- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
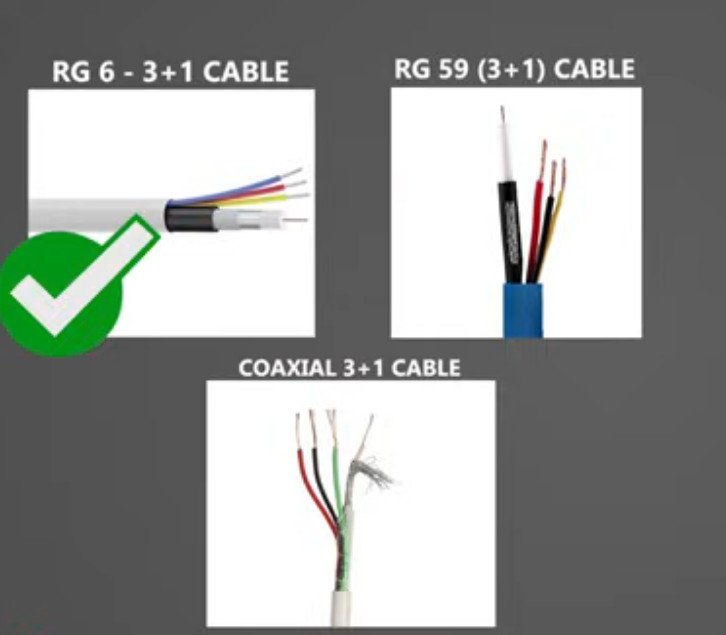
Coaxial cables, commonly referred to as RG6, RG59, and Coaxial 3+1 cables, are essential in various communication and video systems, including CCTV installations, cable TV, and internet connections. Let’s take a look at these three types of coaxial cables, their features, uses, and differences.
RG6 is a thicker, high-performance coaxial cable compared to RG59. It is commonly used for modern cable TV systems, satellite TV, and broadband internet connections. RG6 cables are designed for higher-frequency transmissions, providing better performance over longer distances.
RG59 is a thinner, more flexible coaxial cable that is often used in analog CCTV systems and shorter-distance video transmission. It is a standard choice for residential and low-bandwidth applications.
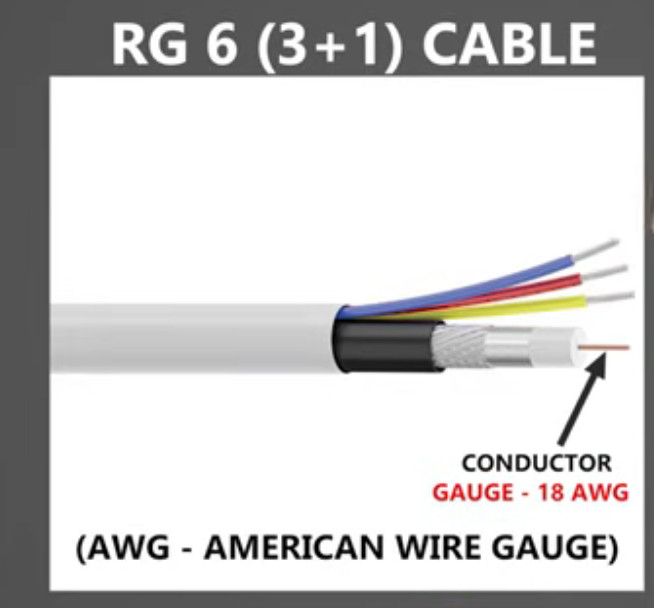
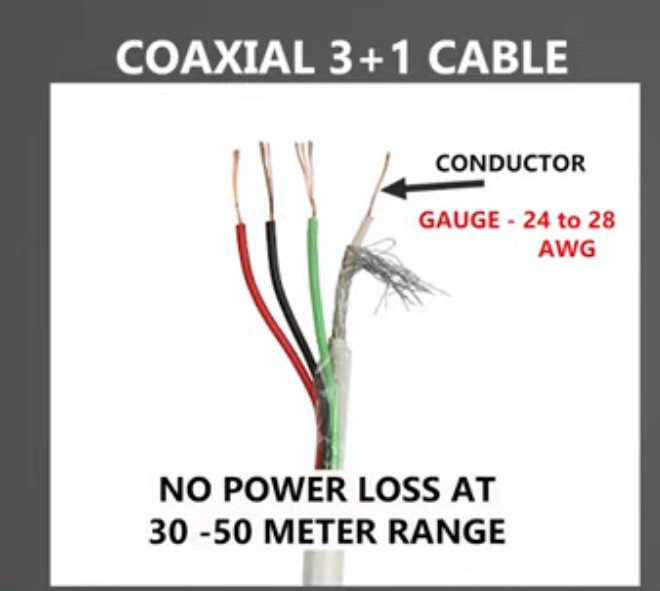
The Coaxial 3+1 cable is a type of cable that includes 3 coaxial cables (often RG59 or RG6) and an additional cable (the “+1” typically refers to a power cable). This configuration is commonly used in applications like CCTV systems where both power and video signals need to be transmitted over a single cable.
| Feature | RG6 Coaxial Cable | RG59 Coaxial Cable | Coaxial 3+1 Cable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Transmission | High-definition video, higher frequencies | Standard-definition video, lower frequencies | Video and power transmission combined |
| Impedance | 75 ohms | 75 ohms | 75 ohms (for coaxial cables) |
| Bandwidth | Up to 3 GHz | Up to 500 MHz | Depends on coaxial cables used |
| Cable Type | Thick, high-quality, less flexible | Thinner, more flexible | Typically includes RG59 or RG6 + additional power cable |
| Applications | Cable/satellite TV, broadband, CCTV (HD) | Analog CCTV, short-range video | CCTV, where both video & power are needed over a single cable |
| Signal Loss | Low, better over long distances | Higher, more loss over longer distances | Depends on coaxial cable type and distance |
| Power Delivery | Separate power cable needed | Separate power cable needed | Includes power cable (for CCTV cameras) |
For High-Definition CCTV Systems (HD and IP cameras): RG6 is the better choice due to its superior shielding, lower signal loss, and higher-frequency bandwidth. It’s especially useful for longer cable runs or higher-quality video transmission.
For Analog CCTV Systems (Standard-definition): RG59 is commonly used in analog CCTV systems. It’s suitable for shorter distances and is easier to work with because it’s more flexible.
For Systems Requiring Both Video and Power Over One Cable: Coaxial 3+1 Cable is ideal when you need to run both video and power to the cameras through a single cable, simplifying installation and reducing cable clutter. However, make sure that the power cable within the 3+1 configuration can handle the voltage and current required by your cameras.
When choosing between these cables, consider factors like the quality of video you need, the distance between devices, and the ease of installation.