- 8777701917
- info@saikatinfotech.com
- Basirhat W.B
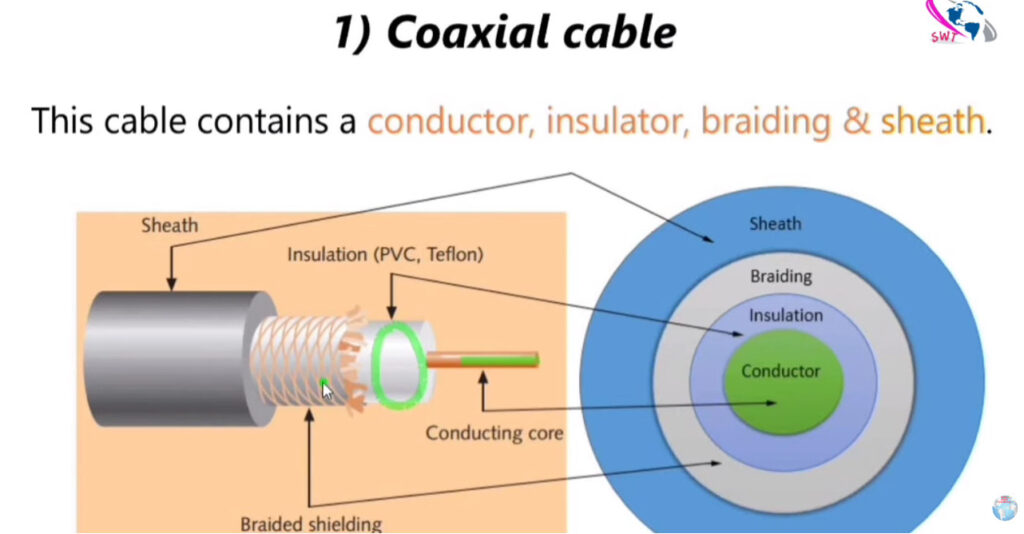
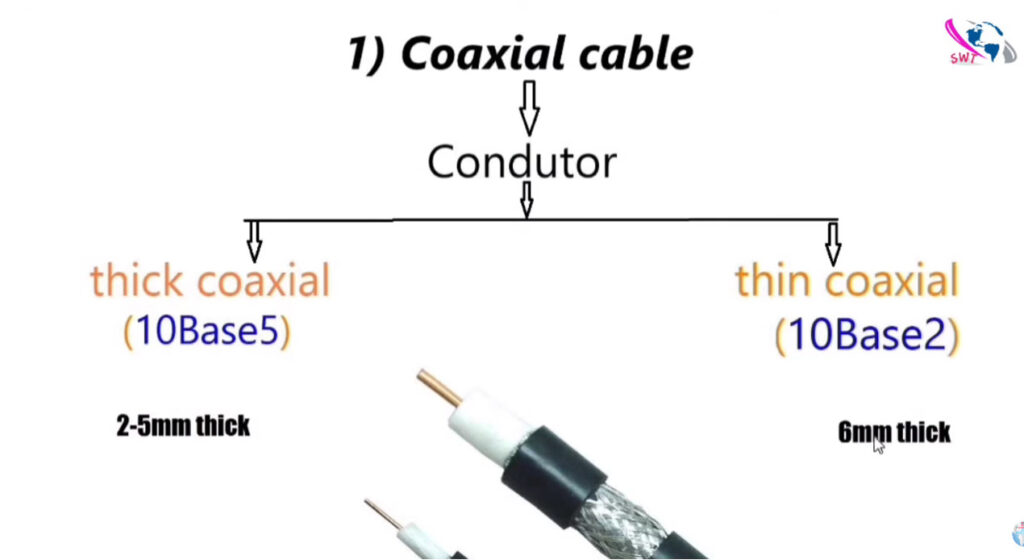
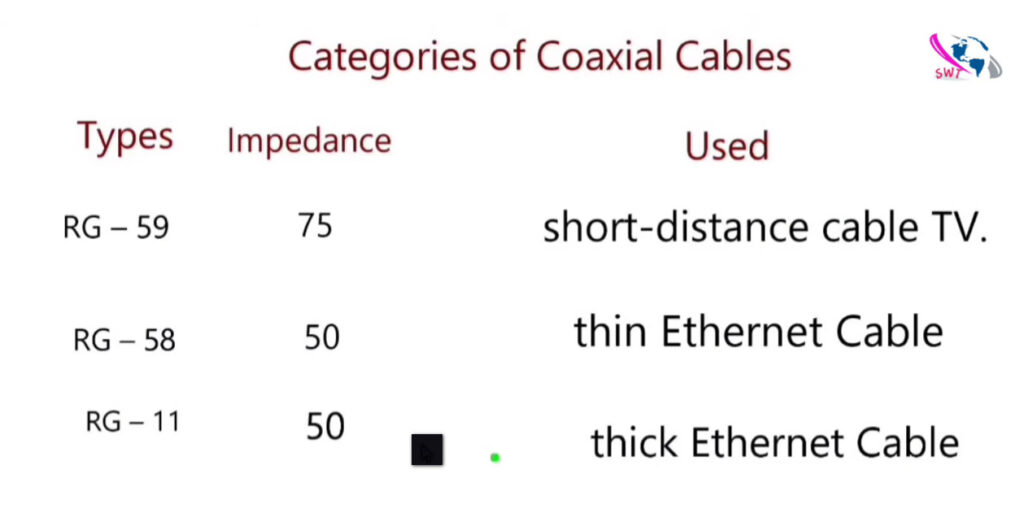
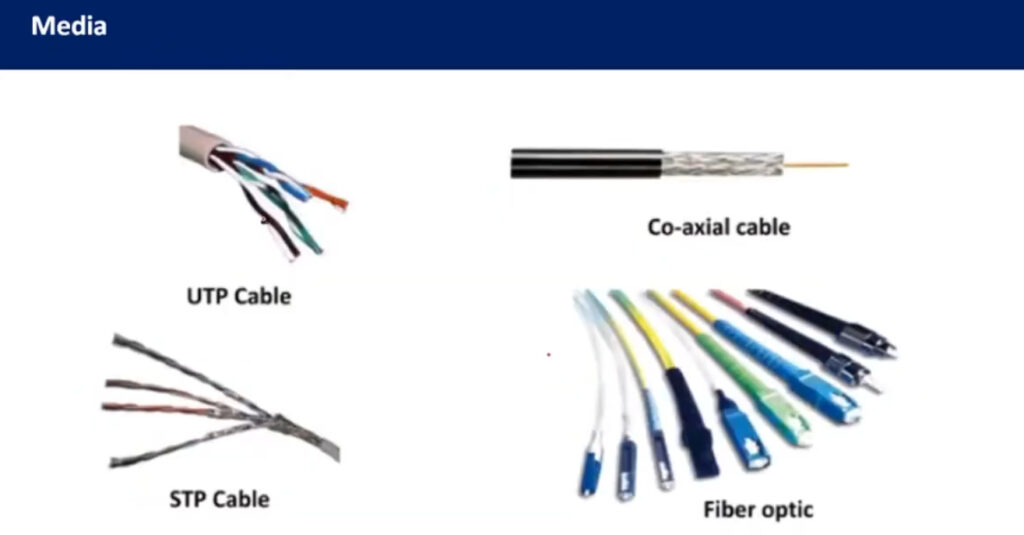
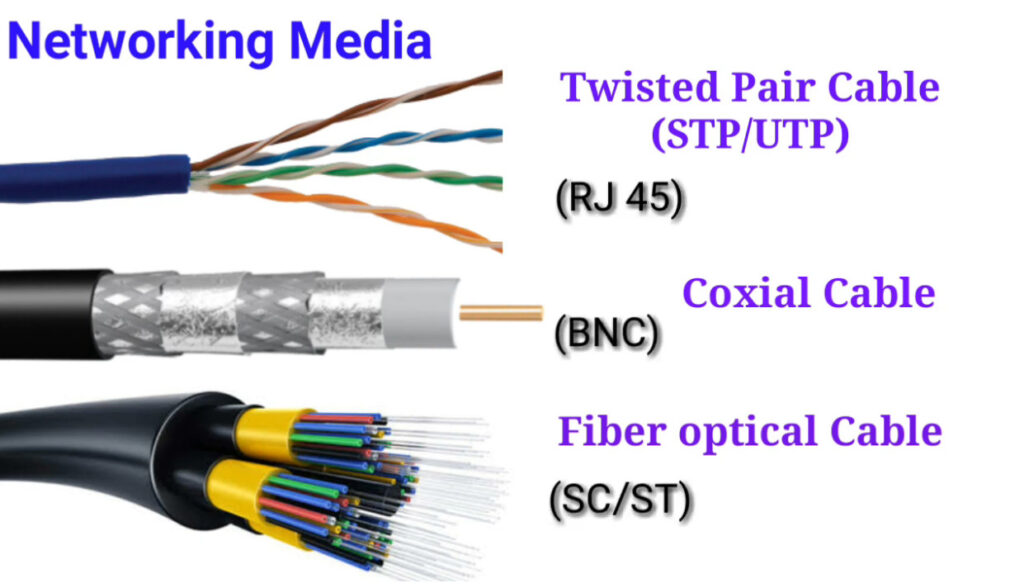
There are several types of networking cables, each designed for specific uses and environments. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
Each cable type has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the network—such as distance, speed, and environmental factors.
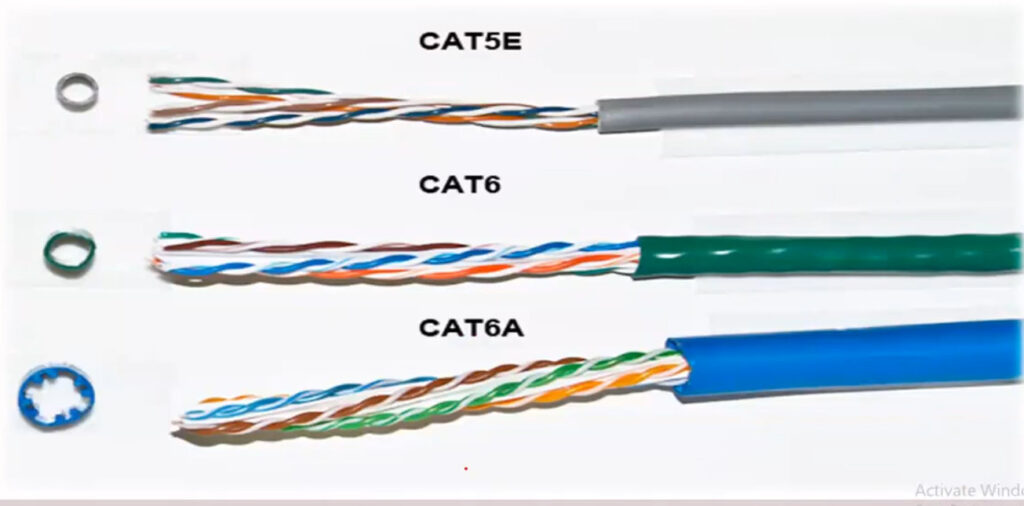
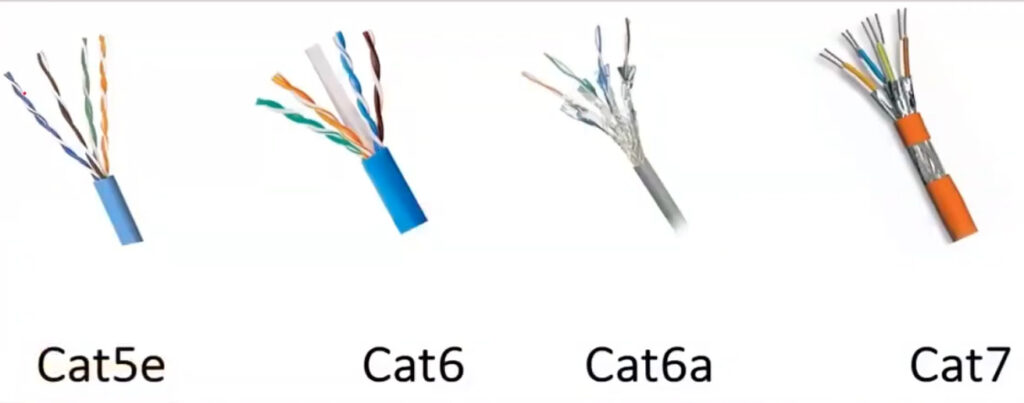

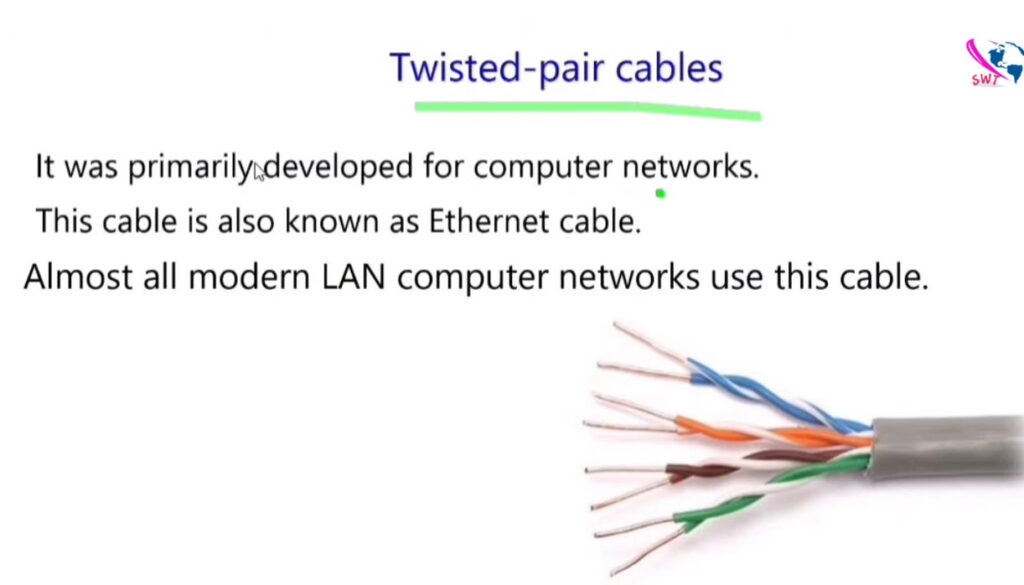
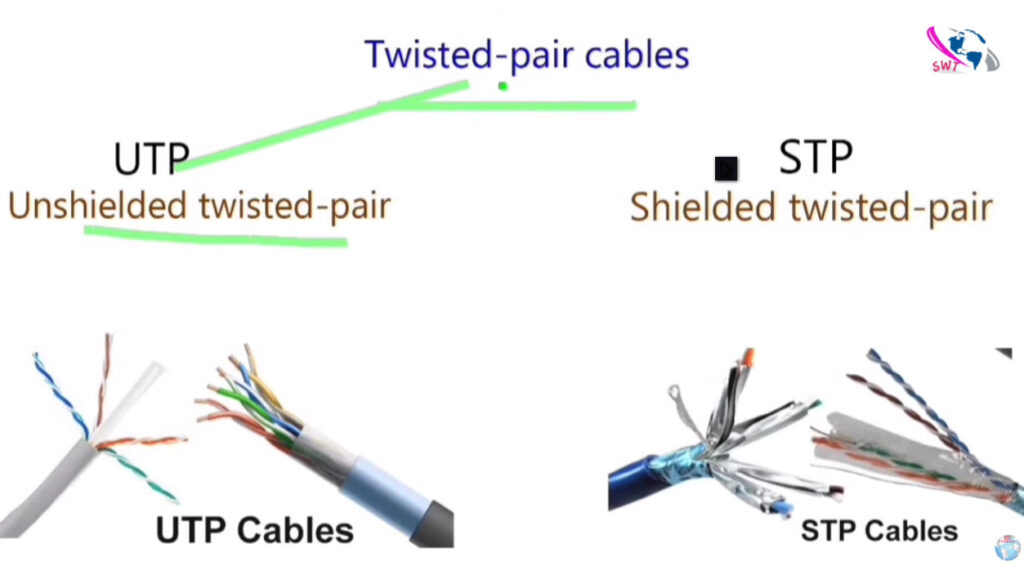
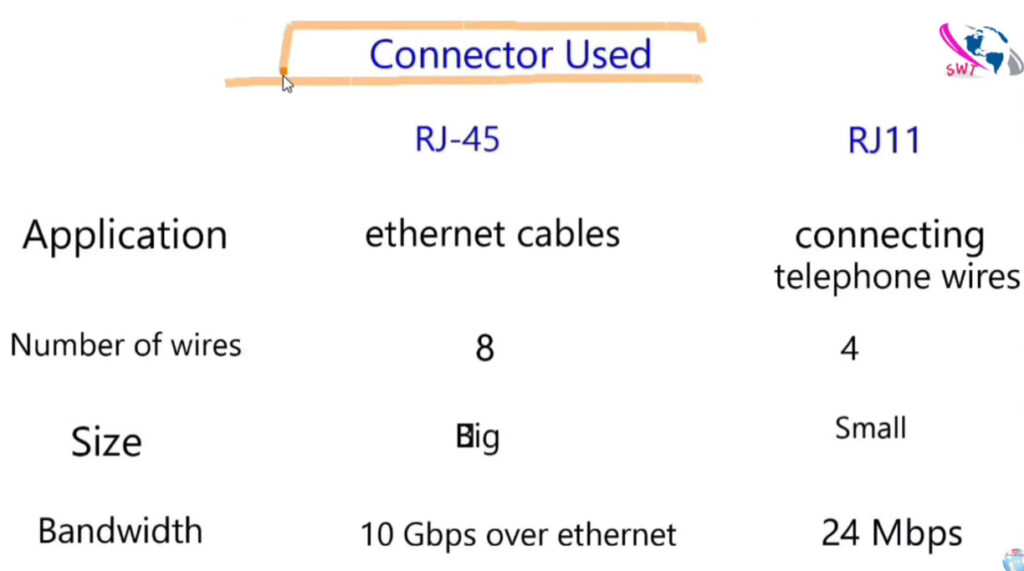
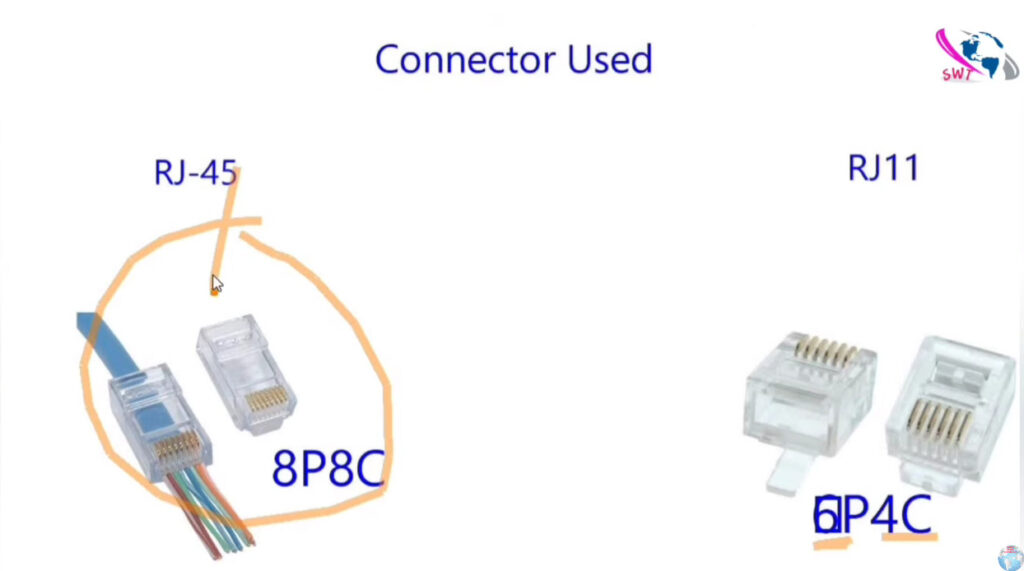



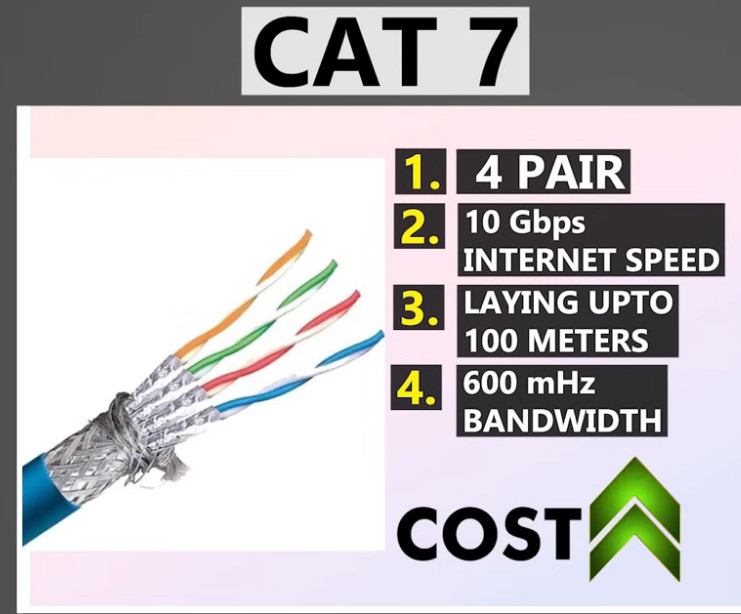
Here’s a detailed comparison of Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7 cables, which are all types of Ethernet cables used in networking.
| Category | Speed | Bandwidth | Max Length (100% Performance) | Common Use | Shielding |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat5 | 100 Mbps | 100 MHz | 100 meters | Older networks, now obsolete | Unshielded (UTP) |
| Cat5e | 1 Gbps | 100 MHz | 100 meters | Home networks, small offices | Unshielded (UTP) |
| Cat6 | 10 Gbps (short) | 250 MHz | 55 meters (10 Gbps) / 100 meters (1 Gbps) | Business, Gigabit and 10-Gigabit Ethernet networks | Unshielded (UTP), Shielded (STP/FTP) |
| Cat6a | 10 Gbps | 500 MHz | 100 meters | Data centers, enterprise networks, high-speed setups | Shielded (STP/FTP) |
| Cat7 | 10 Gbps | 600 MHz | 100 meters | High-performance environments, high EMI areas | Fully shielded (STP) |
Each type of cable provides a different level of performance depending on the needs of your network, with Cat5e being the most common and cost-effective option, while Cat7 is designed for environments where superior performance is necessary.








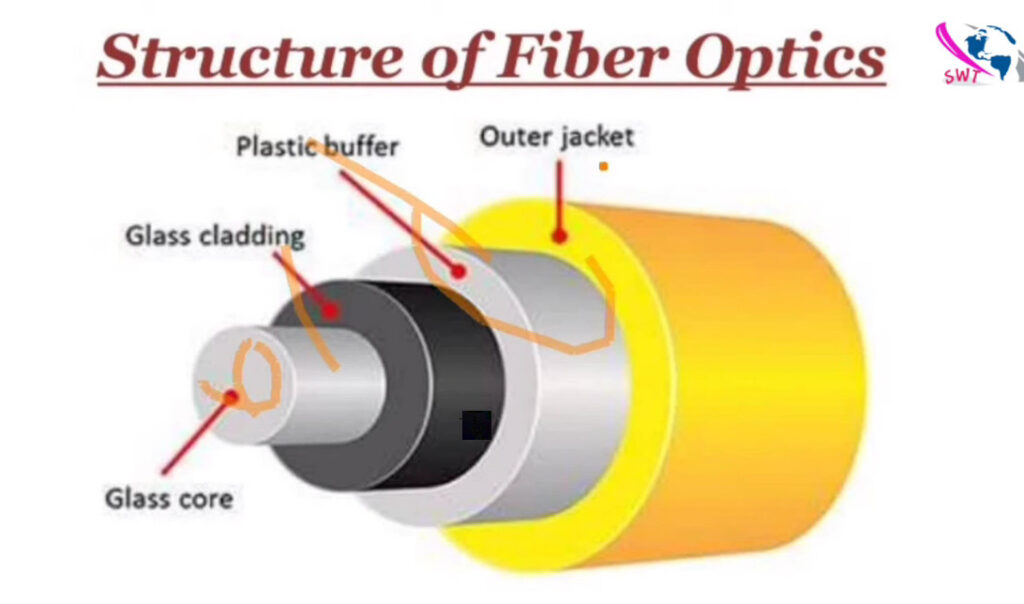
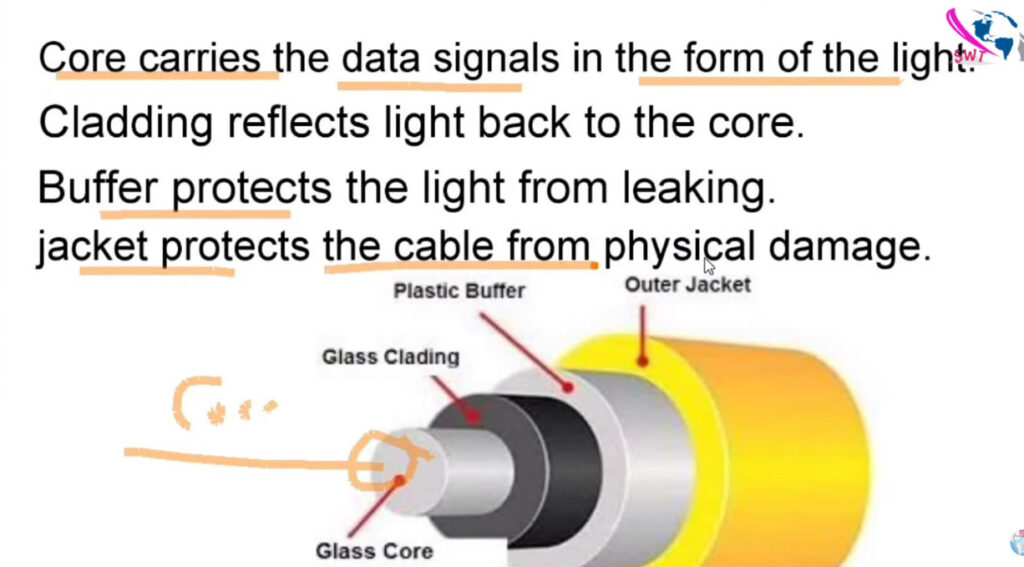
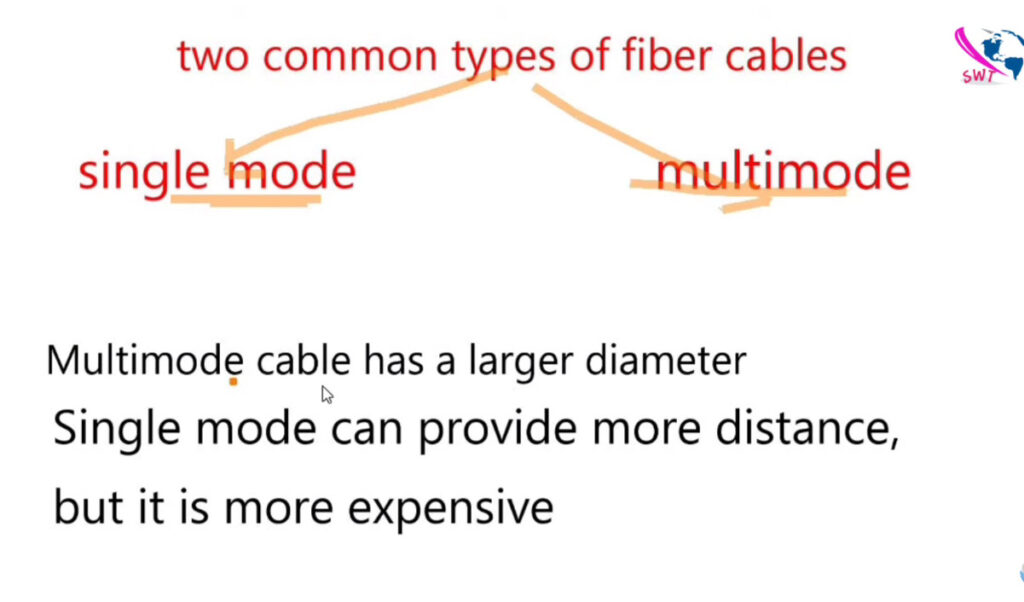
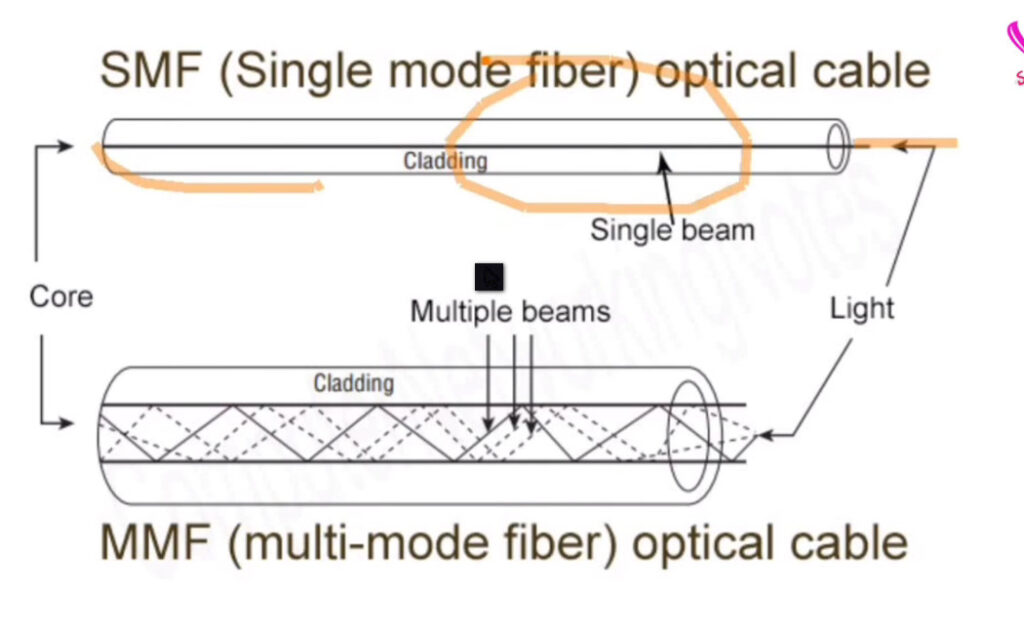
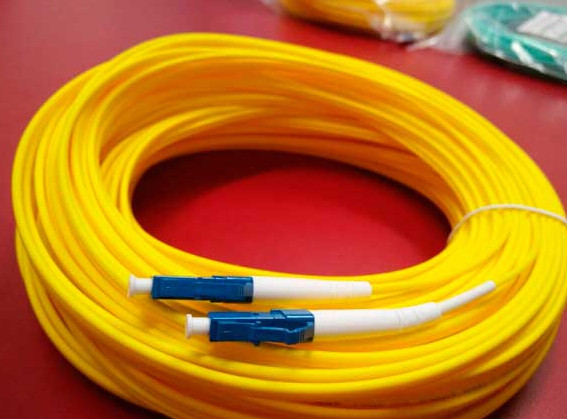
Fiber optic cables are categorized based on their construction and how they transmit light signals. The two main types of fiber optic cables are single-mode fiber (SMF) and multi-mode fiber (MMF). Within these categories, there are variations depending on the performance requirements, the number of cores, and the applications they support.
Here’s a breakdown of the different types of fiber optic cables:
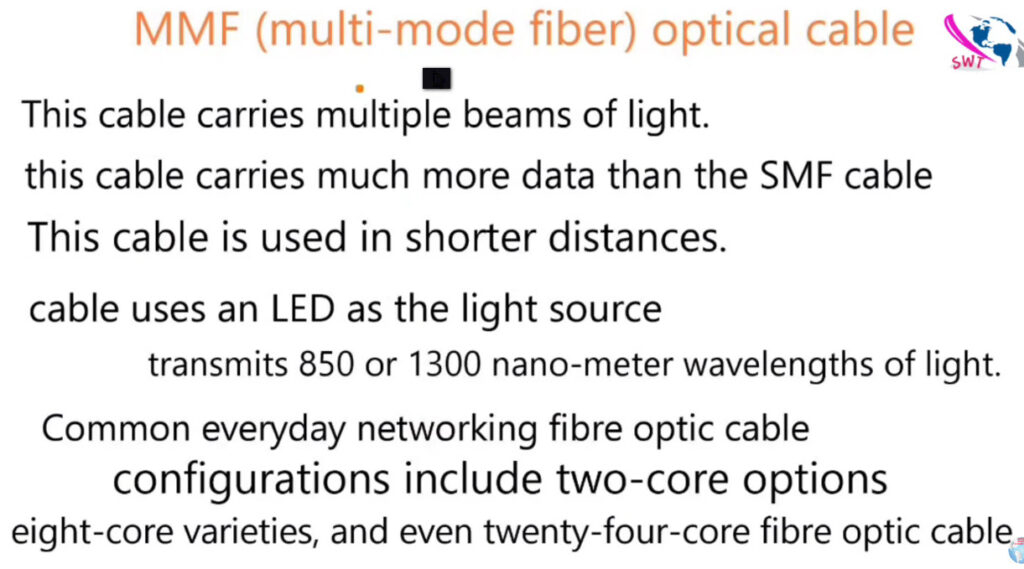
There are different grades or “types” of multi-mode fiber, based on core size and performance:
OM1 (Optical Multi-mode 1):
OM2 (Optical Multi-mode 2):
OM3 (Optical Multi-mode 3):
OM4 (Optical Multi-mode 4):
OM5 (Optical Multi-mode 5):
| Fiber Type | Core Diameter | Transmission Method | Max Distance | Max Bandwidth | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Mode (SMF) | 8-10 microns | Laser (1 light path) | Long distance (up to 40 km or more) | High (e.g., 100 Gbps) | Long-distance communication, telecommunications |
| Multi-Mode (MMF) | 50 or 62.5 microns | LED (multiple light paths) | Short distance (up to 2 km) | Lower (e.g., 1-10 Gbps) | LANs, data centers, enterprise networks |
| OM1 | 62.5 microns | LED | 275 meters (1 Gbps), 33 meters (10 Gbps) | 200 MHz·km | Legacy networks, low-speed applications |
| OM2 | 50 microns | LED | 550 meters (1 Gbps), 82 meters (10 Gbps) | 500 MHz·km | Mid-range speed networks, general use |
| OM3 | 50 microns | LED | 300 meters (10 Gbps), 100 meters (40 Gbps) | 2000 MHz·km | High-speed data centers, enterprise networks |
| OM4 | 50 microns | LED | 400 meters (10 Gbps), 150 meters (100 Gbps) | 4700 MHz·km | High-speed, high-performance applications |
| OM5 | 50 microns | LED | 150 meters (40 Gbps), 100 meters (100 Gbps) | 20000 MHz·km | Future-proof, high-performance networks |





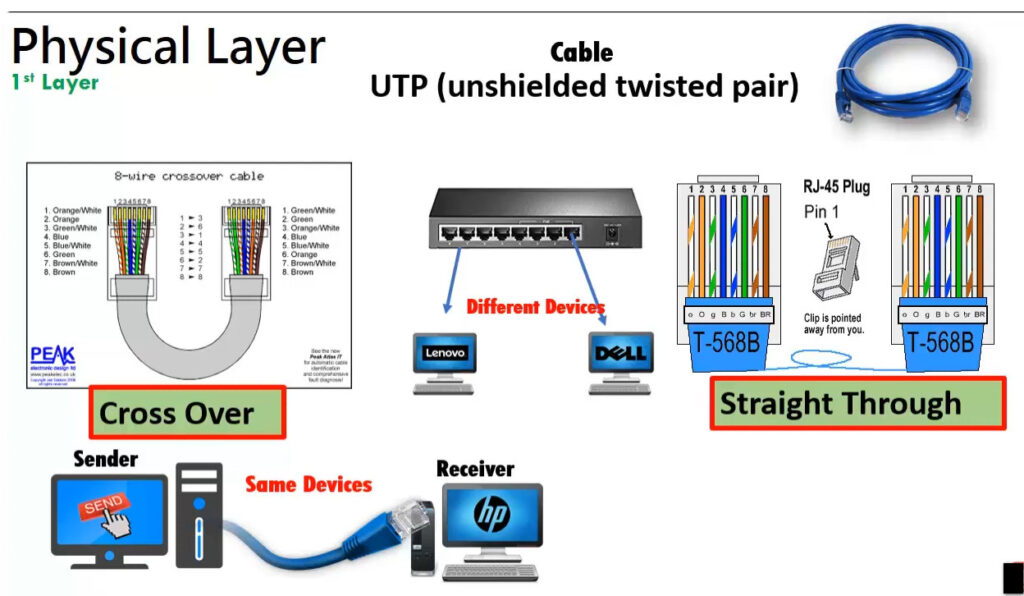
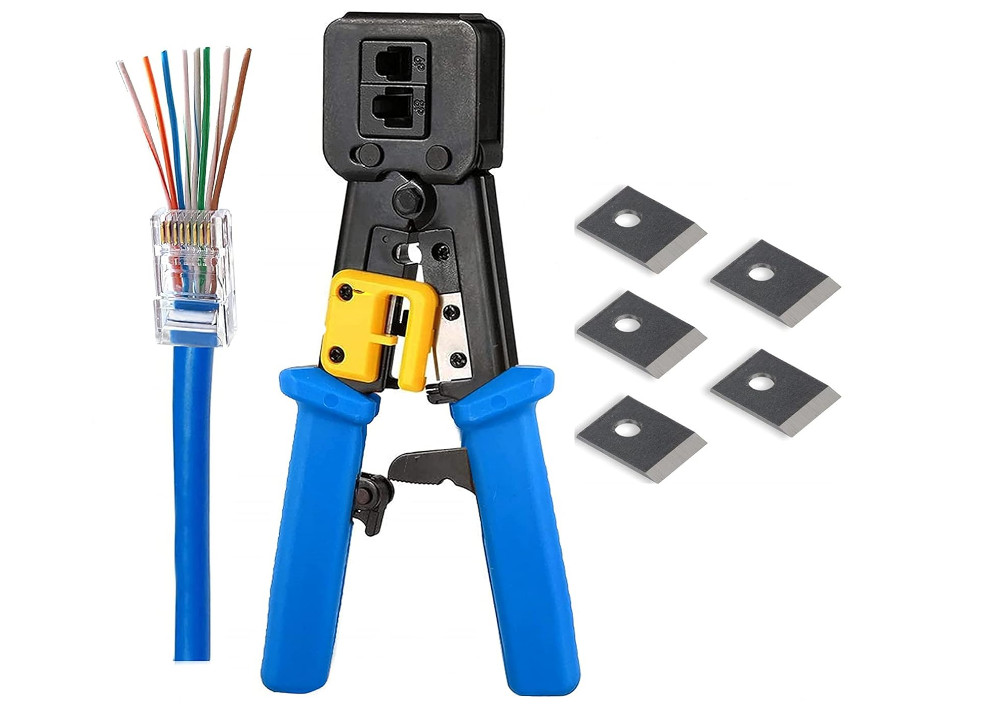
Crimping an RJ45 connector involves attaching an Ethernet cable to an RJ45 plug so it can be used in networking applications. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to crimp an RJ45 connector properly.
Prepare the Cable:
Arrange the Wires:
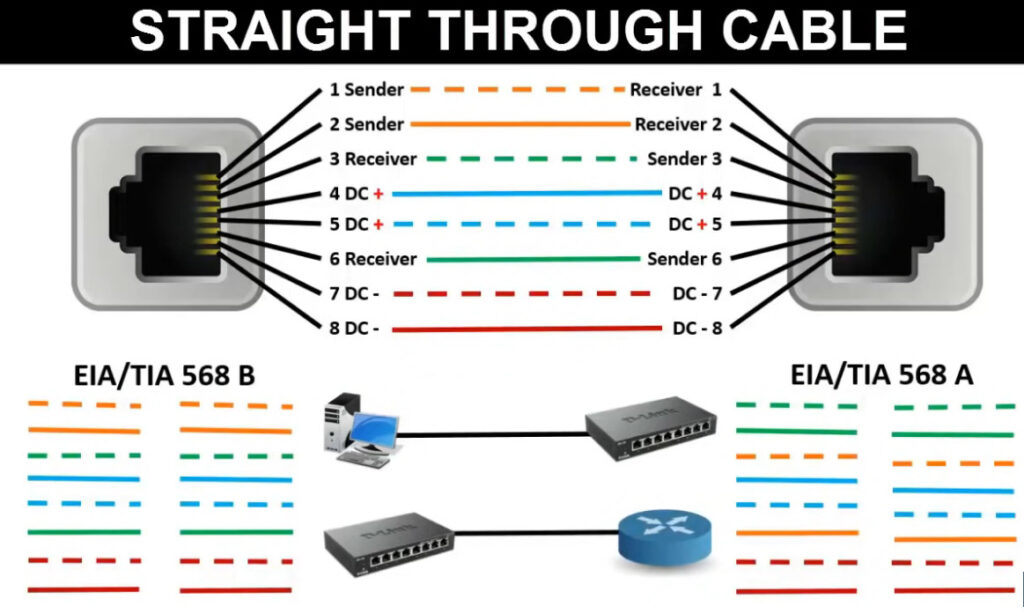
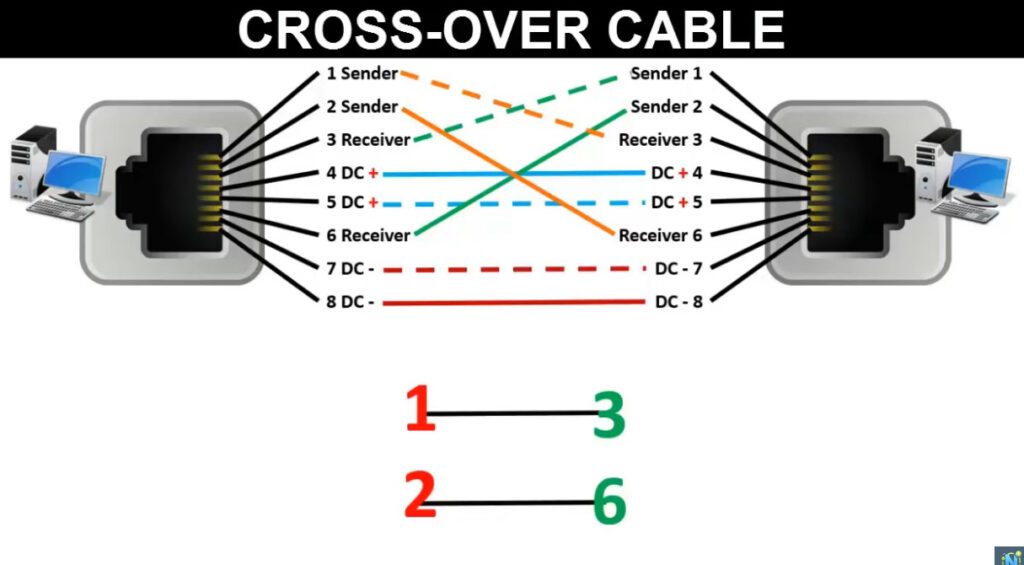
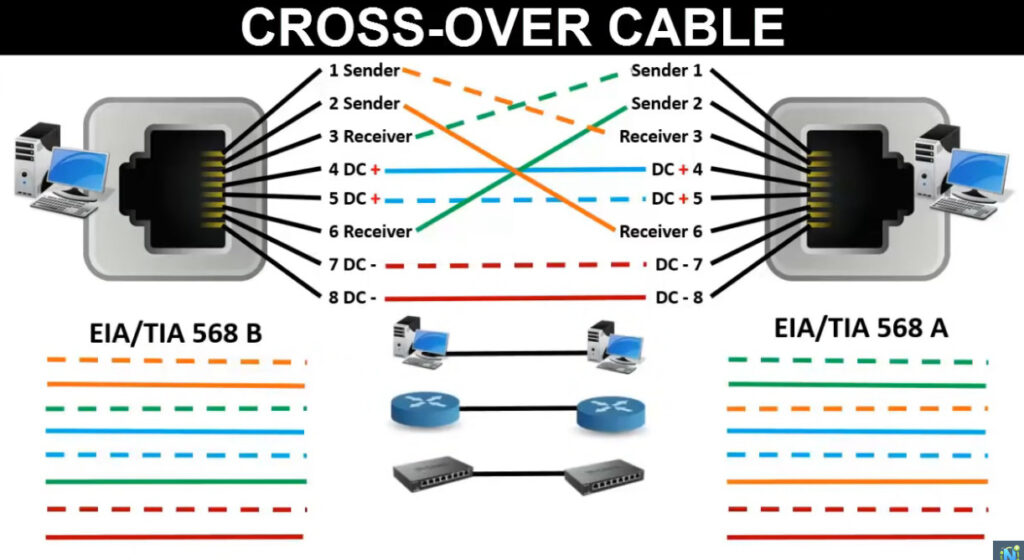
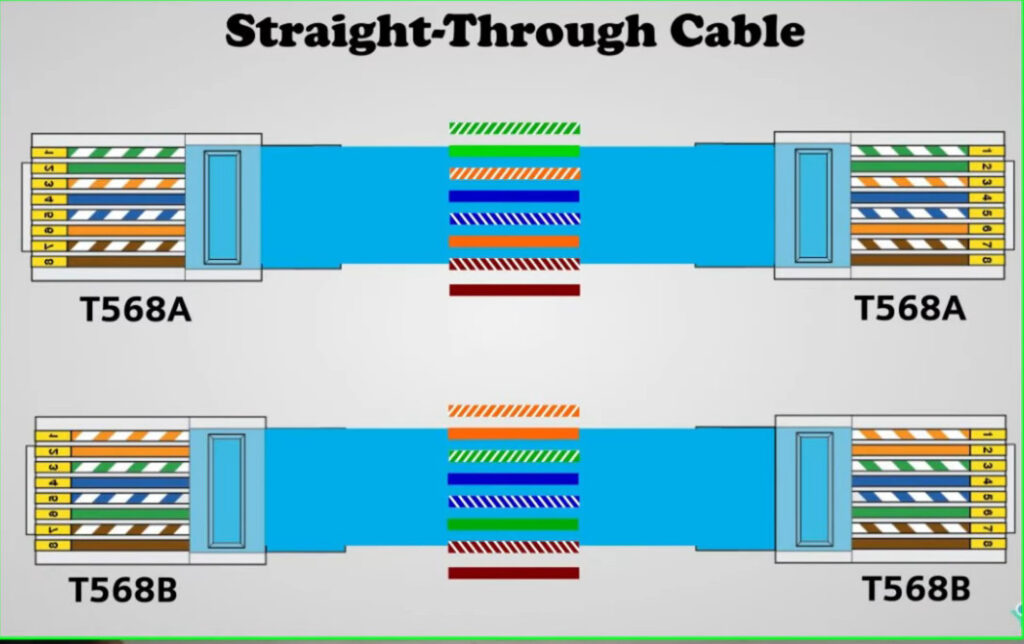
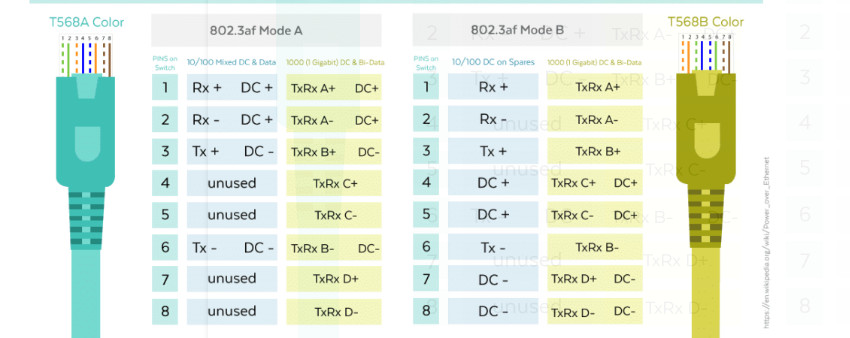
T568A Wiring (often used in residential settings):
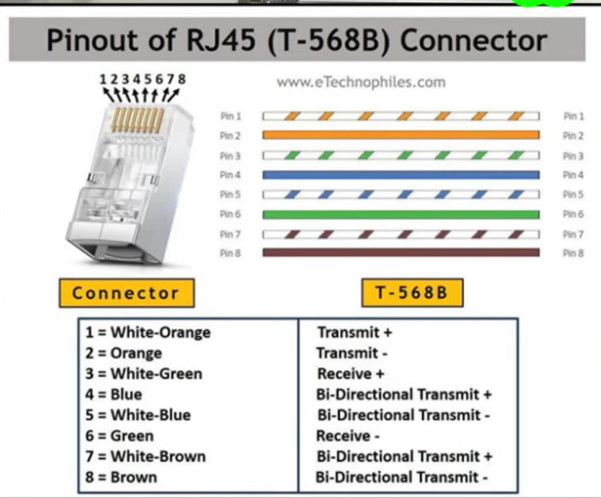
T568B Wiring (often used in commercial and networking environments):
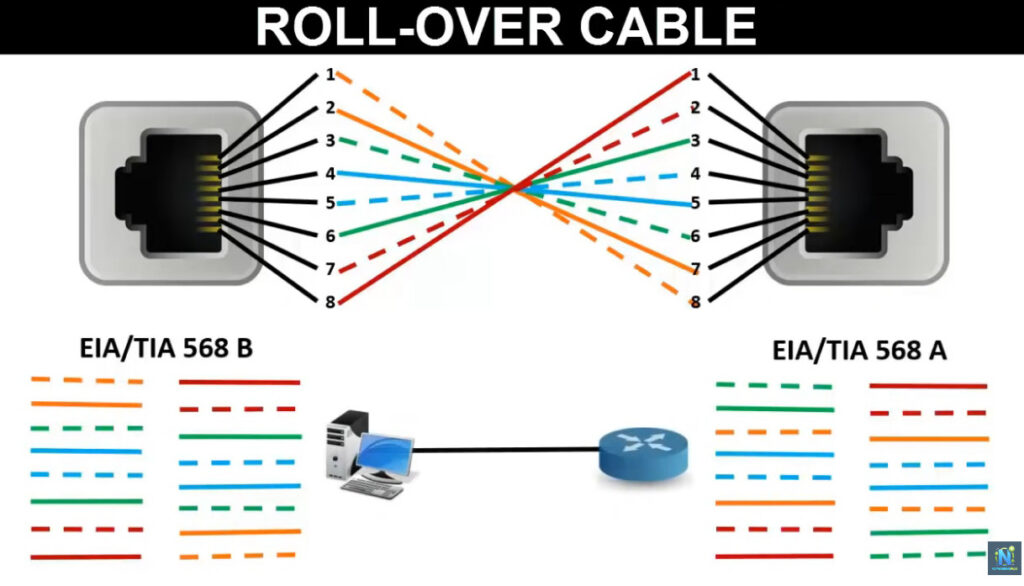
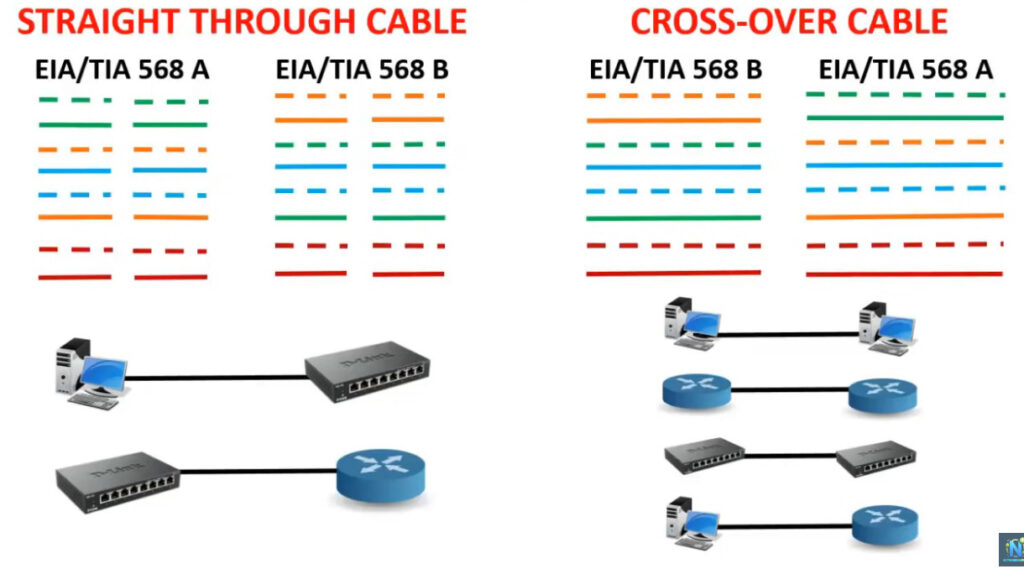
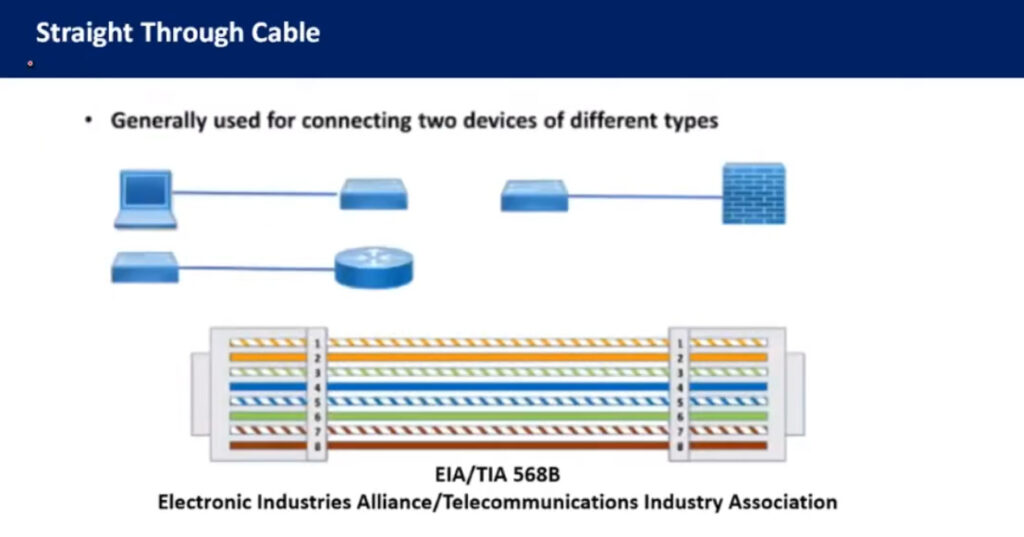
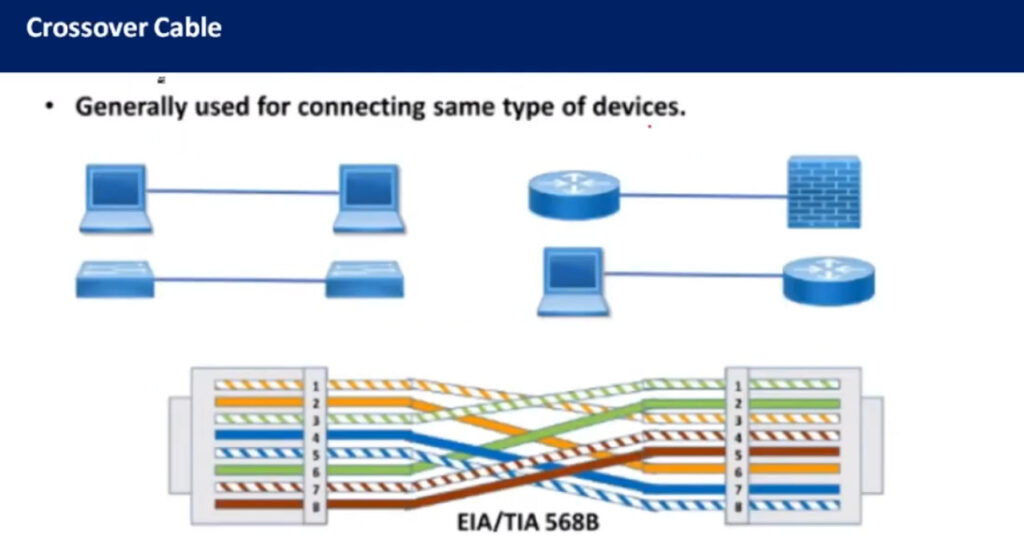
Note: Make sure you are consistent with the wiring standard on both ends of the cable if you are creating a straight-through cable.
Trim the Wires:
Insert the Wires into the RJ45 Connector:
Crimp the Connector:
Test the Cable:
It’s a good idea to test the cable using a cable tester to ensure that all the connections are correct and working properly.
If you don’t have a cable tester, you can check by plugging the cable into a device like a router and a computer to see if the network connection works as expected.
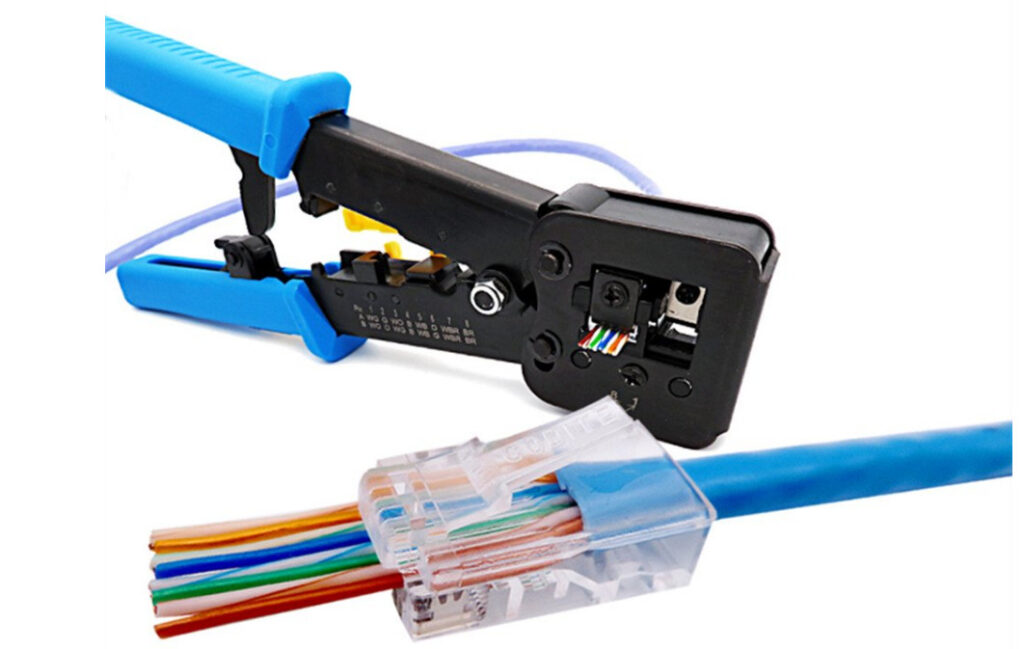
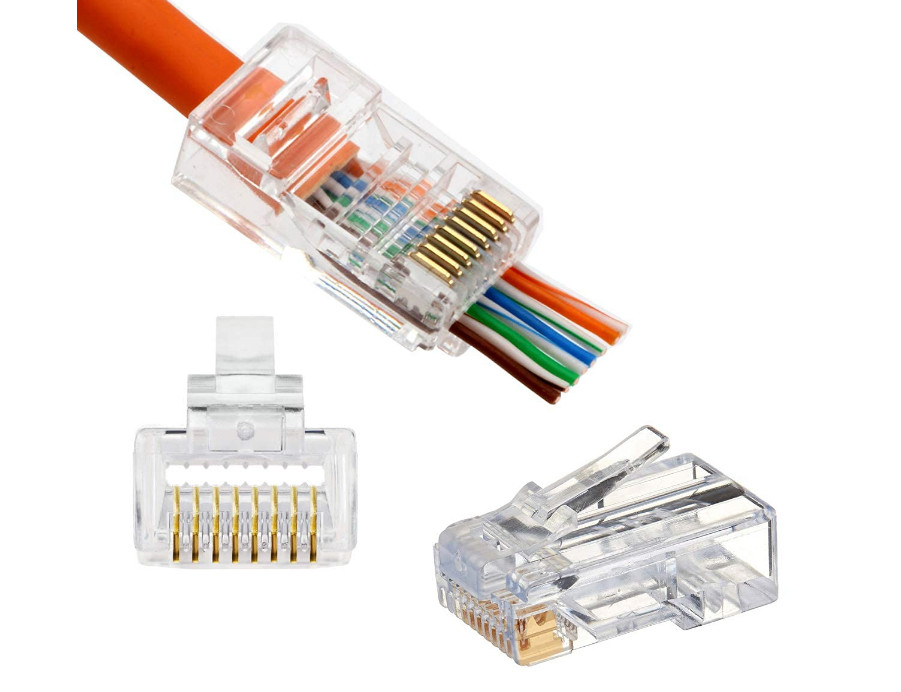
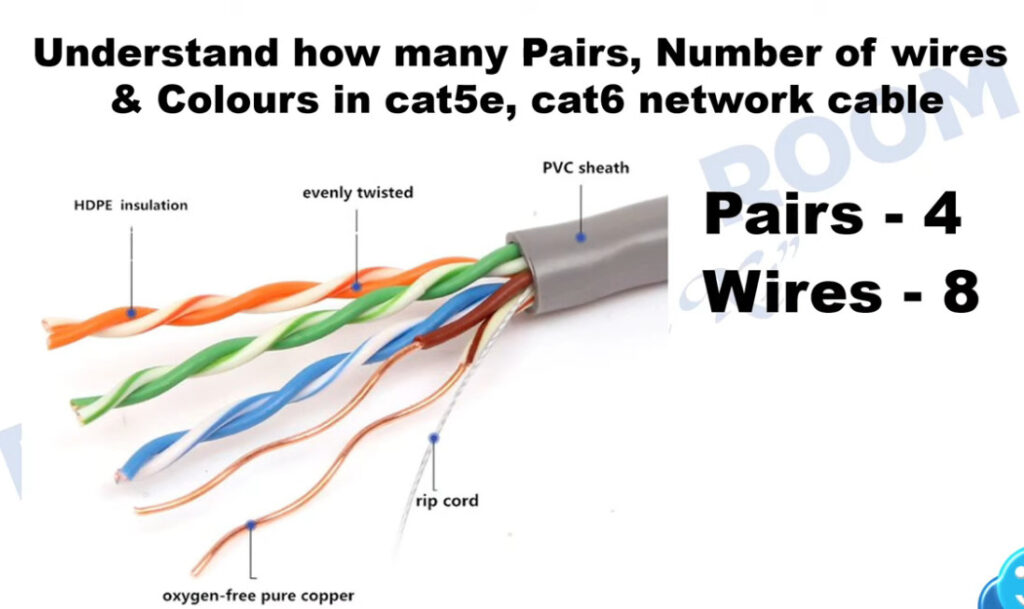
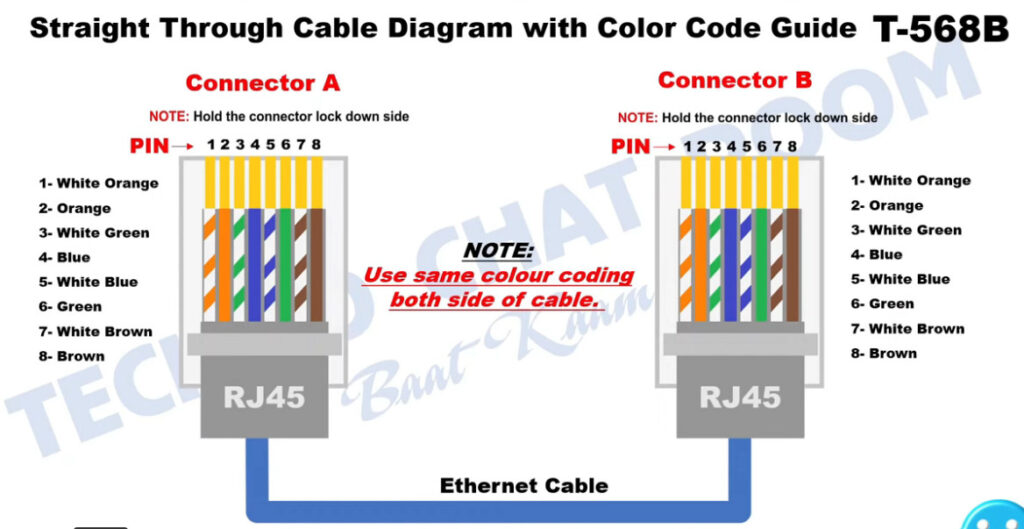
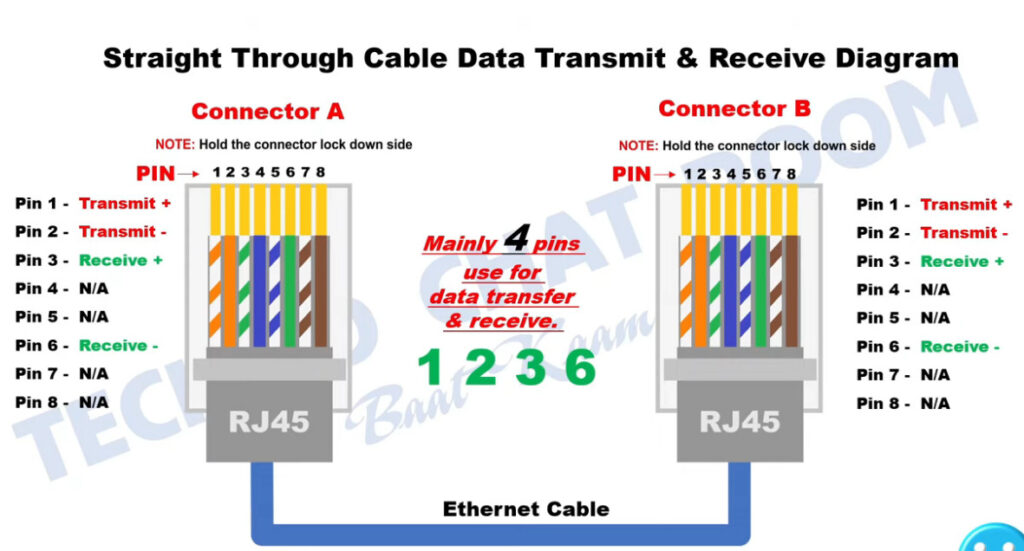
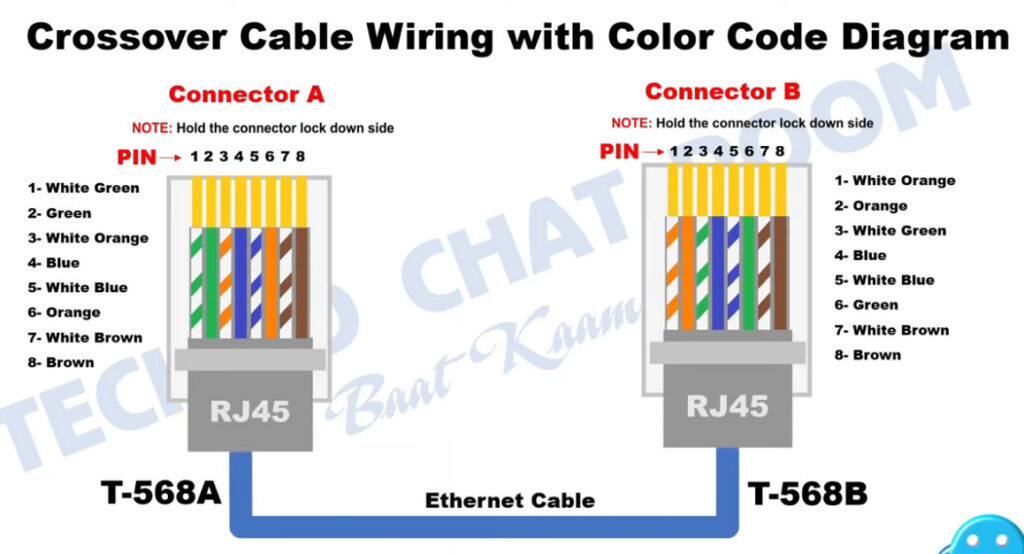
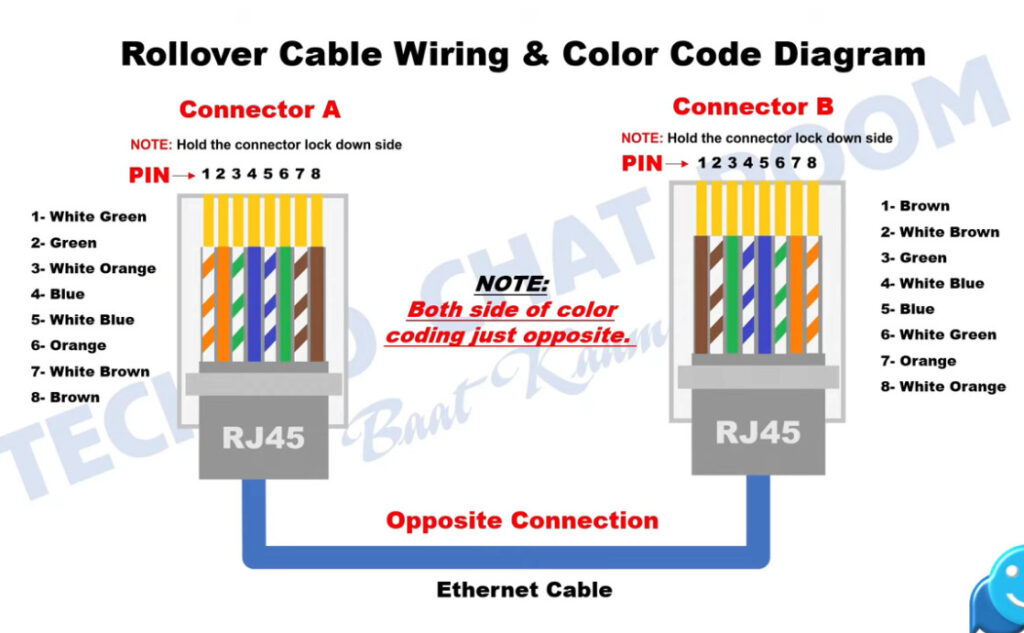
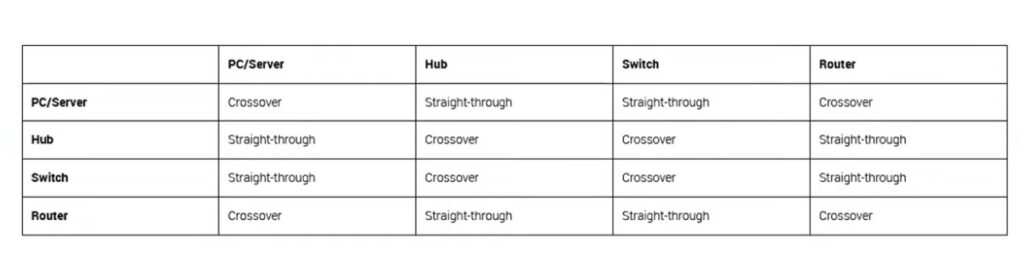
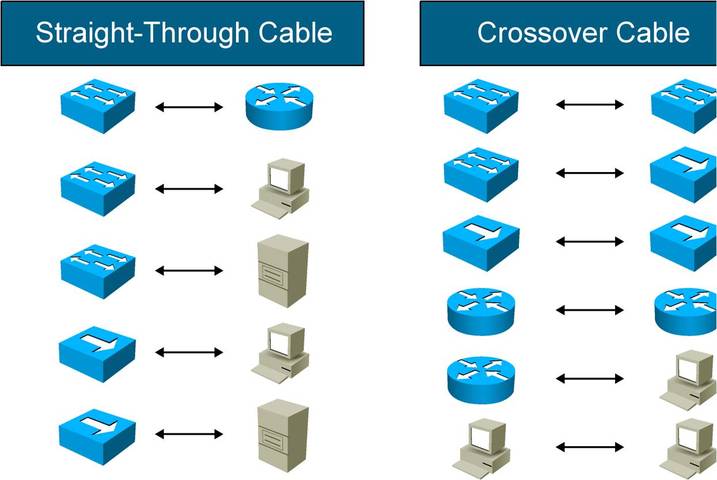








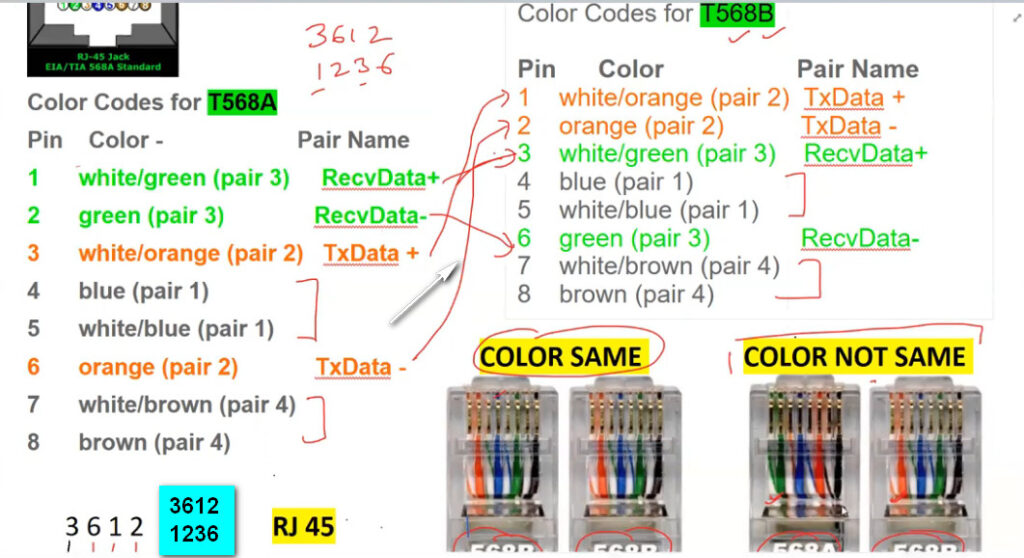
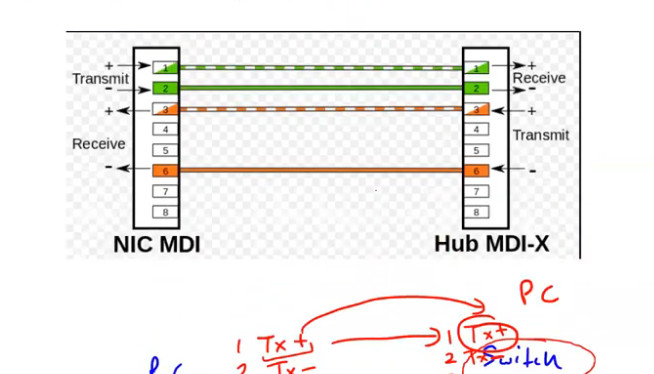
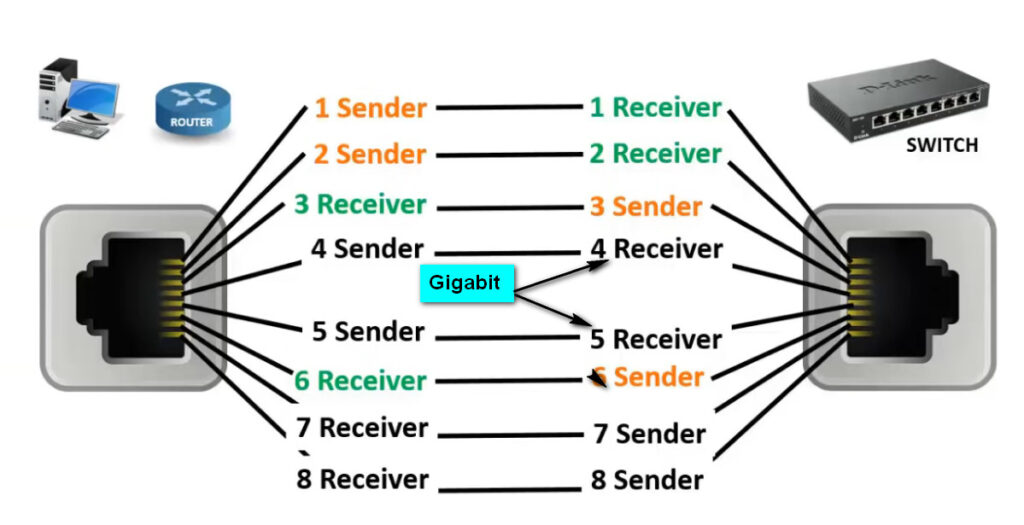
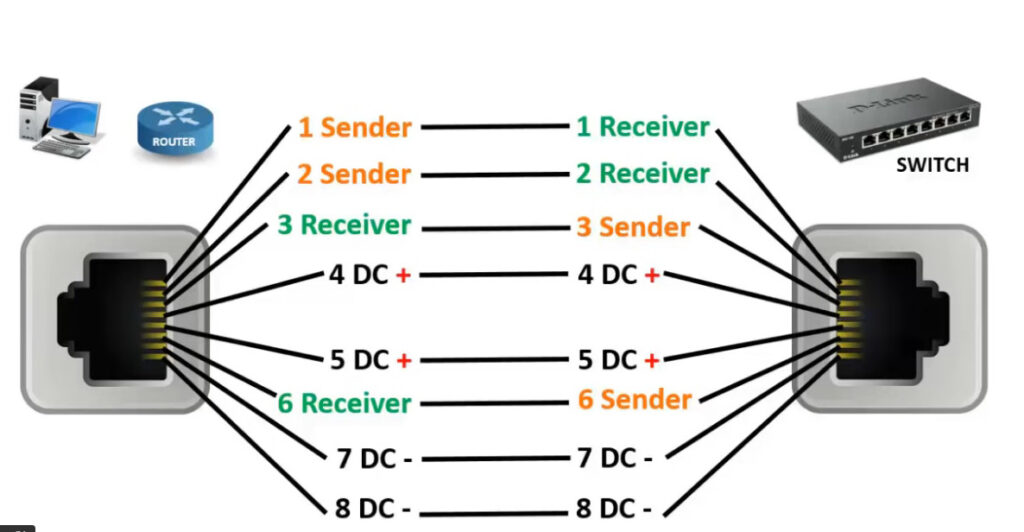
PC To Switch Normal 100Mbps Pins Diagram
4,5,7,8 Pins For Gigabit
1,2- sending data 3,6- receiving data 4,5 – DC + in poe &as a Sender in GEB 7,8- DC- in poe & as a receiver in GEB