing environments. Here are the key reasons why one might consider converting MBR to GPT:
 Overcoming Storage Limitations: GPT supports much larger disk sizes, up to 9.4 zettabytes (ZB), compared to MBR’s 2 terabytes (TB) limit. This makes GPT more suitable for modern high-capacity drives.
Overcoming Storage Limitations: GPT supports much larger disk sizes, up to 9.4 zettabytes (ZB), compared to MBR’s 2 terabytes (TB) limit. This makes GPT more suitable for modern high-capacity drives. Number of partitions: GPT allows up to 128 primary partitions, while MBR is limited to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary and 1 extended partition. This provides greater flexibility in organizing data and partitioning drives.
Number of partitions: GPT allows up to 128 primary partitions, while MBR is limited to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary and 1 extended partition. This provides greater flexibility in organizing data and partitioning drives. Compatibility with modern systems: GPT works with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which is the modern replacement for BIOS. This enables faster boot times and better security features.
Compatibility with modern systems: GPT works with UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which is the modern replacement for BIOS. This enables faster boot times and better security features.After learning why GPT exceeds MBR, let’s explore how to convert MBR to GPT without losing data.
The Diskpart tool can convert MBR to GPT in CMD. However, when changing the disk to GPT, Diskpart will delete all files and folders from your hard drive. After backing up the files, follow the steps below to use Diskpart in CMD to convert MBR to GPT.
Step 1. Type CMD in the Search box. Right-click Command Prompt and choose “Run as administrator”. If CMD isn’t available, you can use PowerShell instead.
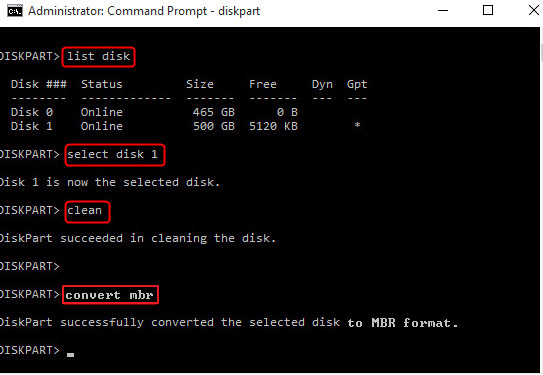
Step 2. Open Command Prompt, type DiskPart, and press Enter.
Step 3. Type list disk and press Enter. (Note down the number of the disk you which you want to convert to GPT)
Step 4. Type select disk X. (Replace the X with the correct number of your hard drive)
Step 5. Now type clean and press Enter. This command will remove all the files and partitions from your hard drive, so back up all important files in advance.
Step 6. Type convert gpt and press Enter.
This method is not suitable for computer beginners. If you mistakenly cleaned a partition using DiskPart, you can undo DiskPart clean to retrieve your files.
To Convert GPT to MBR Using Command Prompt:
Similar to using CMD, you also need to delete all partitions on your disk using Disk Management. Before you convert the disk from MBR to GPT or from GPT to MBR, you should back up your disk. If you want to recover a deleted partition, you can use a partition recovery software tool to get your lost data and partition back.
To Convert MBR to GPT:
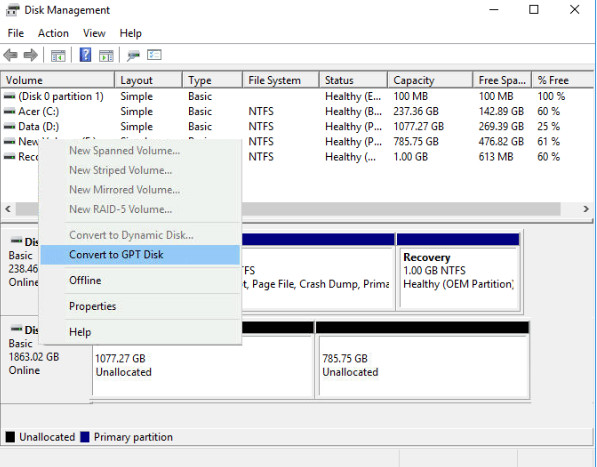
Step 1. Right-click on “This PC“, choose “Manage“, then head to “Disk Management”.
Step 2. Right-click the volumes on your target disk and choose “Delete Volume…”
Step 3. When your disk becomes empty (shows as unallocated space), right-click your disk and choose “Convert to GPT Disk”.
To Convert GPT to MBR in Disk Management:
1. How do I change from GPT to MBR for free?
2. Can I convert MBR to GPT without formatting?
Yes, the way to convert MBR to GPT without formatting is to run a third-party MBR to GPT converter, EaseUS Partition Master.
3. How do I create a GPT partition in CMD?
Open Command Prompt and type the following commands:
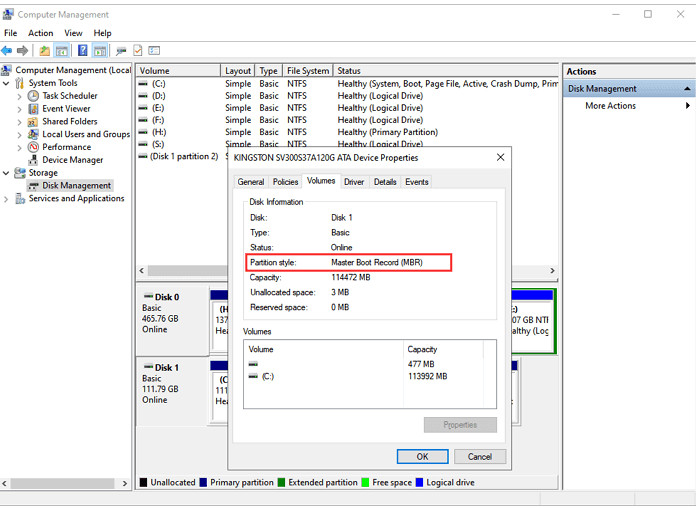
Under Windows Disk Management, you can check the partitioning scheme of a hard drive:
Step 1. Right-click “This PC” and choose “Manage”.
Step 2. Go to “Disk Management”.
Step 3. Right-click the disk you want to check and choose “Properties”.
Step 4. Go to the “Volumes” tab and you will see the partition style under the disk information.
MBR, Master Boot Record, is an older disk-type first introduced with IBM PC DOS 2.0 in 1983. It’s named after the boot sector located at the very beginning of a drive (the first sector) called MBR. Here is a simplified structure of an MBR disk.
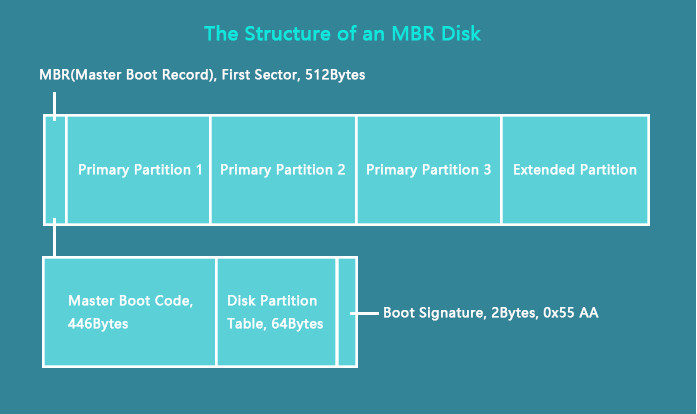
The first sector on both an MBR disk and a GPT disk is the MBR sector. It takes up 512bytes and contains the master boot code (446bytes), disk partition table (DPT, 64bytes), and the boot signature (2bytes) which marks the end of the MBR sector. The information in this sector describes how the partitions are organized on the current storage device. Thus, when it’s corrupted, you won’t be able to use the disk until you rebuild MBR.
To use a disk for data storage, you need to divide it into chunks called partitions. Partitions can be categorized as primary partitions and extended partitions on an MBR disk. Primary partitions are those you can install the operating system on and make active in order to boot the computer from it. Excluding the space taken by primary partitions, the space left on a disk is called an extended partition. Unlike a primary partition, an extended partition is a storage unit that you can only use to create multiple logical drives/partitions, and the extended partition doesn’t have any drive letter or file system. It’s more like a container for 1 or more logical partitions that have driver letters and file systems.
Since the disk partition table is 64bytes in total and the information of each partition is 16bytes, you can create at most four primary partitions. If you prefer more than four partitions on the disk, you should make one primary partition an extended partition to create logical partitions. (Within the extended partition, you can create multiple logical drives.)
The most obvious disadvantage of an MBR disk is that it only works with a maximum size of 2TiB(≈2.2TB) on a disk. That means if you have a disk larger than 2TiB with the MBR partition style, you can only use at most 2TiB space on it.
GPT, GUID Partition Table, is the newer standard compared to MBR first introduced as part of the UEFI initiative. Compared with the MBR partitioning scheme, it’s more flexible and has better compatibility with modern hardware.
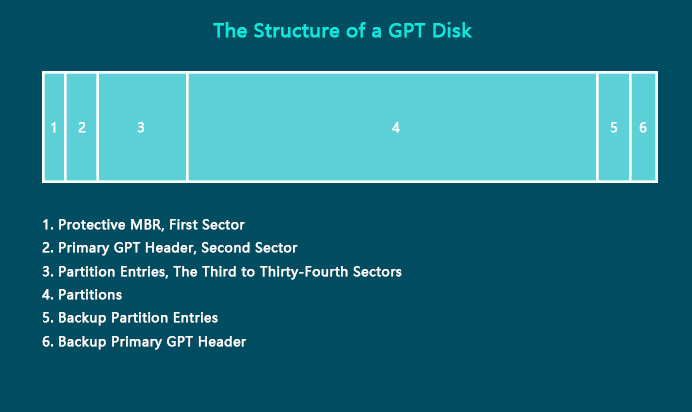
The first sector on a GPT disk is also the MBR sector. Different from the one on an MBR disk, the protective MBR on a GPT disk serves the function of preventing tools that only supports MBR disks from misrecognizing and overwriting GPT disks.
The second sector on a GPT disk stores the primary GUID partition table header. It defines the location and size of the partition entries that consist of the partition table and the cyclic redundancy check (CRC32) checksum that is used to verify the integrity of the GPT header. When CRC detects data corruption, it will attempt to recover the data using the backups stored at the end of the disk.
From the third sector to the thirty-fourth sector (32 sectors in total) are the partitions entries. Theoretically, you can create unlimited partitions on a GPT disk. However, the number of the partition you are able to create will be limited by the operating system. For example, under Windows, each partition entry is 128bytes, thus, you can create a maximum number of 128 (32*512/128=128) partitions under Windows. This is what differs a GTP disk from an MBR disk remarkably.
There is no extended partition or logical partitions on a GPT disk since there are no limits on how many primary partitions you can create.
GPT disks back up the primary GPT header and the partition entries automatically on the last sectors on the disk. That’s why GPT disks are safer and more reliable than MBR disks. When the GPT header or partition table is corrupted, these backups will be helpful to restore the data.
The difference in the structure of MBR and GPT decides they will differ in other aspects. Based on the structure and technique, an MBR disk and a GPT disk mainly vary in the supported boot mode and compatible operating systems.
It’s certainly true that almost all the computers running Windows boot up using one of the two ways, BIOS-MBR method or UEFI-GPT method. This indicates that an MBR disk only supports the legacy BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) mode and a GPT disk UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) mode.
Both BIOS and UEFI are essentially low-level software that starts when you power on your PC. BIOS is the more traditional way and UEFI the newer.
The Boot Process of BIOS:
The Boot Process of UEFI:
The Advantages of UEFI-GPT over BIOS-MBR
The limits of the BIOS-MBR method promote the appearance of the UEFI-GPT method. Due to BIOS’s MBR sector boot process, you can only boot from drives at most 2TiB in size. Besides, you will get a slower boot process using BIOS. Here are the benefits of UEFI:
In addition to the boot method, MBR disks and GPT disks also vary in the operating system supported. As mentioned, GPT is a newer partition scheme, which means there may be an incompatibility with old operating systems. Actually, except for 32-bit Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 editions, all versions of Windows, like Windows 10/8.1/7/XP/Vista, can read and write GPT disks. However, to boot from the GPT disk, you need UEFI-based PCs. Similarly, almost all Windows editions can read and write MBR disks. To boot from an MBR disk, ensure the motherboard in the computer is BIOS or UEFI with BIOS mode.
Do you have a brief understanding of GPT and MBR now? Share this article and let more users know their difference.